A Servlet Filter is a Java object that performs filtering tasks on either the request to a resource, the response from a resource, or both. Filters are part of the servlet specification and are used to intercept client requests, enabling developers to modify or examine requests and responses before reaching the target resource like a Servlet, JSP, or static file.

Filters are commonly used for:
- Authentication and Authorization
- Logging and Auditing
- Data Compression or Encryption
- Image/Content Transformation
Servlet Filter Life Cycle
The lifecycle of a Servlet Filter is similar to that of a Servlet:
- Instantiate: The filter object is created by the container.
- Initialize (init): Called once to configure or allocate resources.
- Filter (doFilter): Called for each request, allowing pre-processing and post-processing.
- Destroy (destroy): Called once before the filter is removed, to release resources.
Interfaces belong to Filters
- Filter.
- FilterConfig.
- FilterChain.
All these interfaces are available in javax.Servlet Package let's understand all filter one by one.
1. Filter
- Filter is an interface defined in the javax.servlet package.
- Every custom filter must implement this interface to work with the servlet container.
- The Filter interface provides three key lifecycle methods first init(), dofilter() and destroy().
Example:
Java
public interface Filter {
void init(FilterConfig config) throws ServletException;
void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException;
void destroy();
}
Key Methods:
- init(FilterConfig config): Initializes the filter once during startup.
- doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain): Core method to process requests/responses; calls chain.doFilter() to pass control.
- destroy(): Cleans up resources before the filter is removed.
Note:
- Filter information must be provide inside web.xml .
- Filter is mapped with one or more than one servlet.
2. Filter Configuration (web.xml)
Filters can be configured in web.xml or via annotations (@WebFilter).
XML
<filter>
<filter-name>f1</filter-name>
<filter-class>MyBlockFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>f1</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/servlet1</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>HelloServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>HelloServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>HelloServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/servlet1</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
Explanation:
- <filter> declares the filter class.
- <filter-mapping> associates the filter with specific URLs.
- <servlet> and <servlet-mapping> define the target servlet and its URL.
3. FilterChain
FilterChain is an interface provided by the servlet container. It is used by filters to pass the request and response to the next filter in the chain or to the target resource (like a servlet or JSP) if it is the last in the chain
Method:
Java
void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException;
Types of Filters
We can Develop three types of filters as listed below as follows:
- Request Filter: Contain only pre-request Processing logic. Example: Request count filter, Authentication filter, Authorization filter, Validation filter and etc.
- Response Filter: Contain only Post-response generation logic. Example: Conversion filter, Compression filter and etc.
- Request-Response Filter: Contain both pre-request and post-response generation logic.
Example Project – Block IP Address
In this example, we will create a simple web application that uses a Filter to block access based on the client's IP address. If the IP address is "127.0.0.1" (localhost), the user will not be able to access the site.
Step 1: Create a Dynamic Web Project
- Open Eclipse IDE.
- Go to File -> New -> Dynamic Web Project.
- Enter Project Name: IPBlockFilterProject.
- Target Runtime: Apache Tomcat (choose version installed).
- Dynamic Web Module version: 3.1 (or compatible).
- Click Finish.
Step 2: Create index.html
Create index file ->WebContent->index.html
index.html
HTML
<html>
<head>
<title>TODO supply a title</title>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
</head>
<body>
<a href="servlet1">click here</a>
<form>
<body>
<html>
Explanation:
- Defines a basic HTML page structure.
- Includes page title and meta tags for encoding and responsiveness.
- Contains a link to trigger a servlet (servlet1).
- An empty <form> tag is present without inputs or action.
- Contains HTML errors like duplicate <body> tags and unclosed elements
Step 3: Create the Filter Class
Create servlet filter inside-> src-> Right click -> New -> Class -> MyBlockFilte.
MyBlockFilter.java
Java
package com.example.filter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.*;
public class MyBlockFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig config) throws ServletException {}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse resp, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
String ip = req.getRemoteAddr();
PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter();
if (ip.equals("127.0.0.1")) {
out.print("<h2>Your IP address is blocked by this website</h2>");
} else {
chain.doFilter(req, resp); // Forward request to next filter or servlet
}
}
@Override
public void destroy() {}
}
Explanation:
- The class MyBlockFilter implements the Filter interface.
- The init() method initializes the filter and is executed once during the filter's lifecycle.
- The doFilter() method checks the IP address of the incoming request.
- If the IP address is "127.0.0.1", the filter blocks access and displays a message.
- If the IP is not blocked, the request continues through the filter chain.
- The destroy() method is called when the filter is taken out of service.
Step 4: Create the Servlet
Create Servlet inside-> src-> Right click -> New -> Class -> HelloServlet
HelloServlet.java
Java
package com.example.servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.print("<h2>Hello Client, welcome to my Website...</h2>");
}
}
Explanation:
- Class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet, making it a servlet that handles HTTP requests.
