How to Create Static Pod in Kubernetes ?
Last Updated :
20 Sep, 2025
A Static Pod is a Pod that is managed directly by the kubelet daemon on a specific node. Unlike regular Pods, they are not managed by the Kubernetes API server or the scheduler.
The kubelet, watches a specific local directory for Pod manifest files (usually YAML or JSON). When a manifest appears in this directory, the kubelet automatically creates the Pod on that node. If the file is removed, the kubelet terminates the Pod. A Static Pod is therefore tied directly to the lifecycle of the kubelet on its host node.
Need of Static Pod
The most important use case for Static Pods is to solve a fundamental bootstrapping challenge in Kubernetes: self-hosting the control plane.
- Kubernetes needs the control plane to run Pods—but the control plane itself runs in Pods. Static Pods solve this by letting the kubelet start key components directly from local files, no API server needed. It’s how Kubernetes bootstraps itself
- On a master node, the
kubelet can be configured to start these critical control plane components as Static Pods by reading their manifests directly from a local file path. This allows the control plane to come online without needing a pre-existing control plane to launch it. - Other use cases include running critical node-level daemons that must always be present on a specific host, such as certain logging or monitoring agents.
How Static Pods Works?
While the kubelet is the sole manager of a Static Pod, Kubernetes still needs a way to make these Pods visible to the rest of the cluster. This is achieved through a Mirror Pod.
For every Static Pod it creates, the kubelet also creates a corresponding "mirror" Pod object on the API server. This mirror Pod is a read-only representation of the Static Pod.
- You can see it using
kubectl get pods. - You can inspect it using
kubectl describe pod. - You cannot delete it using
kubectl delete pod. Any attempt to delete the mirror Pod will be ignored because the kubelet is the true source of authority. The kubelet will simply recreate the mirror Pod if it's removed from the API server.
To stop a Static Pod, you must remove its manifest file from the configured directory on the node itself.
Steps to Create Static Pod in Kubernetes
Step 1: Login into AWS account
Step 2: Launch an EC2 instance
- Navigate to ec2 dashboard.
- Launch an ec2 instance with specifications AMI- amazonlinux2,type- t2.micro,8gb root volume- gp2 type.
- Security groups - allow SSH(22),HTTPS(443),HTTP(80).
- Connect this instance by using SSH secure shell.
ssh -i "keypair" ec2-user2@<instance-public-ip address>compute-1.amazonaws.com
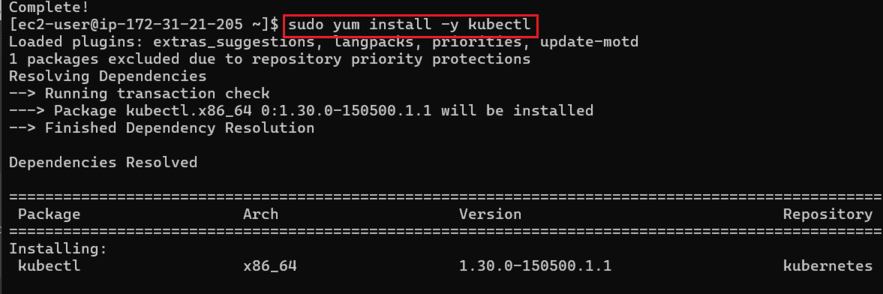
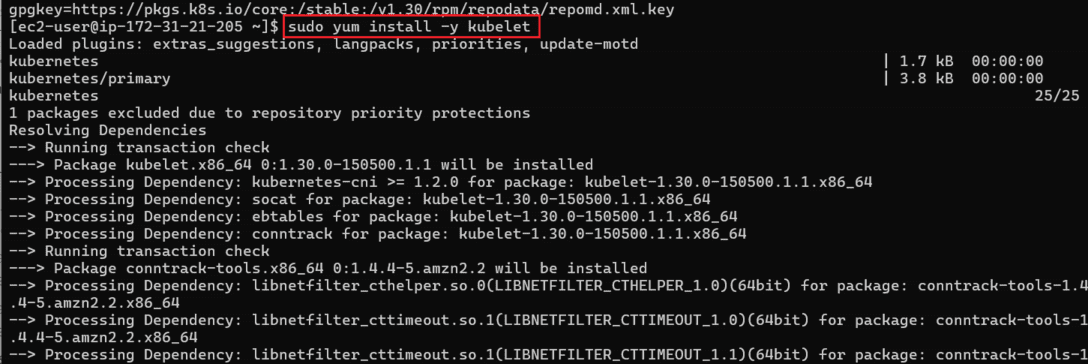
Step 3: Install kubectl and kubelet
- Download the Kubelet and kubectl related packages and repositories from Kubernetes official site https://kops.sigs.k8s.io/getting_started/install/

