Blockchain technology often heralded as a revolutionary advancement, fundamentally transforms how data is stored, managed, and verified across distributed networks. At its core, a blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that maintains a continuous and immutable record of transactions across a network of computers. The structure of a blockchain is crucial to its functionality and security. This article focuses on discussing the Blockchain structure in detail.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a technology where multiple parties involved in communication can perform different transactions without third-party intervention. Special nodes verify and validate these transactions.
Features of Blockchain
- Decentralization: In centralized transaction systems, each transaction must be validated in the central trusted agency (e.g., the central bank), naturally resulting in cost and performance jams at the central servers. In contrast to the centralized mode, a third party is not needed in the blockchain. Consensus algorithms in blockchain maintain data stability in a decentralized network.
- Persistency: Transactions can be validated quickly and invalid transactions would not be admitted by persons or miners who mining the crypto. It is not possible to delete or roll back transactions once they are included in the blockchain network. Invalid transactions do not carry forward further.
- Anonymity: Each user can interact with the blockchain with a generated address, which does not disclose the real identity
of the miner. Note that blockchain cannot guarantee perfect privacy preservation due to the permanent thing. - Auditability: Blockchain stores data of users based on the Unspent Transaction Output (UTXO) model.
Every transaction has to refer to some previous unspent transactions. Once the current transaction is recorded into the
blockchain, the position of those referred unspent transactions switches from unspent to spent. Due to this process, the transactions can be easily tracked and not harmed between transactions. - Transparency: The transparency of blockchain is like cryptocurrency, in Bitcoin for tracking every transaction is done by the address. For security, it hides the person’s identity between and after the transaction. All the transactions are made by the owner of the block associated with the address, this process is transparent and there is no loss for anyone who is involved in this transaction.
- Cryptography: The blockchain concept is fully based on security and for that, all the blocks on the blockchain network want to be secure. For security, it implements cryptography and secures the data using the cipher text and ciphers.
Core Components of Blockchain
- Node: Nodes are network participants and their devices permit them to keep track of the distributed ledger and serve as communication hubs in various network tasks. A block broadcasts all the network nodes when a miner looks to add a new block in transactions to the blockchain.
- Transactions: A transaction refers to a contract or agreement and transfers of assets between parties. The asset is typically cash or property. The network of computers in blockchain stores the transactional data as a copy with the storage typically referred to as a digital ledger.
- Block: A block in a blockchain network is similar to a link in a chain. In the field of cryptocurrency, blocks are like records that store transactions like a record book, and those are encrypted into a hash tree. There are a huge number of transactions occurring every day in the world. The users need to keep track of those transactions, and they do it with the help of a block structure. The block structure of the blockchain is mentioned in the very first diagram in this article.
- Chain: Chain is the concept where all the blocks are connected with the help of a chain in the whole blockchain structure in the world. And those blocks are connected with the help of the previous block hash and it indicates a chaining structure.
- Miners: Blockchain mining is a process that validates every step in the transactions while operating all cryptocurrencies. People involved in this mining they called miners. Blockchain mining is a process to validate each step in the transactions while operating cryptocurrencies.
- Consensus: A consensus is a fault-tolerant mechanism that is used in computer and blockchain systems to achieve the necessary agreement on a single state of the network among distributed processes or multi-agent systems, such as with cryptocurrencies. It is useful in record keeping and other things.
Data Storage and Management
- Header: It is used to identify the particular block in the entire blockchain. It handles all blocks in the blockchain. A block header is hashed periodically by miners by changing the nonce value as part of normal mining activity, also Three sets of block metadata are contained in the block header.
- Previous Block Address/ Hash: It is used to connect the i+1th block to the ith block using the hash. In short, it is a reference to the hash of the previous (parent) block in the chain.
- Timestamp: It is a system that verifies the data into the block and assigns a time or date of creation for digital documents. The timestamp is a string of characters that uniquely identifies the document or event and indicates when it was created.
- Nonce: A nonce number which used only once. It is a central part of the proof of work in the block. It is compared to the live target if it is smaller or equal to the current target. People who mine, test, and eliminate many Nonce per second until they find that Valuable Nonce is valid.
- Merkel Root: It is a type of data structure frame of different blocks of data. A Merkle Tree stores all the transactions in a block by producing a digital fingerprint of the entire transaction. It allows the users to verify whether a transaction can be included in a block or not.
