Spring Boot - Application Properties
Last Updated :
19 Aug, 2025
In Spring Boot applications, configuration plays a very important role in customizing the behavior of the application. Instead of hardcoding values in the code, Spring Boot provides a flexible way to configure application settings using the application.properties or application.yml file.
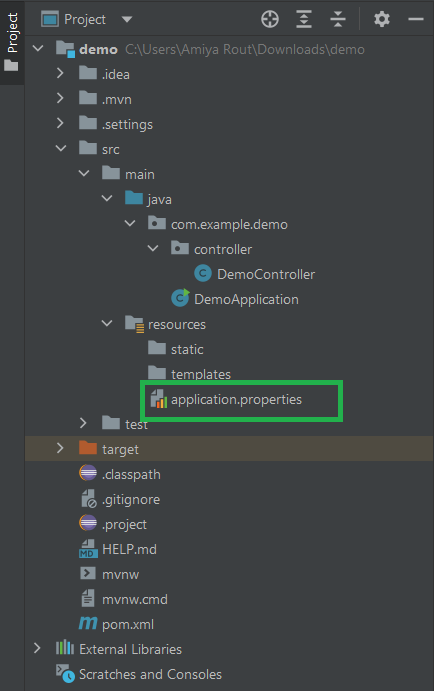
These files allow developers to manage environment-specific settings such as database configuration, server port, logging level and much more, making the application more maintainable and portable. The image below describes the Location of application.properties.
Why Use application.properties?
- Centralized configuration management.
- Easy to override default Spring Boot settings.
- Provides flexibility for different environments (dev, test, prod).
- Reduces hardcoding in source code.
Commonly Used Properties
1. Server Configuration
You can change the default port (8080) of a Spring Boot application by setting the property server.port in the application.properties file. For example: server.port=8989

2. Defining the Application Name
We can set a custom name for your Spring Boot application using the spring.application.name property in the application.properties.
Example:
spring.application.name=userservice
This represents the property as a key-value pair, where each key is associated with a corresponding value.
2. Database Configuration
To connect your Spring Boot application with a database, specify the required properties such as spring.datasource.url, spring.datasource.username and spring.datasource.password in the application.properties file. These properties vary depending on the database (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle).
For MySQL Database:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=admin
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
For PostgreSQL Database
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/Postgres
atasource.username=postgres
spring.datasource.password=postgres
spring.jpa.database-platform=org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQLDialect
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
For MongoDB
spring.data.mongodb.host=localhost
spring.data.mongodb.port=27017
spring.data.mongodb.database=BookStore
Hibernate (JPA) Settings
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
3. Connecting with an Eureka Server
Eureka Server acts as a service registry in microservices architecture. Each microservice registers itself to Eureka, which maintains service discovery details.
eureka.client.register-with-eureka=true
eureka.client.fetch-registry=true
eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=http://localhost:9096/eureka/
eureka.instance.hostname=localhost
Note: The values provided are sample data. Please update them according to your database configuration. However, the keys remain the same.
Using application.yml Instead of application.properties
The application.properties file is not very readable when dealing with complex configurations. Most developers prefer using application.yml (YAML format) instead. YAML is a superset of JSON and provides a more structured and readable way to define hierarchical configuration data. Let's convert some of the previous examples into YAML format.
Case 1: Connecting with a MySQL Database
Let’s pick above example 3 where we were connecting with the MySQL Database, the corresponding properties will be as follows:
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://${MYSQL_HOST:localhost}:3306/db_example
username: springuser
password: ThePassword
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jpa:
hibernate:
ddl-auto: update
Case 2: Connecting with an Eureka Server
Let's pick above example 6 where we were connecting with the Eureka Server, the corresponding properties will be as follows:
eureka:
client:
register-with-eureka: true
fetch-registry: true
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:9096/eureka/
instance:
hostname: localhost
Explore
Spring Boot Basics and Prerequisites
Spring Boot Core
Spring Boot with REST API
Spring Boot with Database and Data JPA
Spring Boot with Kafka
Spring Boot with AOP