Use Git Log to Format the Commit History
Last Updated :
11 Nov, 2025
In Git, keeping track of changes and understanding the project’s history is crucial for efficient collaboration and debugging. The git log command is one of the most powerful tools available to developers for viewing and formatting commit history.
By customizing git log, you can make the output more readable, concise, and visually appealing-helping you quickly find specific commits or understand how your project evolved over time.
Formatting Commit History
Git provides a range of options to customize the format of the commit history displayed by git log. These options allow you to specify which commit metadata to include, how it should be formatted, and even add custom elements to the output.
The various options to format the git log are as follows:
--author=<Name>
It helps to format the log for those commits only where the author was a specific user. This option helps to review any logs made by any specific user overtime on a repository.

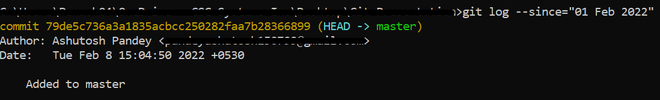
--since=<Date> / --after=<Date>
These options help to format the log based on the timestamps and query only those commit logs which fulfill the criteria.
-n <number>
The -n option helps to limit the log commits view, i.e. only a certain number of recent commits will be displayed instead of showing a bulk of updates.
--grep=<pattern>
The --grep options help the user to search for a particular pattern or word in the whole commit history and display on those commits which consist of the pattern. This option is useful when a user is looking for updates related to a specific file or object.

--graph
The --graph option displays the updates in a graphical format, displaying the branching and the merging commits as diverging and converging graph nodes. Each commit is actually a graph node in the log graph.

--oneline
The --oneline option is used to format the commit log in as compact as much possible way.

--all
The --all option is used to view the commit log of all branches in a single log.

Note: Although, there are various options to format the log messages. The most useful options are the above-listed ones.
Which option in git log is used to limit the number of commits displayed?
Explanation:
-n <number> limits output to the most recent commits, e.g., git log -n 5 shows only last 5 commits.
What does the --author=<Name> option do in git log?
-
Filters commits based on date
-
Displays all commits including message summary
-
Shows commits only made by a specific user
-
Shows commits from all branches
Explanation:
--author=<Name> filters commit history to show logs only by the specified author, useful in team collaborations.
Which option is used for viewing commits from all branches together?
Explanation:
git log --all shows history across every branch, not just the current one.
To search commit history for a word or pattern in messages, you use:
-
git log --after="2025-10-01"
-
-
-
Explanation:
--grep=<pattern> finds commits containing specific words in commit messages, useful for locating features or bug fixes.
What is the purpose of the --graph option in git log?
-
Shows file-level diff output
-
-
Displays commit history with branching visuals
-
Counts commits per author
Explanation:
--graph draws commit history visually, showing branch splits and merges as text-based graph lines.
Quiz Completed Successfully
Your Score : 2/5
Accuracy : 0%
Login to View Explanation
1/5
1/5
< Previous
Next >
Explore
Git Introduction
Git Installation and Setup
All Git Commands
Most Used Git Commands
Git Branch
Git Merge
Git Tools and Integration
Git Remote Repositories
Collaborating with Git
Advanced Git Commands