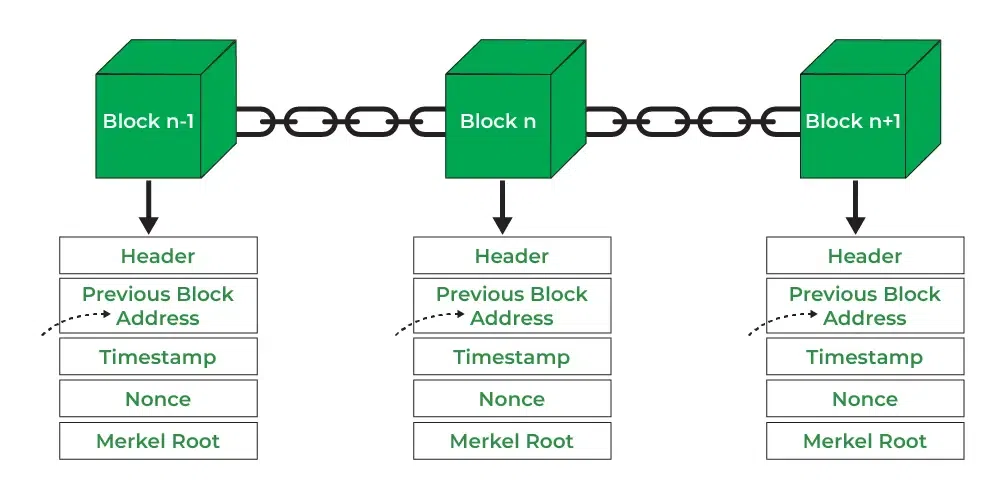 Blockchain Structure
Blockchain StructureTypes of Blockchain
1. Public Blockchain
A public blockchain is a concept where anyone is free to join and take part in the core activities of the blockchain network. Anyone can read, write, and audit the ongoing activities on a public blockchain network, which helps to achieve the self-determining, decentralized nature often authorized when blockchain is discussed. Data on a public blockchain is secure as it is not possible to modify once they are validated.
The public blockchain is fully decentralized, it has access and control over the ledger, and its data is not restricted to persons, is always available and the central authority manages all the blocks in the chain. There is publicly running all operations. Due to no one handling it singly then there is no need to get permission to access the public blockchain. Anyone can set his/her node or block in the network/ chain.
After a node or a block settles in the chain of the blocks, all the blocks are connected like peer-to-peer connections. If someone tries to attack the block then it forms a copy of that data and it is accessible only by the original author of the block.
 Public Blockchain
Public BlockchainAdvantages:
- Decentralization: High level of decentralization, which reduces the risk of single points of failure and increases security.
- Transparency: All transactions are visible to anyone, enhancing transparency and trust.
- Immutability: Once data is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted, providing a permanent record.
Disadvantages:
- Scalability Issues: Public blockchains often face scalability problems, with limited transaction throughput and slower processing times.
- Energy Consumption: Some consensus mechanisms, like Proof of Work (PoW), require significant computational power and energy.
- Privacy Concerns: Public visibility of transactions may lead to privacy issues, as sensitive data can be exposed.
2. Private Blockchain
Miners need permission to access a private blockchain. It works based on permissions and controls, which limit participation in the network. Only the entities participating in a transaction will know about it and the other stakeholders not be able to access it.
It works based on permissions due to this it is also called a permission-based blockchain. Private blockchains are not like public blockchains it is managed by the entity that owns the network. A trusted person is in charge of the running of the blockchain it will control who can access the private blockchain and also control the access rights of the private chain network. There may be a possibility of some restrictions while accessing the network of the private blockchain.
 Private Blockchain
Private Blockchain
Advantages:
- Performance and Speed: Faster transaction processing and higher throughput compared to public blockchains due to fewer nodes and reduced consensus requirements.
- Privacy: Transactions and data are visible only to authorized participants, enhancing privacy.
- Control: Centralized control allows for easier governance and compliance with regulations.
Disadvantages:
- Centralization: Less decentralized than public blockchains, which can introduce single points of failure and reduce the security benefits.
- Trust: Requires participants to trust the central authority or consortium managing the blockchain.
- Limited Transparency: Reduced transparency can make it harder for external auditors to verify data.
3. Consortium Blockchain
A consortium blockchain is a concept where it is permissioned by the government and a group of organizations, not by one person like a private blockchain. Consortium blockchains are more decentralized than private blockchains, due to being more decentralized it increases the privacy and security of the blocks. Those like private blockchains connected with government organizations' block networks.
