What is Low Level Design or LLD?
Last Updated :
30 Aug, 2025
Low-Level Design (LLD) plays a crucial role in software development, transforming high-level abstract concepts into detailed, actionable components that developers can use to build the system.
- LLD is the blueprint that guides developers on how to implement specific components of a system, such as classes, methods, algorithms, and data structures.
- Whether we are working on a microservice architecture, a web application, or a mobile app, understanding LLD is essential for building scalable, maintainable, and efficient systems.
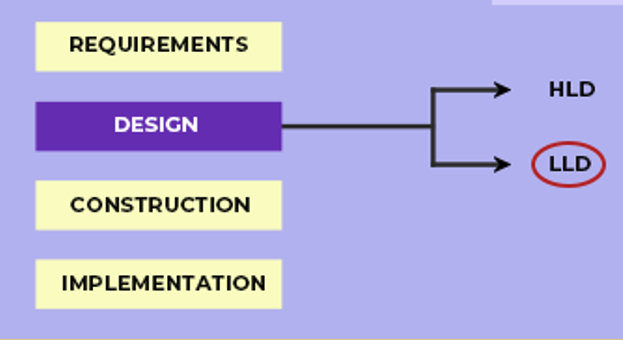
How is LLD different from HLD?
While both HLD (High-Level Design) and LLD (Low-Level Design) are critical in system architecture, they serve different purposes.
1. High-Level Design (HLD): Focuses on the overall architecture of the system. It addresses questions such as which frameworks to use, what databases are suitable, how to integrate different components, and how the system will function at a broader level.
2. Low-Level Design (LLD): Once the high-level structure is in place, LLD takes over by focusing on specific components, modules, and interactions. It provides detailed design diagrams (like UML diagrams) and breaks down how each component should behave, how it will interact with others, and what algorithms and data structures will be used.
For HLD to LLD conversion, we generally use Unified Modelling Language (UML) diagrams. Adding to these diagrams we use OOP principles and SOLID principles and design patterns while designing.
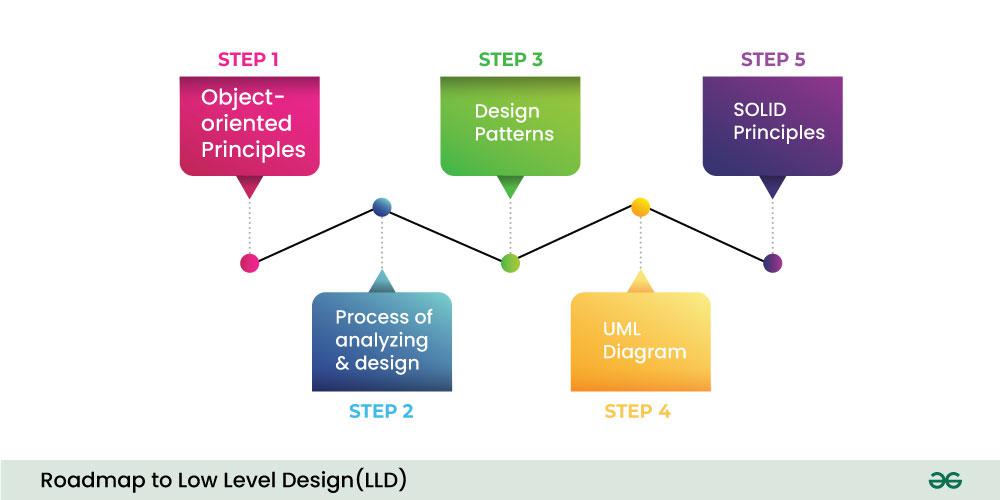
Step 1. Understanding Object-Oriented Principles
The user requirement is processed by using concepts of OOPS programming. OOP concepts serve as the foundation for LLD, and having a deep understanding of them will help you design maintainable and scalable software components. Hence it is recommended to have a strong grip on Object-Oriented Programming principles such as:
- Encapsulation: Bundling data and the methods that operate on that data within one unit.
- Inheritance: Mechanism where a new class can inherit the properties and methods of an existing class.
- Polymorphism: Ability of different classes to respond to the same method in different ways.
- Abstraction: Hiding the complex implementation details while showing only the essential features of an object.
