Class 11 RD Sharma Solutions - Chapter 23 The Straight Lines- Exercise 23.12 | Set 3
Last Updated :
23 Jul, 2025
Chapter 23 of RD Sharma's Class 11 mathematics textbook covers "The Straight Lines" focusing on the various aspects and properties of the straight lines in coordinate geometry. Exercise 23.12 | Set 3 delves into the solving problems involving the equations of straight lines their slopes and intersections. This section aims to the reinforce students' understanding of the line equations and their practical applications.
Straight Lines
The Straight lines are fundamental elements in the coordinate geometry represented by the linear equations in the two variables. The general form of a straight line equation is Ax+By+C=0 where A, B and C are constants. The slope-intercept form y=mx+c expresses a line where m is the slope and c is the y-intercept. Understanding the slope helps in determining the line's inclination and parallelism.
Question 21. Find the coordinates of the foot of the perpendicular from the point (-1, 3) to the line 3x - 4y - 16 = 0.
Solution:
Let us considered the foot of perpendicular of P(-1, 3) on line 3x - 4y = 16 be Q(a, b)
So, (slope of given line) x (slope of PQ) = -1
\frac{3}{4} \times \frac{b-3}{a+1}
3(b - 3) = -4a - 4
3b - 9 = -4a - 4
4a + 3b = 5 .......(1)
It is given that Q(a, b) lie on the line 3x - 4y = 16
3a - 4b = 16 .......(2)
On solving eq(1) and (2), we get
a = (68/25) and b = (-49/25)
Hence, the coordinate of Q is (68/25, -49/25)
Question 22. Find the projection of the point (1, 0) on the line joining the points (-1, 2) and (5, 4).
Solution:
Let us considered P(-1, 2) and Q(5, 4) are the given point
So, the equation of line PQ is
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y-2=\frac{4-2}{5+1}(x+1)\\ y-2=\frac{2}{6}(x+1)
3y - x = 7 ........(1)
And the slope of line PQ = 1/3
Let us considered point A(1, 0) is the given point and B(x1, y1) be the projection of A
So, the slope of AB = -3
The equation of PQ is
y - 0 = -3(x - 1)
y = -3x + 3 .......(2)
On solving eq(1) and (2), we get
3y-(\frac{y-3}{-3})=7
-9y - y + 3 = -21
-10y = -24
y = 12/5
12/5 = -3x + 3
-3x = 12/5 - 3 = (12 -15)/5 = -3/5
x = 1/5
Hence, the B(1/5, 12/5)
Question 23. Find the equation of a line perpendicular to the line √3x - y + 5 = 0 and at a distance of 3 units from the origin.
Solution:
Let us considered the required equation of line is
y - y1 = m'(x - x1) ..........(1)
It is given that the required line is perpendicular to the line √3x - y + 5 = 0
So, the slope of the line is
y = √3x + 5
On comparing y = mx + c, we get
m = √3
m' = -1/m = -1/√3
and the point is (x1, y1) = (3, 3)
Now put the value of m' and (x1, y1) is eq(1), we get
y - 3 = -1/√3(x - 3)
x + √3y - 6 = 0
Hence, the required equation of line is x + √3y - 6 = 0
Question 24. The line 2x + 3y = 12 meets the x-axis at A and y-axis at B. The line through (5, 5) perpendicular to AB meets the x-axis and the line AB at C and E respectively. If O is the origin of coordinates, find the area of figure OCEB.
Solution:
It is given that the line 2x+3y=12 meets the x-axis at A and y-axis at B
So, A is 2x = 12 = x = 6
A is (6, 0)
B is 3y = 12
y = 4
B is (0, 4)
It is given that line through (5, 5) perpendicular to 2x + 3y = 12 will have slope = 3/2
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
(y - 5) = 3/2(x - 5)
And 2y - 3x = -5 is equation of line which meets x-axis at C and the line at E
So, C is -3x = -5
x = -5/3
E is (5/3, 0)
Here, E is the point of intersection of two lines
So, 2x + 3y = 12
2y - 3x = -5
Now we find the area of OBCE = area of AOB - area of ACE
= 1/2 x AO x OB - 1/2 x AC x CE
= 24/2 - 1/2 x √13 x 2/3√13
= 24/2 - 1/2 x 2/3 x 13
= 12 - 13/3
= 23/3 sq.unit
Question 25. Find the equation of the straight line which cuts of intercepts on x-axis twice that on y-axis and is at unit distance from the origin.
