Area and Perimeter of Shapes | Formula and Examples
Last Updated :
23 Jul, 2025
Area and Perimeter are the two fundamental properties related to 2-dimensional shapes. Defining the size of the shape and the length of its boundary. By learning about the areas of 2D shapes, we can easily determine the surface areas of 3D bodies and the perimeter helps us to calculate the length of the boundary of any 2D closed shape.
In this article, we will learn how to find the Area and Perimeter of different shapes, with the help of solved examples.
Definition of Area
Area is a measure of a region's size on a surface.
In simple words, area helps us to know how much space is occupied by a closed surface in a plane. The area is defined only for closed shapes. For a 2D geometric entity, area depends upon the shape and dimensions of the entity. It is calculated in sq units of units2 (eg: cm2, m2).
Definition of Perimeter
Perimeter is the length of a boundary or closed path that outlines a two dimensional shape.
For curved 2D shapes such as circles and ellipses, the perimeter is called their circumference. By calculating the perimeter of a region, one can determine the length required to surround that region on its boundaries.
The table below provides a list of area and perimeter formulas to find values of area and perimeter of various 2D shapes.
Area and Perimeter Formulas for all Shapes |
|---|
Shape | Area | Perimeter | Variables description |
|---|
Triangle | A = 1/2(b × h) | P = a + b + c | b = base, h = height
a,b and c are sides of triangle |
|---|
Rectangle | A = l × b | P = 2(l+b) | l = length,
b = breadth |
|---|
Square | A = s × s | P = 4 × s | s = side |
|---|
Circle | A = πr2 | P = 2πr | r = radius,
π = 22/7 or 3.14 |
|---|
Ellipse | A = π×b | P = π(a+b) | a = semi major axis
b = semi minor axis |
|---|
Parallelogram | A = b × h | P = 2(a+b) | b = base, h = height
a and b are the opposite sides |
|---|
Rhombus | A = 1/2 (d1 × d2) | P = 4 × a | d1, d2 = diagonals
a = side of rhombus |
|---|
Trapezium | A = 1/2 × (a+b) × h | P = Sum of all Sides | a,b = length of parallel sides,
h = height |
|---|
For polygons, perimeter can be calculated as sum of lengths of its sides. And, for a regular polygon, i.e a polygon having equal sides, perimeter is calculated as n × a, where n is number of sides or edges of the polygon and a is the measure of its one side.
Area and Perimeter of All Shapes
The 2D shapes have some specific properties related to their dimensions and orientation of their dimensions which they adhere to. Every shape have defined formulae to calculate their area and perimeter.
Let's discuss the formulas to calculate area and perimeter for various shapes.
Triangle
A triangle is closed figure having three sides. It has three vertices. Altitude or height of a triangle is the perpendicular drawn from one of its vertex to meet the opposite side.
The side to which the perpendicular meets is called as the base of a triangle.
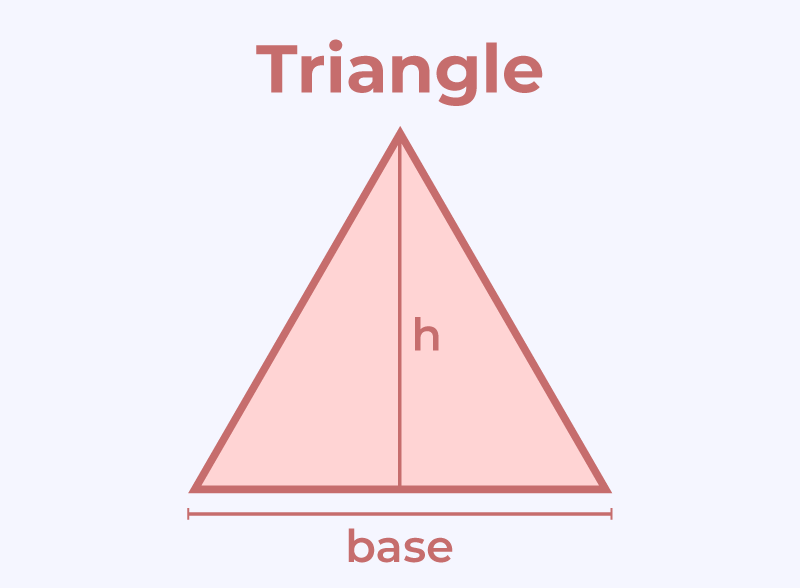
Area of a triangle = 1/2 × (base) × (height)
Perimeter of a triangle = Sum of all three sides
Rectangle
A rectangle is a four sided polygon having opposite sides equal and parallel. All the angles of a rectangle are equal to 90°.