Consortium blockchains lie between public and private blockchains. They are designed by organizations and no one person outside of the organizations can gain access. In Consortium blockchains all companies in between organizations collaborate equally. They do not give access from outside of the organizations/ consortium network.
Advantages:
- Efficiency: Better performance and efficiency than public blockchains due to fewer nodes and optimized consensus mechanisms.
- Shared Control: Governance is shared among consortium members, which can enhance trust and cooperation.
- Privacy and Security: Improved privacy and security compared to public blockchains, as access is restricted.
Disadvantages:
- Complex Governance: Decision-making can be complex due to multiple stakeholders with potentially conflicting interests.
- Less Decentralization: While more decentralized than private blockchains, consortium blockchains still have a limited number of participants, which can reduce some decentralization benefits.
- Interoperability: Challenges can arise when integrating with other blockchain networks or systems.
4. Hybrid Blockchain
Hybrid blockchains combine elements of both public and private blockchains. They aim to offer the benefits of both types, allowing for controlled access and transparency. Examples include Dragonchain and IBM's Food Trust.
Advantages:
- Flexibility: Offers the ability to balance transparency and privacy based on the needs of the organization or project.
- Scalability and Performance: Can be designed to optimize performance and scalability while maintaining some degree of transparency.
- Customizable Access: Allows organizations to control who can access certain data while making some data available to the public.
Disadvantages:
- Complexity: Implementation can be more complex due to the need to manage different access levels and integrations.
- Governance Challenges: Balancing governance between public and private aspects can be challenging.
- Potential for Confusion: This mayrequires lead to confusion among users and stakeholders about the nature and scope of access and transparency.
Consensus Mechanisms in Blockchain
There are different kinds of consensus mechanism algorithms, each of which works on different principles:
- Proof of Work (PoW): Proof of Work requires a stakeholder node to prove that the work is done and submitted by them certifying them to receive the right to add new transactions in the blockchain. Examples include Bitcoin and Ethereum (before Ethereum 2.0).
- Proof of Stake (PoS): The Proof of Stake is also a common consensus algorithm that evolved as a low-cost low-energy-consuming, low-energy-consuming alternative for the PoW algorithm. For providing the responsibilities the public ledger provides by the virtual currency token like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Examples include Ethereum 2.0 and Cardano.
- Proof of Elapsed Time (PoET): PoET encrypts the passage of time cryptographically to reach an agreement without expending many resources.
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): Stakeholders elect a limited number of delegates to validate transactions and create blocks on their behalf. It has higher transaction throughput and faster block creation. In DPoS, risk of centralization and reliance on elected delegates. Examples include EOS and TRON.
- Proof of Authority (PoA): A small number of pre-approved validators are responsible for creating blocks and validating transactions. PoA has high efficiency and low energy consumption. There is a risk of centralization and dependency on the trustworthiness of validators. Examples include VeChain and private Ethereum networks.
- Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT): In PBFT, nodes reach consensus through voting, even if some nodes act maliciously or fail. It is effective in handling Byzantine faults and offers fast transaction processing. There is a complexity in scaling to large networks. Examples include Hyperledger Fabric.
Cryptographic Foundations in Blockchain
Cryptography is important to the security and functionality of blockchain technology. Here is an overview of the key cryptographic foundations used in blockchain:
- Hash Functions: Hash functions are algorithms that generate a fixed-size output (hash) from variable-size input data. They are designed to be fast and produce unique outputs for different inputs. Hash functions are used to create block hashes, ensuring the integrity of the data within the block and linking blocks together in the chain. Examples include SHA-256 used in Bitcoin.
- Digital Signatures: Digital signatures use asymmetric cryptography to verify the authenticity and integrity of messages or transactions. They involve a private key to sign data and a public key to verify the signature. Digital signatures secure transactions by allowing users to sign transactions with their private keys and enabling others to verify these signatures with the corresponding public keys. Examples include the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA) used in Bitcoin and Ethereum.
- Public and Private Keys: In asymmetric cryptography, a key pair consists of a public key, which is shared with others, and a private key, which is kept secret. The public key encrypts data, and the private key decrypts it, or vice versa. Public and private keys are fundamental for creating and managing wallets, securing transactions, and authenticating users on the blockchain. Examples include RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman), ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography), etc.
