Multilevel Queue (MLQ) CPU Scheduling
Last Updated :
26 Aug, 2025
Multilevel Queue(MLQ) CPU scheduling is a type of scheduling that is applied at the operating system level with the aim of sectioning types of processes and then being able to manage them properly. As with the MQ Series, processes are grouped into several queues using MLQ based on known parameters such as priority, memory, or type. Every queue has its scheduling policy and processes that are in the same queue are very similar too. This article will explain the Multilevel Queue in detail.
Multilevel Queue Scheduling divides processes into multiple queues arranged in a hierarchy.
- Each queue has its own priority level and process type.
- Different scheduling algorithms can be applied to different queues.
- Once assigned, a process is permanently mapped to a specific queue.
- Assignment is usually based on factors like priority, resources, or process characteristics.
Features of Multilevel Queue (MLQ) CPU Scheduling
- Multiple Queues: Processes are divided into queues based on priority (e.g., system, interactive, batch).
- Priorities: Higher-priority processes get higher queues; lower ones go to lower queues.
- Preemption: A high-priority process can interrupt a low-priority one.
- Different Algorithms: Each queue uses its own scheduling method (e.g., RR for interactive, FCFS for batch).
- Feedback: Priority may be adjusted if a process waits too long.
- Efficient CPU Use: High-priority processes run first, but low-priority ones also get CPU when higher queues are empty.
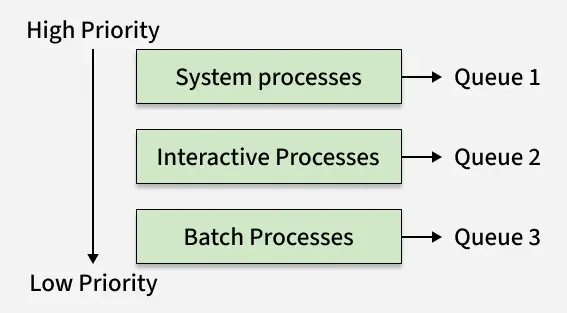
Ready Queue is divided into separate queues for each class of processes. For example, let us take three different types of processes System processes, Interactive processes, and Batch Processes. All three processes have their own queue. Now, look at the below figure.
 Multilevel Queue (MLQ) CPU Scheduling
Multilevel Queue (MLQ) CPU Scheduling
The Description of the processes in the above diagram is as follows:
- System Processes: The CPU itself has its own process to run which is generally termed a System Process.
- Interactive Processes: An Interactive Process is a type of process in which there should be the same type of interaction.
- Batch Processes: Batch processing is generally a technique in the Operating system that collects the programs and data together in the form of a batch before the processing starts.
All three different type of processes have their own queue. Each queue has its own Scheduling algorithm. For example, queue 1 and queue 2 use Round Robin while queue 3 can use FCFS to schedule their processes.
Scheduling among the queues: What will happen if all the queues have some processes? Which process should get the CPU? To determine this Scheduling among the queues is necessary. There are two ways to do so -
- Fixed priority preemptive scheduling method: Each queue has absolute priority over the lower priority queue. Let us consider the following priority order queue 1 > queue 2 > queue 3. According to this algorithm, no process in the batch queue(queue 3) can run unless queues 1 and 2 are empty. If any batch process (queue 3) is running and any system (queue 1) or Interactive process(queue 2) entered the ready queue the batch process is preempted.
- Time slicing: In this method, each queue gets a certain portion of CPU time and can use it to schedule its own processes. For instance, queue 1 takes 50 percent of CPU time queue 2 takes 30 percent and queue 3 gets 20 percent of CPU time.
Example Problem:
Consider the below table of four processes under Multilevel queue scheduling.
We have 3 processes:
- P1: Uses Round Robin (RR) in Queue 1
- P2: Uses First-Come-First-Serve (FCFS) in Queue 2
- P3: Uses Shortest Job First (SJF) in Queue 3
In Multilevel Queue Scheduling, processes are divided into different queues based on priority or process type.
- Each queue uses a different scheduling algorithm (e.g., Round Robin, FCFS, SJF).
- Higher priority queues are always served first.
- Once a queue is empty, the CPU moves to the next lower-priority queue.
This ensures fast response for interactive processes, while still allowing batch processes to complete in lower queues.
Advanatages and Disadvantages
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Separates processes (e.g., system, interactive, batch) into distinct queues, making management more organized. | If high-priority queues are underloaded, CPU may stay idle while lower-priority processes wait. |
Since queue priorities are fixed, system administrators can easily predict how processes will be scheduled. | Once placed in a queue, processes cannot move between queues, leading to inefficiency if workload type changes. |
Interactive and system processes get higher priority, leading to improved response times for user-centric tasks. | Handling multiple queues requires more bookkeeping and resources. |
Suitable for systems handling a wide variety of process types, as multiple queues can be designed for different workloads. | Some queues may dominate CPU time while others rarely get a chance |
Ensures critical processes are not delayed behind non-essential tasks. | In real-world workloads where process behavior changes, fixed queues reduce flexibility and adaptability. |
Multilevel queue Scheduling
Explore
OS Basics
Process Management
Memory Management
I/O Management
Important Links