The longer side of a rectangle is known as the length of rectangle and the other side is called the breadth or width of rectangle. 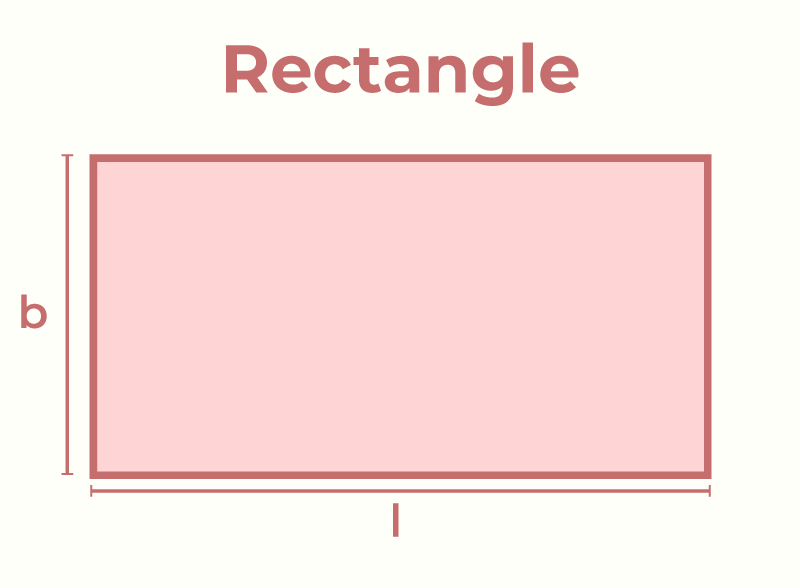
Area of a rectangle = length × breadth
Perimeter of a rectangle = 2 × (length + breadth)
Square
A square is a four sided polygon having all four sides equal and parallel to each other. Also, all angles of a square have a measure of 90° each. Thus, a square can be said to be a special type of rectangle having all four sides equal.
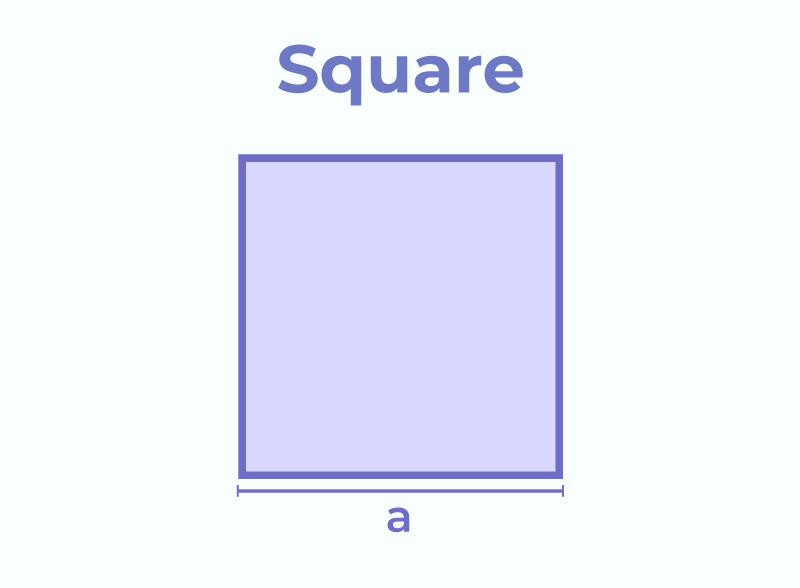
Area of a Square = (side) × (side)
Perimeter of a Square = 4 × (side)
Parallelogram
A parallelogram is a four sided polygon having opposite sides equal and parallel. The perpendicular distance between two opposite sides is called as the height of a parallelogram. The length of those sides is called as the base of a parallelogram.
