Struts 2 Email Validation
Last Updated :
28 Apr, 2025
EmailValidator verifies that a given String field, if not empty, has a valid email address. It is utilized. Check to ensure that the string field has a valid email address and is not empty. Struts 2 validation is specified via XML or annotations. Manual validation within the action is also feasible, and it may be integrated with XML and annotation-driven validation. Validation is also dependent on the validation and workflow interceptors (which are both included in the default interceptor stack).
Example of Struts 2 Email Validation
XML
<validators>
<validator type="email">
<param name="fieldName">myEmail</param>
<message>Must provide a valid email</message>
</validator>
</validators>
<field name="myEmail">
<field-validator type="email">
<message>Must provide a valid email</message>
</field-validator>
</field>
<field name="myEmail">
<field-validator type="email">
<param name="regexExpression">${emailPattern}</param>
<param name="caseSensitiveExpression">${emailCaseSensitive}</param>
<param name="trimExpression">${trimEmail}</param>
<message>Must provide a valid email</message>
</field-validator>
</field>
Struts 2 Email Validation step by step implementation
Step 1: Create index.jsp for input
This JavaScript website uses struts UI tags to generate a form. The user provides it with their email address, password, and name.
XML
<%@ taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s" %>
<html>
<head>
<STYLE type="text/css">
.errorMessage{color:red;}
</STYLE>
</head>
<body>
<s:form action="register">
<s:textfield name="email" label="Enter Email Id"></s:textfield>
<s:submit value="register"></s:submit>
</s:form>
</body>
</html>
Step 2: Make the action class
The execute function is overridden by this action class, which derives from the ActionSupport class.
Java
import org.geeksforgeeks.xwork2.ActionSupport;
public class Login extends ActionSupport{
private String userName;
private String email;
public String execute(){
return SUCCESS;
}
//generating getters and setters
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
}
Step 3: Assemble the validation file
In this case, the validation is being carried out via bundled validators.
XML
<!DOCTYPE validators PUBLIC
"-//OpenSymphony Group//XWork Validator 1.0.2//EN"
"http://www.opensymphony.com/xwork/xwork-validator-1.0.2.dtd">
<validators>
<field name="userName">
<field-validator type="requiredstring">
<param name="trim">true</param>
<message>
Username is required.
</message>
</field-validator>
</field>
<field name="email">
<field-validator type="email">
<message>
Invalid email address.
</message>
</field-validator>
</field>
</validators>
Step 4: Create struts.xml
This XML file specifies an interceptor called jsonValidatorWorkflowStack and an additional result called input.
XML
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0.1//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.1dtd">
<struts>
<package name="user" extends="struts-default">
<action name="Login"
class="org.geeksforgeeks.action.Login">
<result name="success">/welcome.jsp</result>
<result name="input">/login.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
</struts>
Step 5: Create a view component
It is a basic JavaScript file that displays the user's information.
XML
<%@ taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s"%>
<html>
<head>
<title>Struts 2 email validator/title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>This is an email validator</h3>
Hello <s:property value="userName" />
</body>
</html>
Output:
Enter UserName and Email:
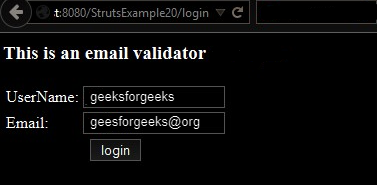
Click on login button:
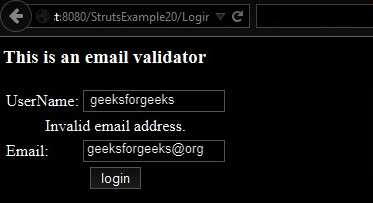
Conclusion
We hope you learned something new from this article on the Java Struts 2 Email Validation. EmailValidator verifies that a given String field, if not empty, has a valid email address. Struts 2 validation is specified via XML or annotations. Manual validation within the action is also feasible, and it may be integrated with XML and annotation-driven validation.
Explore
Java Enterprise Edition
Multithreading
Concurrency
JDBC (Java Database Connectivity)
Java Frameworks
JUnit