Setting Upstream Branch in Git
Last Updated :
03 Oct, 2025
An upstream branch is the remote branch your local branch tracks. It acts as a reference for syncing changes, so you can fetch, pull, and push without repeatedly specifying branch names.
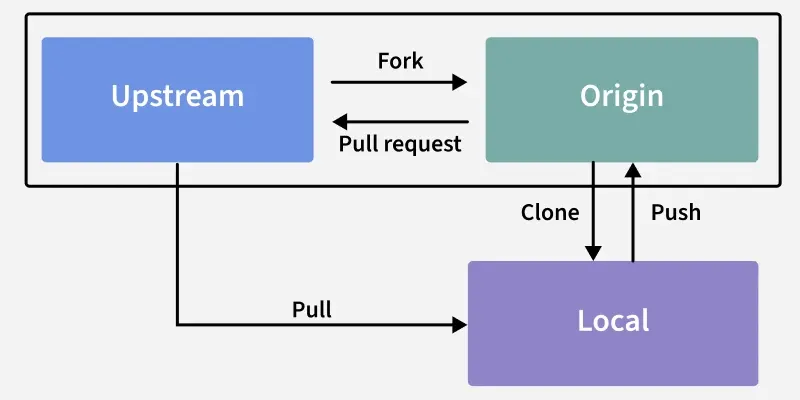 Setting Upstream Branch in Git
Setting Upstream Branch in Git- Usually a branch from the remote repo (origin/main).
- Simplifies
git push and git pull. - Each local branch tracks one upstream branch.
- Set with
git push -u or git branch -u.
Set Upstream Branch using Git Push command
To set Upstream Branch using Git Push, you first have to Create a new branch with the name '' and switch to the current branch using the -b option
git checkout -b <branch name>
Switching the branch confirmation appears below:
 Switching the branch confirmation
Switching the branch confirmation When the current branch i.e ('new_branch') has no Upstream branch set and we try to run the command "Git push". After running the below command in cmd:

Now, you need to set the upstream branch using the Git push command with the -u option. Replace <branch name> with your branch name.
git push -u origin <branch name>
Alternatively, you can use the '--set-upstream' command as well to set the Upstream branch
git push --set-upstream origin <branch name>

Change Upstream Branches in Git
Now, you need to track a new upstream branch than the one you just setup running:
git branch -u <remote/branch name>
For example:
git branch main -u <origin/new_branch>
git branch main -u <origin/main>
The terminal prints out the confirmation message:


Check Which Branches Are Tracking Upstream Branches
Now To check which Git Branches are tracking which Upstream Branches,you can list all your branches that are tracking upstream branches using "Git branch" with the -vv option:
git branch -vv

The main branch has a tracking branch of [origin/main]. The test branch has a tracking branch of [origin/test]. The new_branch branch has a tracking branch of [origin/new_branch].
What is an upstream branch in Git?
-
A backup copy of your local branch
-
A remote branch your local branch tracks for syncing changes
-
A temporary branch created during merging
-
A branch that only stores tags
Explanation:
An upstream branch is the remote branch (usually on origin) that your local branch tracks. This relationship allows you to run commands like git push and git pull without specifying remote and branch names every time
Which command sets the upstream branch when pushing a new branch for the first time?
-
-
git branch -u origin/main
-
git push -u origin <branch name>
-
git remote add upstream <branch>
Explanation:
git push -u origin <branch> pushes your branch and sets its upstream tracking branch. After this, you can run plain git push or git pull without specifying the branch name again.
Which command is used to manually change the upstream branch of an existing local branch?
-
git merge <remote/branch>
-
git branch -u <remote/branch>
-
git remote rename upstream
-
Explanation:
git branch -u <remote/branch> changes the upstream branch for your currently checked-out branch. This is used when you want your local branch to track a different remote branch than before.
What does the command git branch -vv display?
-
Only a list of local branches
-
-
Local branches along with their upstream tracking branches and latest commit info
-
The commit history of all branches
Explanation:
git branch -vv lists all local branches plus:
- which upstream branch each one tracks
- the most recent commit on each
This is useful for verifying upstream branch relationships.
What happens if you run git push on a new branch that has no upstream branch set?
-
Git automatically creates a remote branch
-
Git deletes the local branch
-
Git shows an error message telling you to specify a remote and branch
-
Git performs a force push
Quiz Completed Successfully
Your Score : 2/5
Accuracy : 0%
Login to View Explanation
1/5
1/5
< Previous
Next >
Explore
Git Introduction
Git Installation and Setup
All Git Commands
Most Used Git Commands
Git Branch
Git Merge
Git Tools and Integration
Git Remote Repositories
Collaborating with Git
Advanced Git Commands