Step 2. Analyzing and Designing Components
LLD requires you to analyze real-world problems and break them down into object-world problems using OOP concepts. This is a critical step where real-world entities are modeled into objects and classes.
You should focus on:
- Identifying classes and objects based on the system requirements.
- Determining relationships (like associations, inheritance, etc.) between different entities.
- Using SOLID principles to ensure your design is clean, maintainable, and scalable.
Step 3. Implementing Design Patterns
Now the implementation of our above object oriented problem is carried out with the help of design patterns. Design patterns are reusable solutions to common problems encountered in software design. They provide a structured approach to design by capturing best practices and proven solutions, making it easier to develop scalable, maintainable, and efficient software. By using these patterns, developers can solve problems more effectively while adhering to best practices.
- Creational Patterns (e.g., Singleton, Factory): These patterns deal with object creation mechanisms, trying to create objects in a way that is appropriate to the situation.
- Behavioral Patterns (e.g., Observer, Strategy): Focus on communication between objects and how they interact with each other.
- Structural Patterns (e.g., Adapter, Composite): These patterns are concerned with simplifying the structure of the system and its components.
Step 4. Use of UML Diagram in LLD
Unified Modeling Language is a visual representation used to design and model the system. UML diagrams play an important role in converting HLD to LLD. They provide a proper and clear visual representation of the components and their relationships, which helps developers significantly.S ome of the most important UML diagrams used in LLD include:
- Class Diagrams: Represent the structure of the system in terms of its classes and the relationships between them.
- Sequence Diagrams: Illustrate how objects interact over time, showing the sequence of method calls.
- Activity Diagrams: Show the workflow or activities of a system component.
- State Diagrams: Represent the different states of a component or object and the transitions between these states.
- Use Case Diagrams: Define the functional requirements of the system by showing different user interactions.
These diagrams play a significant role in LLD, providing a clear visual representation of the components and their interactions.
5. Implementing SOLID Principles
These are sets of 5 principles(rules) that are strictly followed as per requirements of the system or requirements for optimal designing. In order to write scalable, flexible, maintainable, and reusable code:
- Single-responsibility principle (SRP)
- Open-closed principle (OCP)
- Liskov’s Substitution Principle(LSP)
- Interface Segregation Principle (ISP)
- Dependency Inversion Principle (DIP)
It's important to keep in mind that SOLID principles are just guidelines and not strict rules to be followed. The key is to strike a balance between following these principles and considering the specific needs and constraints of your business requirement.
Benefits of Low-Level Design(LLD)
Low-Level Design offers a detailed and structured approach to building software systems, providing multiple benefits:
- Clear Component Functionality: LLD provides a detailed plan for how each part of the software will work, making development and debugging easier.
- Scalability and Flexibility: It provides a well-structured design, which makes simpler to update or fix parts of the system without affecting the entire software.
- Improved Communication: LLD helps team members communicate more effectively because everyone has a clear understanding of how components are working.
- Cleaner Code: Following the design principles in LLD leads to more cleaner, organized code, making it less prone to errors.
- Faster Coding: A proper LLD speeds up the coding process because developers can follow the detailed plan made earlier.
Best Practices for Low-Level Design(LLD)
Below are some of the best practices to form a good Low-Level Design:
- Modular Design: Always try to break down the system into small, independent components that contain specific functionalities.
- Clear Interfaces: Clearly define the interfaces for each component, which should include methods, inputs, outputs. This helps in maintaining proper communication between components
- Use Design Patterns: Include OOPS Principles to promote code reusability, flexibility and maintainability.
- Adopt SOLID Principles: Follow Solid Principles which will lead to more robust and maintainable design.
- Error Handling: plan in advance for error handling and validation of the system by including validation checks in the design
Roadmap to Learn LLD
To master Low-Level Design, follow this structured learning path:
1. Object-Oriented and Design Principles
2. Design Patterns
3. UML and Modeling in LLD
4. LLD Best Practices
5. LLD Case Studies
6. Interview Preparation
Explore
What is System Design
System Design Fundamentals
Scalability in System Design
Databases in Designing Systems
High Level Design(HLD)
Low Level Design(LLD)
Design Patterns
Interview Guide for System Design
System Design Interview Questions & Answers