Solution:
Let us considered the equation of line in intercept form is \frac{x}{a}+\frac{y}{b}=1
It is given that its intercept on y-axis = 2a
So, the equation is
\frac{x}{2a}+\frac{y}{a}=1
ax + 2ay = 2a2 ........(1)
Now, perpendicular distance of eq(1) from origin is given unity
So, \frac{|ax_1+by_1+c|}{\sqrt{a^2+b^2}}=1
a = a, b = 2a, c = -2a2, x1 = 0, y1 = 0
\frac{|a(0)+2a(0)-2a^2|}{\sqrt{(2a)^2+(a)^2}}=1\\ -2a^2=\sqrt{5}a
4a4 = a25
a2 = 5/4
a = ±√5/4
So, the intercept form of straight line is
\frac{x}{2a}+\frac{y}{a}=1\\ \frac{x}{±\frac{2\sqrt{5}}{4}}+\frac{y}{±\frac{\sqrt{5}}{4}}=1
x + 2y = ±√5
Hence, the required equation of line is x + 2y = ±√5
Question 26. The equations of the perpendicular bisector of the sides AB and AC of a triangle ABC x - y + 5 = 0 and x + 2y = 0 respectively. If point A is (1, -2), find the equation of the line BC.
Solution:
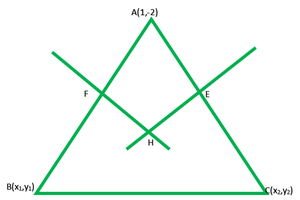
Let us considered (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) be the coordinates of B and C.
It is given that perpendicular bisector of AB is x - y + 5 = 0
So, its slope = 1
The coordinates of F=(\frac{x_1+1}{2},\frac{y_1-2}{2})
From the figure it is given that F lie on the x - y + 5 = 0
\frac{x_1+1}{2}-\frac{y_1-2}{2}+5=0
x1 + 1 - y1 + 2 + 10 = 0
x1 - y1 + 13 = 0 ......(1)
From the figure it is given that AB is perpendicular to HF
So, (slope of AB) x (slope of HF) = -1
(\frac{y_1+2}{x_1-1})(1)=-1
x1 + y1 + 1 = 0
Now on solving equation (1) and (2), we get
x1 = -7, y1 = 6
So, B is (-7, 6)
Now, perpendicular bisector of AC is x + 2y = 0
So, its slope = -1/2
The coordinate of E =(\frac{x_2+1}{2},\frac{y_2-2}{2})
From the figure it is given that E lies on perpendicular bisector of AC
(\frac{x_2+1}{2})+2(\frac{y_2-2}{2})=0
x2 + 1 + 2y2 - 4 = 0
x2 + 2y2 - 3 = 0 ......(3)
Also, AC is perpendicular to HE
So, (slope of AC) x (slope of HE) = -1
(\frac{y_2+2}{x_2-1})(-\frac{1}{2})=-1
y2 + 2 = 2x2 - 2
2x2 - y2 = 4 .....(4)
On solving equation (3) and (4), we get
x2 = 11/5 , y2 = 2/5
Thus, point C is (11/5, 2/5)
So, the equation of BC is
y - y1=\frac{y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1}(x-x_1)\\ y-6=\frac{\frac{2}{5}-6}{\frac{11}{5}+7}(x+7)
y-6=\frac{-\frac{28}{5}}{\frac{46}{5}}(x+7)
y - 6 = -14/23(x + 7)
23y - 138 = -14x - 98
14x + 23y - 40 = 0
Hence, the required equation of line is 14x + 23y - 40 = 0
Question 27. Find the equation of the straight line passing through the point of intersection of the lines 5x - 6y -1 = 0 and perpendicular to the line 3x - 5y + 11 = 0.
Solution:
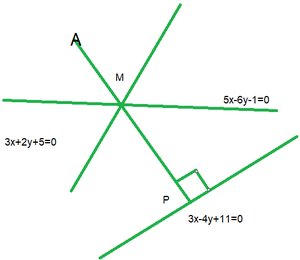
Let us considered M be the point of intersection of the given lines 5x - 6y - 1 = 0 and 3x + 2y + 5 = 0
On solving both the equations we get the point of intersection as M (-1, -1).
Now we find the slope of 3x - 5y + 11 = 0
5y = 3x + 11
y = 3x/5 + 11/5
On comparing y = mx + c, we get
m = 3/5
From the figure we can see that AP is perpendicular to line 3x - 5y + 11 = 0
So, the slope of AP = -5/3
Now the equation of AP is
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y + 1 = -5/3(x + 1)
3y + 3 = -5x - 5
5x + 3y + 8 = 0
Hence, the equation of the line AP is 5x + 3y + 8 = 0
Read more :
Explore
Basic Arithmetic
Algebra
Geometry
Trigonometry & Vector Algebra
Calculus
Probability and Statistics
Practice