The Reader class in Java is an abstract class for reading character streams. Its subclasses (FileReader, BufferedReade) provide implementations, with read() being the main method to read characters.
- It implements the Readable interface that defines the read(CharBuffer cb) method.
- It implements the Closeable interface that defines the close() method to release resources.
 Reader
ReaderDeclaration of Reader Class
Declaration of Reader class is given below:
public abstract class Reader implements Readable, Closeable
Example: Read a text file character by character using the Reader class.
Java
import java.io.*;
public class Geeks {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try {
// Create a FileReader object which is a subclass of Reader
Reader r = new FileReader("example1.txt");
// Read one character at a time from the file
int data = r.read();
while (data != -1) {
// Convert the int to char and print
System.out.print((char)data);
data = r.read();
}
// Close the reader
r.close();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
System.out.println("An error occurred: " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
}
Output :
 output
outputNote: To ensure the program runs correctly, create a file named example1.txt in the working directory.
Add the following content to the file, or you can add any text.
Hello welcome to Geeks for Geeks
Save the file and run the program. The program will read and display the contents of example1.txt as output.
Constructors of Reader Class
There are two constructors used with Java Reader Class as mentioned below:
- protected Reader():Creates a new character-stream reader whose critical sections will synchronize on the reader itself.
- protected Reader(Object lock): Creates a new character-stream reader whose critical sections will synchronize on the given object.
Methods of Java Reader Class
Example: The below program demonstrate the working of various functionalities of the Reader class in Java.
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.CharBuffer;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Geeks {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws IOException
{
// Open a file reader
Reader r = new FileReader("file.txt");
PrintStream out = System.out;
// Create a character array and CharBuffer
char[] buffer = new char[10];
CharBuffer charBuffer = CharBuffer.wrap(buffer);
// Check if the reader supports marking
if (r.markSupported()) {
r.mark(100); // Mark the current position
out.println("mark method is supported");
}
// Skip 5 characters in the stream
r.skip(5);
// Check if the stream is ready to read
if (r.ready()) {
// Read 10 characters into the buffer
r.read(buffer, 0, 10);
out.println("Buffer after reading 10 chars: "
+ Arrays.toString(buffer));
// Read characters into the CharBuffer
r.read(charBuffer);
out.println(
"CharBuffer contents: "
+ Arrays.toString(charBuffer.array()));
// Read a single character
out.println("Next character: "
+ (char)r.read());
}
// Close the reader
r.close();
}
}
Output:
 Output
OutputImplementation of Reader Classes
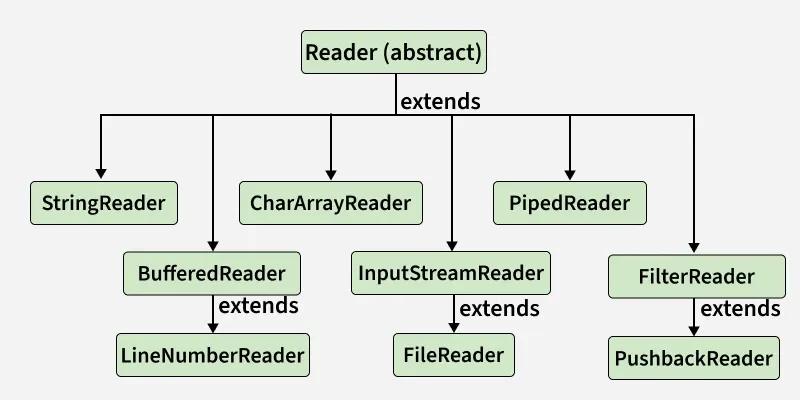
Some of the implementations of Reader classes in Java are mentioned below:
Explore
Java Basics
OOP & Interfaces
Collections
Exception Handling
Java Advanced
Practice Java