NPDA for accepting the language L = {aibjckdl | i==k or j==l,i>=1,j>=1}
Last Updated :
11 Jul, 2025
Prerequisite -
Pushdown automata,
Pushdown automata acceptance by final state
Problem - Design a non deterministic PDA for accepting the language L = {
a^i b^j c^k d^l : i==k or j==l, i>=1, j>=1}, i.e.,
L = {abcd, aabccd, aaabcccd, abbcdd, aabbccdd, aabbbccddd, ......}
In each string, the number of a's are followed by any number of b's and b's are followed by the number of c’s equal to the number of a's and c's are followed by number of d’s equal number of b's.
Explanation -
Here, we need to maintain the order of a’s, b's, c's and d’s.That is, all the a's are coming first then all the b's are coming and then all the c's are coming then all the d's are coming . Thus, we need a stack along with the state diagram. The count of a’s and b’s is maintained by the stack.We will take 2 stack alphabets:
\Gamma = { a, b, c, d, z }
Where,
\Gamma = set of all the stack alphabet
z = stack start symbol
Approach used in the construction of PDA -
In designing a NPDA, for every a’, ‘b’, ‘c’ and ‘d’ will comes in proper order.
- For i==k : Whenever ‘a’ comes, push it in stack and if ‘a’ comes again then also push it in the stack.After that, if 'b' comes not do any operation. After that, when ‘c’ comes then pop ‘a’ from the stack each time.After that, if 'd' comes not do any operation.
- For j==l : Whenever ‘a’ comes, not do any operation.After that, if 'b' comes push it in stack and if ‘b’ comes again then also push it in the stack. After that, when ‘c’ comes not do any operation.After that, if 'd' comes then pop ‘b’ from the stack each time.
So that the stack becomes empty.If stack is empty then we can say that the string is accepted by the PDA.
Stack transition functions -
\delta(q0, a, z) \vdash (q1, az)
\delta(q0, a, z) \vdash (q3, z)
\delta(q1, a, a) \vdash (q1, aa)
\delta(q1, b, a) \vdash (q1, a)
\delta(q1, c, a) \vdash (q2, \epsilon)
\delta(q2, c, a) \vdash (q2, \epsilon)
\delta(q2, d, \epsilon ) \vdash (q2, \epsilon)
\delta(q2, \epsilon, z) \vdash (qf1, z)
\delta(q3 a, z) \vdash (q3, z)
\delta(q3 b, z) \vdash (q3, bz)
\delta(q3 b, b) \vdash (q3, bb)
\delta(q3 c, b) \vdash (q3, b)
\delta(q3, d, b) \vdash (q4, \epsilon)
\delta(q4, d, b) \vdash (q4, \epsilon)
\delta(q4, \epsilon, z) \vdash (qf2, z)
Where, q0 = Initial state
qf1, qf2 = Final state
\epsilon = indicates pop operation
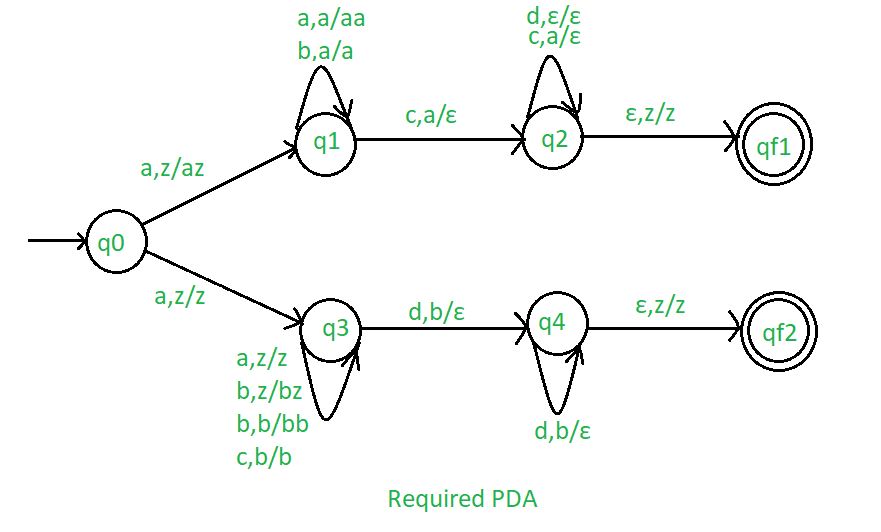
So, this is our required non deterministic PDA for accepting the language L ={
a^i b^j c^k d^l : i==k or j==l, i>=1, j>=1}.
Explore
Automata _ Introduction
Regular Expression and Finite Automata
CFG
PDA (Pushdown Automata)
Introduction of Pushdown Automata
5 min read
Pushdown Automata Acceptance by Final State
4 min read
Construct Pushdown Automata for given languages
4 min read
Construct Pushdown Automata for all length palindrome
6 min read
Detailed Study of PushDown Automata
3 min read
NPDA for accepting the language L = {anbm cn | m,n>=1}
2 min read
NPDA for accepting the language L = {an bn cm | m,n>=1}
2 min read
NPDA for accepting the language L = {anbn | n>=1}
2 min read
NPDA for accepting the language L = {amb2m| m>=1}
2 min read
NPDA for accepting the language L = {am bn cp dq | m+n=p+q ; m,n,p,q>=1}
2 min read
Construct Pushdown automata for L = {0n1m2m3n | m,n ≥ 0}
3 min read
Construct Pushdown automata for L = {0n1m2n+m | m, n ≥ 0}
2 min read
NPDA for accepting the language L = {ambncm+n | m,n ≥ 1}
2 min read
NPDA for accepting the language L = {amb(m+n)cn| m,n ≥ 1}
3 min read
NPDA for accepting the language L = {a2mb3m|m>=1}
2 min read
NPDA for accepting the language L = {amb2m+1 | m ≥ 1}
2 min read
NPDA for accepting the language L = {aibjckdl | i==k or j==l,i>=1,j>=1}
3 min read
Construct Pushdown automata for L = {a2mc4ndnbm | m,n ≥ 0}
3 min read
NPDA for L = {0i1j2k | i==j or j==k ; i , j , k >= 1}
2 min read
NPDA for accepting the language L = {anb2n| n>=1} U {anbn| n>=1}
2 min read
NPDA for the language L ={wЄ{a,b}* | w contains equal no. of a's and b's}
3 min read
Turing Machine
Decidability
TOC Interview preparation
TOC Quiz and PYQ's in TOC