- Merkle Trees: Merkle trees are a type of hash tree where each leaf node represents a hash of data, and each non-leaf node represents a hash of its child nodes. They are used to efficiently and securely verify the integrity of large sets of data. Merkle trees are used to organize and verify transactions within a block, allowing for efficient and secure validation. Examples include the Merkle root in Bitcoin blocks.
Smart Contracts and Decentralized Applications (DApps)
Here is an overview of smart contracts and dApps in blockchain systems:
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automatically execute, enforce, and verify the conditions of a contract without the need for intermediaries.
Key Features:
- Automation: Automatically performs actions (e.g., transferring assets) when predefined conditions are met.
- Transparency: Code and execution are visible on the blockchain, ensuring all parties can verify the contract’s operation.
- Immutability: Once deployed, smart contracts cannot be altered, providing a secure and tamper-proof execution environment.
Usage:
- Financial Agreements: Automating complex financial transactions such as loans, insurance claims, or trading agreements.
- Supply Chain: Tracking and verifying the movement and provenance of goods.
- Governance: Implementing rules and governance structures in decentralized organizations or DAOs.
Examples:
Ethereum’s ERC-20 and ERC-721 tokens use smart contracts to define token standards and manage transactions.
Decentralized Applications (DApps)
DApps are applications that run on a decentralized network, typically a blockchain. They leverage smart contracts to operate autonomously and ensure transparency and security.
Key Features:
- Decentralization: Operate on a peer-to-peer network rather than a centralized server, distributing data and processing across multiple nodes.
- Trustless Interaction: Users interact directly with the application and smart contracts without needing to trust a central authority.
- Open Source: Often open source, allowing for transparency and community collaboration in development.
Usage:
- Financial Services: Decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms for lending, borrowing, and trading cryptocurrencies.
- Gaming: Blockchain-based games that use NFTs for in-game assets and rewards.
- Social Networks: Platforms where users retain control over their data and content.
Example:
Uniswap is a decentralized exchange (DEX) that allows users to trade cryptocurrencies without relying on a central authority.
Blockchain Architecture Vs Database
Below are some of the differences between blockchain architecture and database:
| Parameters | Blockchain Architecture | Database |
|---|
| Control | Blockchain is decentralized because there is no single point of failure and there is no central authority to control the blockchain. | The database is Centralized. |
|---|
| Operations | Blockchain has only an Insert operation. | The database has Create, Read, Update, and Delete operations. |
|---|
| Strength | It is robust technology. | The database is not fully robust technology. |
|---|
| Mutability | Blockchain is an immutable technology and we cannot change it or we cannot go back. | The database is a fully mutable technology, The data can be edited in the database. |
|---|
| Rights | Anyone with the right proof of work can write on the blockchain. | In the database reading and writing can do so. |
|---|
| Speed | It is slow. | It is faster as compared to blockchain. |
|---|
Security Challenges in Blockchain Structures
Here are some key security challenges in blockchain structures:
- 51% Attacks: If a single entity or group controls more than 50% of the network's computational power (in PoW) or stake (in PoS), they can potentially manipulate the blockchain by double-spending, halting transactions, or reversing transactions. 51% attacks can be mitigated by increasing network size, using consensus mechanisms resistant to centralization, and incorporating additional security layers.
- Sybil Attacks: An attacker creates multiple fake identities (nodes) to gain disproportionate influence over the network. In PoW, this involves creating numerous fake mining nodes; in PoS, it involves acquiring a large amount of stake from multiple fake accounts. This can disrupt network consensus, compromise the integrity of the blockchain, and skew decision-making processes. Sybil attacks can be mitigated by implementing identity verification and reputation systems and utilizing robust consensus mechanisms.
- Double Spending: A form of fraud where a digital currency or asset is spent more than once. This typically occurs when an attacker manages to alter the blockchain history or exploit network delays. This results in financial loss and undermines trust in the blockchain's ability to securely manage transactions. Double spending can be mitigated by employing consensus mechanisms to ensure transaction finality and using transaction confirmation strategies to detect and prevent double spending.
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Flaws or bugs in smart contracts can lead to unintended behaviors or security breaches. Common issues include reentrancy attacks, integer overflows/underflows, and logic errors. This can lead to loss of funds, unauthorized access, and exploitation of contract logic. These can be mitigated by conducting thorough code audits, using formal verification methods, and following best practices in smart contract development.