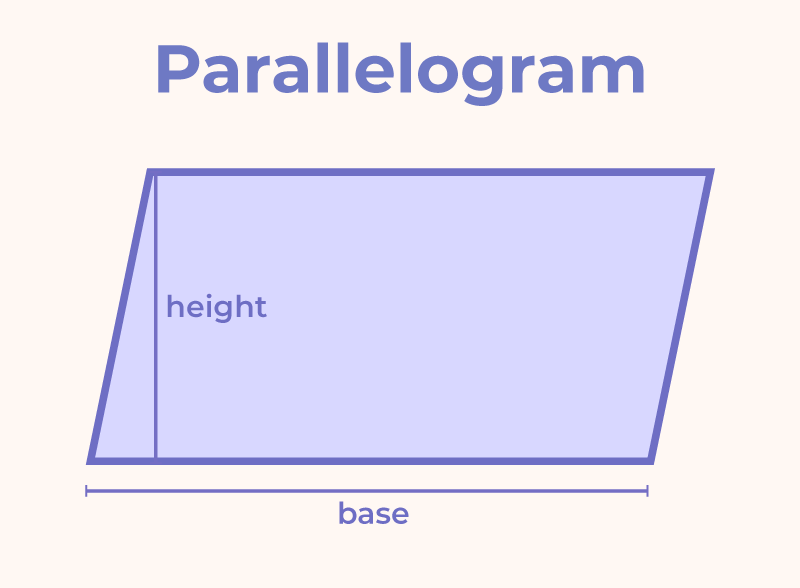
Area of a Parallelogram = Base × Height
Perimeter of a Parallelogram = 2 × (Sum of opposite sides)
Rhombus
A rhombus is a four sided polygon having all four sides equal and opposite sides being parallel to each other. The area of a rhombus is calculated by the measure of length of its diagonals.
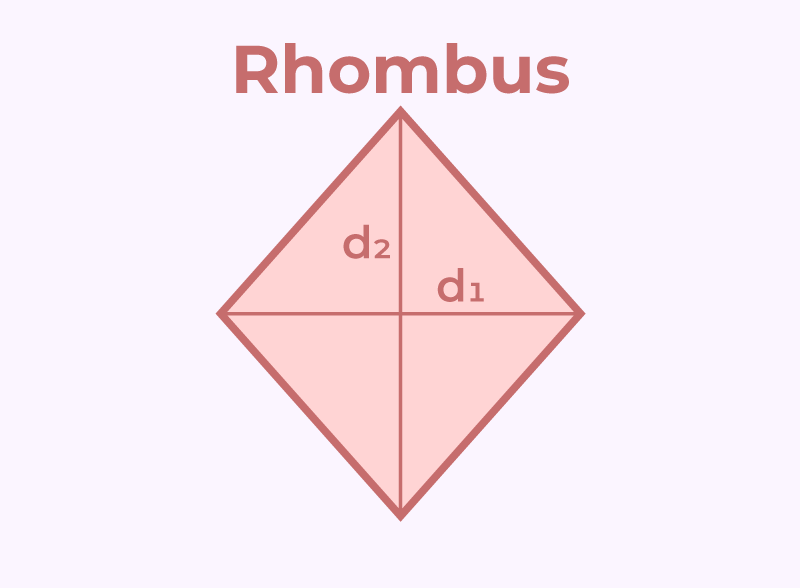
Area of a Rhombus = 1/2 × ( Product of diagonals)
Perimeter of a Rhombus = 4 × side
Trapezium
Trapezium is a four sided polygon having two opposite sides parallel to each other. The other two sides may or may not be parallel. The distance between two parallel sides is known as the height of the trapezium.