- Successfully download kubectl and kubelet repos and keys then the install and setup the kubelet and the kubectl which is Kubernetes CLI tool.
sudo yum install -y kubectl
sudo yum install -y kubelet
Step 4: Create a YAML File to create static pod
- Make the YAML file to create static case which will characterizes the determinations of the static pod. The YAML file ought to incorporate subtleties like the pod's name, container determinations, labels, and some other arrangement required. Here is a example of YAML manifest for a NGINX static pod.
sudo vi static-pod.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx-static-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:latest
Step 5: Move or Copy the Manifest
- Here, we have to move our YAML file to manifest directory because the manifest directory directly controlled by kubectl and kubelet.
- Settle on the node where you need to run the static pod. Every node in the Kubernetes cluster has a staticPodPath registry where static pods manifest are there. As a matter of course, this directory is /etc/kubernetes/manifest.
- Move the YAML manifest file you made to create the staticPodPath registry on the chosen node. You can utilize the commands like scp or kubectl cp to copy or move files to the one. For example:
- Here, We move the static-pod.yml record to the kubernetes manifest registry.
sudo mv static-pod.yml /etc/kubernetes/manifest/

- We can check the moved YAML file navigate to kubernetes's manifest directory
cd /etc/kubernetes/manifest/
ls
Step 6: Verifying the created pod
- When you have copy and moved the manifest YAML file to static-pod directory the Kubernetes will automatically detect and kubelet is going to run on the node to create the static pod according the specification you provide in manifest YAML file.
- You can verify the running pod by execute the below command.
kubectl get pods

- The command will list out the all the pods on kubernetes cluster
- The output of created static pod is nginx-static-pod there you can see.
Step 7: Edit the static pod
- You can edit the static-pod for this again you need to navigate to Kubernetes's directory .
- And there you see the previous static-pod.yml manifest file edit that file with the command.
sudo vi static-pod.yml

- Configure this Yml file with your desired name and container name.
- We configure with httpd static server
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: httpd-static-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: httpd
image: httpd:latest
- The kubernetes automatically detects the manifest file and kubelet runs the static-pod.
- You can check the edited static-pod file.

Step 8: Delete the Static-pod
- If you want to remove static-pod simple navigate to Kubernetes's manifest directory where you place the static-pod manifest file simply remove the file.
- The static-pod will be deleted
cd /etc/kubernetes/manifest/
sudo rm static-pod.yml

- Either simple execute the below command
kubectl delete pod <pod_name>
Static Pods Vs. Daemon Sets
Characteristics | Static Pods | Daemon Sets |
|---|
Definition | Manually defined and managed by users | Automatically managed by Kubernetes |
|---|
Pod Placement | Runs on specific nodes specified by user | Runs on all or specific nodes in the cluster |
|---|
Management | managed by kubectl | managed by kubernetes API Automatically |
|---|
Use Case | Testing, troubleshooting, specialized workloads | Running a single pod on every node, log collection, monitoring |
|---|
Scaling | Not scalable | Scalable |
|---|
Maintenance | Requires manual updates | Automatically updates |
|---|
controlling | Not controlled by kubernetes master | Controlled by kubernetes master |
|---|
Explore
DevOps Basics
Version Control
CI & CD
Containerization
Orchestration
Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Monitoring and Logging
Security in DevOps