- Network Partitioning (Eclipse Attacks): An attacker isolates a node from the rest of the network, feeding it false or malicious information to manipulate its view of the blockchain. This can lead to incorrect transaction validation, loss of consensus, and disruptions in the network’s functionality. Eclipse attacks can be mitigated by enhancing network connectivity, implementing robust peer discovery protocols, and monitoring for unusual network behaviors.
- Endpoint Security: The security of endpoints (e.g., user devices, wallets) is crucial, as vulnerabilities can lead to unauthorized access to private keys and other sensitive information. This can result in theft of assets, unauthorized transactions, and loss of control over blockchain assets. Endpoint security can be taken care of by encouraging best practices in device security, using hardware wallets, and implementing strong authentication measures.
Best Practices for Enhancing Blockchain Security
Here are key best practices to enhance blockchain security:
- Regular Code Audits: Conduct thorough and regular audits of blockchain code, especially smart contracts. Engage with reputable security firms or experts to perform comprehensive code reviews and testing.
- Use of Strong Cryptographic Techniques: Employ robust cryptographic algorithms and protocols to secure data. Use well-established algorithms like SHA-256 for hashing and ECDSA for digital signatures, and stay updated on cryptographic advancements.
- Implement Multi-Signature Wallets: Use multi-signature (multi-sig) wallets that require multiple signatures to authorize transactions. Configure multi-sig wallets based on organizational needs, such as requiring approvals from multiple executives or stakeholders.
- Adopt Secure Development Practices: Follow best practices in software development to minimize vulnerabilities. Implement secure coding practices, conduct threat modeling, and use development frameworks that emphasize security.
- Enhance Endpoint Security: Secure all endpoints interacting with the blockchain, including user devices and servers. Use antivirus software, and firewalls, and ensure devices are kept up-to-date with security patches.
- Implement Access Controls and Permissions: Use strict access controls to manage who can interact with and modify blockchain components. Implement role-based access controls (RBAC) and enforce least privilege principles.
Conclusion
In conclusion, blockchain technology offers a powerful way to securely and transparently record transactions and data through its decentralized, immutable ledger. By organizing data into blocks linked together in a chain, blockchain ensures that once information is added, it cannot be altered or deleted. This structure provides enhanced security, trust, and integrity across various applications, from cryptocurrencies to supply chain management. As blockchain continues to evolve, its foundational principles of decentralization, transparency, and cryptographic security will remain crucial to its effectiveness and reliability.
Similar Reads
Blockchain Tutorial
Blockchain technology in simple words is a digital database where information or data is stored in blocks that are linked together to form a chain. This Blockchain Tutorial covers all basic to advanced topics of blockchain like cryptography, Blockchain Algorithms, Blockchain Architecture, Blockchain
6 min read
Introduction to Blockchain Technology
Introduction to Blockchain technology | Set 1
Blockchain could be a data structure that could be a growing list of information blocks. The knowledge blocks area unit coupled along, such recent blocks can't be removed or altered. Blockchain is the backbone Technology of the Digital CryptoCurrency BitCoin. What is Blockchain? The blockchain is a
10 min read
History of Blockchain
Blockchain can be defined as the Chain of Blocks that contain some specific Information. Thus, a Blockchain is a ledger i.e file that constantly grows and keeps the record of all transactions permanently. This process takes place in a secure, chronological (Chronological means every transaction happ
5 min read
Features of Blockchain
Here In this article, we will discuss the features of blockchain technology and how they make it a revolutionary and highly desirable platform for various applications. A blockchain is a chain of blocks that contains information. Most people think that Blockchain is Bitcoin and vice-versa. But it’s
7 min read
Important Blockchain terminologies
In this article, we will get acquainted with some on the most commonly used and hence, important to know terminologies in the blockchain area. As blockchain is a booming technology with active research being conducted on, this article can help you to understand and take part in conversations around
6 min read
Different Version of BlockChain
BlockChain is buzzword in today's technology. Thus, a BlockChain is defined as the digital record of transaction which is stored in the Chain of Blocks.Each time a block is completed by storing Information, the next new block is created to store further information. BlockChain is a secure technology
5 min read
Types of Blockchain
Blockchain technology has evolved into a versatile tool with various applications across industries. Understanding the different types of blockchain is essential for selecting the right solution for specific needs. Broadly categorized into public, private, consortium, and hybrid blockchains, each ty
10 min read
Public Blockchain
Public blockchains are decentralized networks that allow anyone to participate, read, and write data without needing permission from a central authority. They operate on an open-source framework, ensuring transparency and security through cryptographic principles. Transactions on public blockchains
7 min read
An Introduction to Private Blockchain
Private blockchains are a specialized form of blockchain technology for use within a specific organization or consortium. Unlike public blockchains, which are open to anyone and offer full transparency, private blockchains operate on a permission basis, allowing only authorized participants to acces
9 min read
Hybrid Blockchain
The Blockchain is a decentralized distributed database that is shared among computer network nodes. Blockchain can be used in four different ways: Public, Private, Consortium, and Hybrid. The Hybrid blockchain is a revolutionary type of blockchain that is a mix of both worlds, both private and publi
7 min read
What is Consortium Blockchain?