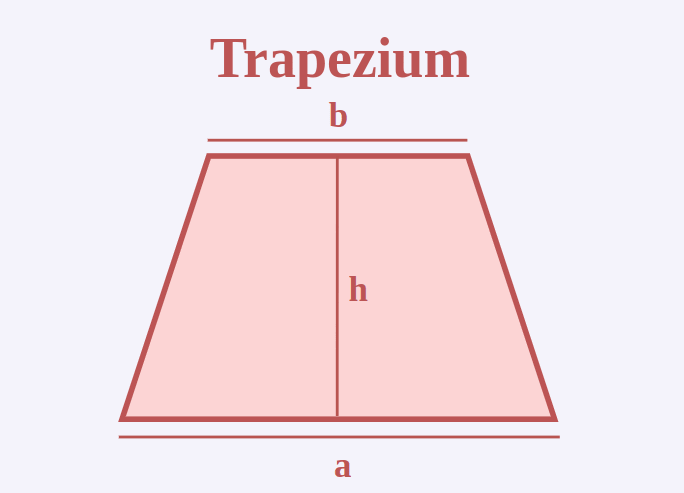
Area of a trapezium = 1/2 × (Sum of parallel sides) × (height)
Perimeter of a trapezium = (Sum of all 4 sides)
Circle
A circle is a round shaped figure in which distance of all points lying on it from its center is equal . This distance is callled the radius of the circle. The perimeter of a circle is known as its circumference. 
Area of a Circle = πr2
Perimeter of a Circle = 2πr
Semicircle
A semicircle is half of the circle whose one side is curved and other side is bounded by the diameter of the circle.
Area of Semicircle = 1/2 × π × r2
Perimeter of Semicircle = πr + 2r
Difference between Area and Perimeter
The differences between Area and Perimeter are listed in form of a table below:
Area vs Perimeter |
|---|
Area | Perimeter |
|---|
Area is a measure of a region's size on a surface. The region is a closed 2D figure. | Perimeter is a measure of the length of boundary of any closed 2D shape. |
Area is expressed in square units, such as m2, cm2, mm2, etc. | It is expressed in units, such as m, cm, mm, etc. |
Example: The space occupied by a park. | Example: The length of boundary of park. |
Also, Check:
Solved Examples on Area and Perimeter
Let's solve some example problems on the Area and Perimeter formulas of different shapes.
Example 1: Find the values of perimeter and area for rectangular park having length as 40 m and the breadth as 50 m.
Solution:
Given,
Length of rectangle, l = 40 m
Breadth of rectangle, b = 50 m
We know that,
Perimeter of rectangle = 2(l+b) = 2×(40+50) = 2 × 90 = 180 m.
Area of rectangle = l × b = 40 × 0 = 2000 m2
Thus,
Perimeter = 180 m. and Area = 2000 m2
Example 2: A circular running track has a radius of 7 meters. Find its circumference. Take π = 22/7.
Solution:
We have,
Radius, r = 7 m and Circumference of a Circle = 2πr
Therefore,
Circumference = 2 × (22/7) × 7 = 44 meters
Thus, circumference of the circular track comes out to be 44 meters.
Example 3: The opposite sides of a parallelogram have values as 12 units and 8 units. Find the value of its perimeter.
Solution:
We know that,
Perimeter of parallelogram = 2 × (Sum of opposite sides)
Thus,
Perimeter = 2 × (12+8) = 2 × 20 = 40 units
Practice Questions on Area and Perimeter
Following are some practice questions based on calculating area and perimeter for you to solve.
Q1. Find the area of a trapezium whose parallel sides measure 12 cm and 14 cm. The distance between parallel sides is equal to 6 cm.
Q2. Calculate the perimeter of a regular pentagon having each side equal to 5 inches.
Q3. A circle has a diameter of 14 cm. Find the values of its circumference and area. Use, = 22/7.
Q4. The perimeter of a circle is 44 m. Find its radius and then calculate its area.
Conclusion
Area and perimeter of different shapes is essential for solving various geometric problems and real-life applications. The area helps determine the space a shape occupies, while the perimeter measures the length of boundary around it. Learning these area and perimeter formulas for shapes like triangles, rectangles, squares, circles, is crucial in fields like architecture, engineering, and design. By practicing these concepts, one can easily calculate dimensions and solve various problems, making this knowledge extremely useful for students.
Explore
Basic Arithmetic
Algebra
Geometry
Trigonometry & Vector Algebra
Calculus
Probability and Statistics
Practice