Bash Script - File Permissions
Last Updated :
31 Jul, 2023
In this article, we will discuss file permission in Bash Script
To understand the scenario let's take an example. Let's consider there is a system admin A for company XYZ he designs a script that is to be executed by a user at 8:00 PM daily to send a report. He designs the script but forgets to give permission to the user to execute the script. Whenever a user tries to execute a script, he gets the error You are not authorized to take this action so why did this happen?
In the above case, we see that the system admin created a script but he did not give permission to the user as he was unable to execute it so to go into depth about this let's explain how can we set file permission and how to check them.
Solution: Now for the above example the system admin only has to give or set the user file permission to execute so that he can execute that file
So, what are the file permissions?
File permissions can be described as who, what, and which activities can be done to a file or directory.
- who refers to users, groups, or others
- what means to add, delete and set
- which means read, write, and execute
Basic list views of file and their permissions
The command we use is ls -l to show us the list of files/directory in the current folder we are present. This screenshot is a common example to show permission (using normal centos7 )
 List of all files and directories with their permissions
List of all files and directories with their permissionsFrom the above screenshot, let's take a file let's say luser_t04.sh, and see its file permissions
-rwx rwx rwx 1 root root 0 Feb 27 17:35 luser_t04.sh
1 2 3
(r = read , w= write , x = execute)
- 1 represents the permission of the user, they have all the 3 permission to read, write and execute the file
- 2 represents the group to which the file is associated it also has all the permissions
- 3 represent others which also contains all the 3 permissions
Manage file permissions
To manage file permissions, we have a command called chmod which we can use to change the permission of files and directories.
Method to use chmod command
There are 2 methods to use the command
- Symbolic method
- Numeric method
Symbolic Method
Syntax:
chmod whowhatwhich File|directory
- who is u(user) , g(group) , o(other)
- what is to +(add) ,-(remove) ,+(set)
- which is r (read), w(write), x(execute)
Let's see an example: -
Suppose you want to remove read and write permission of group and others from the file
chmod go-rw <FILE> (can be any file name)
Example:
chmod go-rw luser_t04.sh. The new permission will be like this
-rwx--x--x 1 root root 0 Feb 22 02:28 luser_t04.sh
 changing permission using Symbolic method
changing permission using Symbolic methodNumeric method
Syntax:
chmod ### file|directory
#: represents each digit the permission for user, group and others.
4 =read 2=write 1 = execute
Let's see the example from above:
 Example to understand the numeric method
Example to understand the numeric method -rwx--x--x 1 root root 0 Feb 22 02:38 luser_t04.sh
- user permission has been represented by rwx (4+2+1=7)
- group permission has been described as --x (0+0+1 =1)
- other permission has been described as --x ( 0+0+1=1)
Let us take another example of a file
File with permission of 640 what it means in numeric method
-rw- r-- --- 1 root root 0 Feb 22 02:36 file1.txt
- user have read(4) and write(2) permission represented by rw- (4+2+0=6)
- the group has read(4) permission represented by r-- (4+0+0=4)
- other have no permission(0) ,represented by --- (0+0+0=0)
 Example of file with chmod 640
Example of file with chmod 640 In this example to set file permission for a file (Example: FILE )
We want the user to be able to read, write and execute files but we don't want groups to write and execute the file and others to only be able to execute the file so what command and syntax we should use
Solution:
chmod 741 FILE1 (can be any file name)
The new permission set will be rwx r-- --x for FILE
-rwx r-- --x 1 root root 0 Feb 22 02:28 file.txt
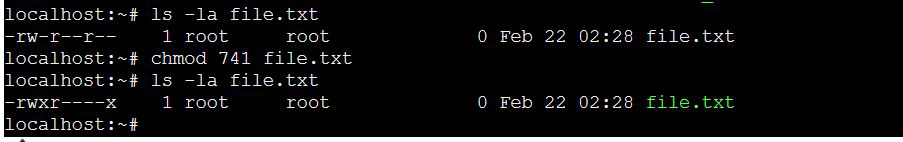 Changing permission using numeric method
Changing permission using numeric methodScript for File permission
We can explain the file permission by creating a simple script to execute and change the permission of the file after understanding file permissions.
Step-By-Step commands in script:
Step 1. First, we create a file or check if an existing file is there as mentioned in the screenshot. If the file is not present then we execute the command
touch <FILENAME> (this will create a new file)
Step 2. Our aim is to remove the write permission of others and groups as mentioned in the screenshot we will execute the command in the script
chmod 744 <FILENAME>
Step 3. Finally, to check if permission is changed or not, we will use
ls -l
The Script
#!/bin/bash
# script to change permission of file
# File variable to store file.txt location
FILE="file.txt"
# to check the file we want to change
# exists or not
if [[ ! -e "${FILE}" ]]
then
echo "creating ${FILE} file"
touch file.txt
fi
# to remove write permission of other and group of file
chmod 744 "${FILE}"
#to check if the permission are removed
ls -l "${FILE}"
Now we will execute this script and check if it works
./file_perm.sh
Output
 Output of script
Output of scriptNOTE: In writing script and executing it is important to check permission always after creating script ls -l command
Explore
Linux/Unix Tutorial
5 min read
Getting Started with Linux
Installation with Linux
Linux Commands
Linux File System
Linux Kernel
Linux Networking Tools
Linux Process
Linux Firewall
Shell Scripting & Bash Scripting