A consortium blockchain is a group of multiple financial institutions where each financial institution has its private blockchain. In this blockchain, a pre-selected set of nodes are allowed to control the consensus process. What is Consortium Blockchain?Consortium blockchains are managed and run by
9 min read
Top Applications of Blockchain in the Real World
The last time this world changed a lot was with the invention of the Internet! Can you imagine ever living without the ever-present Google or all the other social media sites like Facebook, YouTube, etc? It sounds impossible. Well, this time the world might change again because of the applications o
8 min read
Advantages and Disadvantages of Blockchain
Blockchain technology is a revolutionary digital ledger system that allows for secure, transparent, and decentralized transactions. It underpins cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and has potential applications across various sectors, including finance, healthcare, and supply chain management. The advant
5 min read
Benefits of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology offers a range of transformative benefits that can revolutionize various industries. By providing enhanced security, improved transparency, and increased efficiency, blockchain enables secure and trustworthy transactions without the need for intermediaries. Its decentralized na
4 min read
How does the Blockchain Work?
A blockchain is a distributed database that stores information electronically in a digital format and is shared among the nodes of a computer network. A typical difference between a blockchain and a database is how data is structured. A blockchain is a shared, immutable ledger as the name suggests s
8 min read
What is P2P (Peer-to-Peer Process)?
The P2P process deals with a network structure where any participant in the network known as a node acts as both a client and a server. This means that, rather than relying on a basis server to supply resources or services, everybody from the network of nodes can trade resources and services with on
9 min read
What is Decentralization? Definition, Working, Need, Benefits
Decentralization is known as the distribution of functions among several units. It is an interconnected system where no single entity has complete authority. It is the architecture in which the workloads, both hardware, and software, are distributed among several workstations. The functions are dist
5 min read
Components of Blockchain Network
Blockchain networks have various interdependent components that work together to ensure secure, transparent, and efficient data transactions. Key elements include nodes, which validate and relay transactions; a decentralized ledger that records all activity; and consensus mechanisms that maintain th
6 min read
Centralized vs. Decentralized vs. Distributed Systems
Understanding the architecture of systems is crucial for designing efficient and effective solutions. Centralized, decentralized, and distributed systems each offer unique advantages and challenges. Centralized systems rely on a single point of control, providing simplicity but risking a single poin
8 min read
Difference between Public and Private blockchain
1. What is Public Blockchain ? Public blockchains are open networks that allow anyone to participate in the network i.e. public blockchain is permissionless. In this type of blockchain anyone can join the network and read, write, or participate within the blockchain. A public blockchain is decentral
5 min read
Cryptography Tutorial
Cryptography is a technique of securing communication by converting plain text into unintelligible ciphertext. It involves various algorithms and protocols to ensure data confidentiality, integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation. The two primary types of cryptography are symmetric key cryptogr
7 min read
Consensus Algorithms
Consensus Algorithms in Blockchain
Prerequisites: Introduction to Blockchain technology | Set 1, Set 2 We know that Blockchain is a distributed decentralized network that provides immutability, privacy, security, and transparency. There is no central authority present to validate and verify the transactions, yet every transaction in
5 min read
Blockchain - Proof of Work (PoW)
Proof of Work consensus is the mechanism of choice for the majority of cryptocurrencies currently in circulation. The algorithm is used to verify the transaction and create a new block in the blockchain. The idea for Proof of Work(PoW) was first published in 1993 by Cynthia Dwork and Moni Naor and w
6 min read
Proof of Burn (PoB) Consensus Algorithm in Blockchain
The Proof of Burn (PoB) consensus algorithm is a unique blockchain mechanism that allows participants to validate transactions by "burning" or permanently destroying a portion of their cryptocurrency. This process, which involves sending coins to an unspendable address, demonstrates a commitment to
6 min read
Proof of Stake (PoS) in Blockchain
Proof of Stake (PoS) is a type of algorithm which aims to achieve distributed consensus in a Blockchain. This way to achieve consensus was first suggested by Quantum Mechanic here and later Sunny King and his peer wrote a paper on it. This led to Proof-of-Stake (PoS) based Peercoin. A stake is value
5 min read
Byzantine Generals Problem in Blockchain
The article focuses on discussing the following topics of Byzantine Generals Problem in Blockchain: What is Byzantine General's Problem?Money and Byzantine General's ProblemHow Bitcoin Solves the Byzantine General's Problem?Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT)Byzantine General's Problem in a Distributed
8 min read
Cryptographic Consensus Mechanisms in Blockchain
A consensus mechanism is an algorithm that is used to achieve agreement, trust, and security across a decentralized computer network. These protocols help to make sure that all the nodes are synchronized with each other and agree on transactions, which are legitimate and are added to the blockchain.