- It overrides the doGet() method to handle GET requests from the client.
- response.setContentType("text/html") line sets the response type to HTML so the browser can properly render the output.
- A PrintWriter object is created to send character text to the client.
- servlet sends a simple HTML message: "Hello Client welcome to my Website." to the client browser.
- This servlet is typically mapped in the web.xml file or via annotations to respond to a specific URL.
Create Configuration file inside -> WebContent->WEB-INF->web.xml
XML
<web-app version="2.5"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd">
<!-- Servlet -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>HelloServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.filter.HelloServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>HelloServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/servlet1</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<!-- Filter -->
<filter>
<filter-name>f1</filter-name>
<filter-class>com.filter.MyBlockFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>f1</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/servlet1</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
</web-app>
6. Change Tomcat Port
By default, Tomcat runs on port 8080. We changed it to 2021:
- In Eclipse -> Servers tab -> Double-click Tomcat -> Ports -> Change HTTP/1.1 to 2021.
- Restart Tomcat.
Step 7: Deploy and Run
- Right-click project -> Run As -> Run on Server.
- Choose Tomcat Server.
- Open browser -> http://localhost:2021
- Click the link:
Output:
If our PC IP address is "127.0.0.1" we cannot visit the website and show below message
Your IP address is blocked by this website
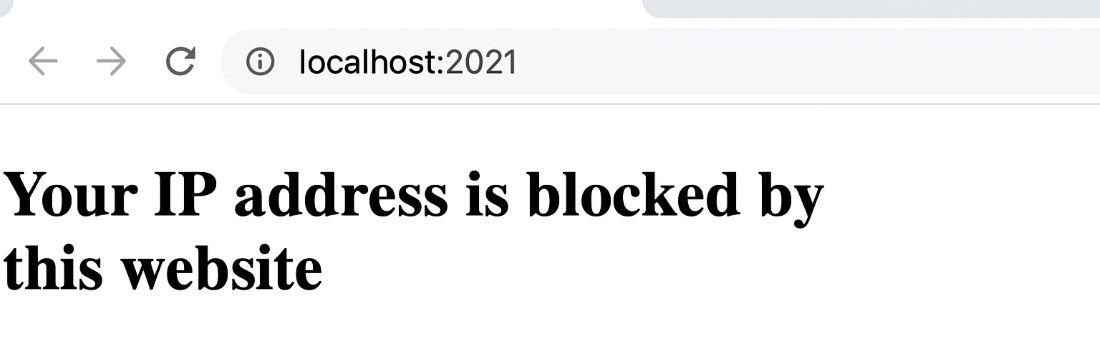 output
outputIf our PC IP address is not "127.0.0.1" then we can visit the website
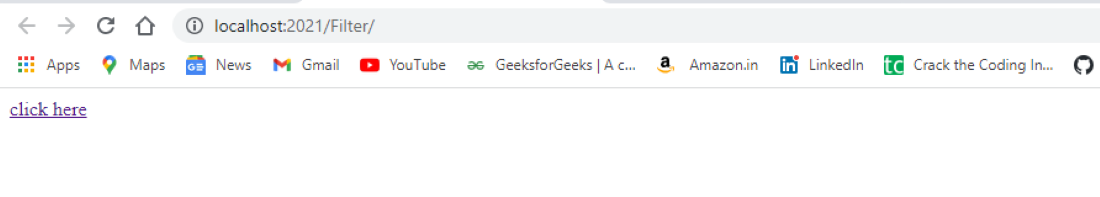 output
outputOn the page, user clicks "click here"
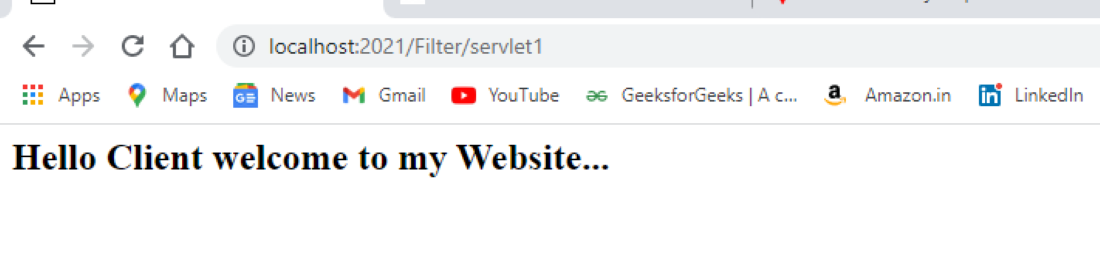 output
output
Explore
Java Basics
OOP & Interfaces
Collections
Exception Handling
Java Advanced
Practice Java