The SQL MAX() function helps quickly identify the highest value within any column, making it useful for summarizing and analyzing data trends. It is widely used in reports to find top values like peak sales, latest dates, or highest scores.
- Returns the maximum value from the specified column.
- Supports numeric, date, and text data types.
- Skips NULL values during calculation.
Example: First, we create a demo SQL database and table, on which we use the MAX() functions.
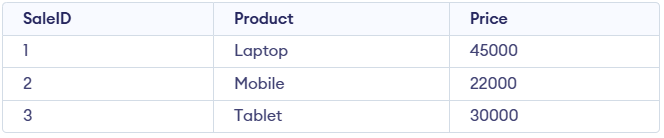 SalesData Table
SalesData TableQuery:
SELECT MAX(Price) AS HighestPrice
FROM SalesData;
Output:

- Finds the highest price from the Price column in the SalesData table.
- Returns a single value labeled as HighestPrice.
Syntax:
SELECT MAX(column_name)
FROM table_name;
Examples of SQL MAX() Function
Here, we demonstrate the usage of the MAX() function using a single sample table named Products. Consider this Products table for all the examples below:
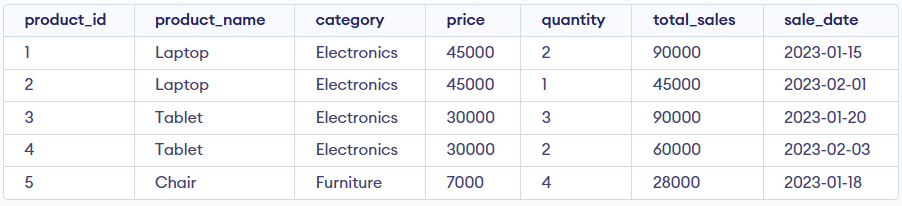 Products Table
Products TableExample 1: Find the Maximum Price in a Table
In this example, we see how the MAX() function retrieves the highest total_sales value from the Products table while ignoring NULL values.
Query:
SELECT MAX(total_sales) AS [Highest Total Sales]
FROM Products;
Output:

- Returns the largest value from the total_sales column.
- Helps identify the highest sales amount in the entire table.
Example 2: Use MAX() with a Condition
In this example, we see how the MAX() function returns the highest price after filtering rows based on a specific condition.
Query:
SELECT MAX(price) AS [Highest Price in Electronics]
FROM Products
WHERE category = 'Electronics';
Output:

- Applies WHERE to include only products in the Electronics category.
- MAX() then returns the highest price within that filtered group.
Example 3: Find the Latest Sale Date
In this example, we use MAX() to get the most recent sale date from the table.
Query:
SELECT MAX(sale_date) AS [Latest Sale Date]
FROM Products;
Output:

- MAX(sale_date) returns the latest date stored in the column.
- Useful for identifying the most recent sale activity.
Example 4: Using MAX() with GROUP BY
In this example, we use MAX() with GROUP BY to find the highest sale amount for each product.
Query:
SELECT product_name, MAX(total_sales) AS [Top Sales Amount]
FROM Products
GROUP BY product_name;
Output:

- Groups rows by product_name and applies MAX() to each group.
- Returns the top sales amount for every individual product.
Example 5: Using MAX() in Subqueries
In this example, we use MAX() inside a subquery to get the product with the highest total_sales.
Query:
SELECT *
FROM Products
WHERE total_sales = (SELECT MAX(total_sales) FROM Products);
Output:
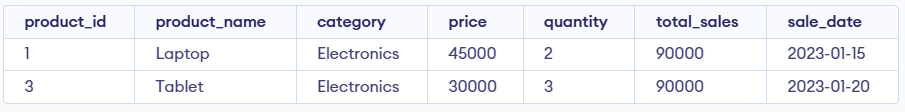
- The subquery returns the maximum total_sales value from Products.
- The main query fetches the full record that matches this highest value.
Example 6: Using MAX() with HAVING
In this example, we use MAX() with HAVING to filter product groups based on their highest total sales.
Query:
SELECT product_name, MAX(total_sales) AS HighestSale
FROM Products
GROUP BY product_name
HAVING MAX(total_sales) > 50000;
Output:

- GROUP BY creates groups for each product_name and calculates their MAX(total_sales).
- HAVING filters only those products whose highest sale exceeds 50,000.
Explore
Basics
Queries & Operations
SQL Joins & Functions
Data Constraints & Aggregate Functions
Advanced SQL Topics
Database Design & Security