13 min read
Delegated Proof Of Stake (DPoS)
Delegated Proof Of Stake (DPoS) is a consensus algorithm which is an advancement of the fundamental concepts of Proof Of Stake. Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) consensus algorithm was developed by Daniel Larimer, founder of BitShares, Steemit and EOS in 2014. In Proof of Stake consensus system, each
5 min read
practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance(pBFT)
Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance is a consensus algorithm introduced in the late 90s by Barbara Liskov and Miguel Castro. pBFT was designed to work efficiently in asynchronous(no upper bound on when the response to the request will be received) systems. It is optimized for low overhead time. Its
6 min read
Blockchain Architecture
Blockchain Structure
Blockchain technology often heralded as a revolutionary advancement, fundamentally transforms how data is stored, managed, and verified across distributed networks. At its core, a blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that maintains a continuous and immutable record of transactions across a n
15+ min read
Candidate block in Blockchain
As we are aware that blockchain is decentralized network which is focused mainly on transparency, Blockchain is list of growing records titled as blocks. Please refer this article, if you are beginner in blockchain domain. Role of Miners in Blockchain : Whenever transaction is made on bitcoin networ
2 min read
Actors Involved in Blockchain Solution
Blockchain is a booming technology that is used as distributed ledgers for cryptocurrency. Blockchain is a ledger that continuously grows by keeping a record of all the transactions in order, secure, and in an immutable way. Each transaction is treated as a block that is connected to a previous tran
3 min read
Blockchain Transaction Lifecycle
The blockchain transaction lifecycle refers to the series of stages a transaction goes through from its creation to its final confirmation on the blockchain. It begins with the initiation of the transaction, where details are entered and signed by the sender. The transaction is then propagated throu
5 min read
Blockchain Forks
Prerequisites - Blockchain Technology Introduction, How Blockchain technology works, Introduction to Blockchain The decentralized nature of public blockchains (for example, Bitcoin and Ethereum) means that participants on the network must be able to come to an agreement as to the shared state of th
9 min read
Blockchain and Block Header
Blockchain is a database, or broadly distributed database, used mainly for concurrent transactions and one of the most popular implementations of blockchain is Bitcoin. Blockchain has several blocks, also called nodes, and all the blocks are managed with the help of the block header. Constituents of
3 min read
Blockchain Incentives to Miners
Blockchain incentives to miners are essential mechanisms that motivate individuals to participate in the network by validating transactions and securing the blockchain. These incentives primarily come in the form of coinbase rewards and transaction fees, which compensate miners for their computation
5 min read
Core Component of Blockchain
Blockchain : In 1991, the term blockchain was coined. Blockchain's founder was an anonymous person who goes by the pseudonym Satoshi Naka Moto. For the first time in 2009, the blockchain was implemented in accordance with bitcoin and bitcoin is a crypto valuta. Due to its open-source nature, Blockch
3 min read
Blockchain Protocols and Their Working
Blockchain protocols are the foundational rules that govern how data is recorded, shared, and secured on a blockchain network. They dictate how transactions are validated, how consensus is achieved, and how nodes communicate. This article discusses Blockchain Protocols in detail.Table of ContentWhat
8 min read
What is Blockchain Authentication?
Blockchain authentication is a secure method of verifying the identity of users and devices in a digital environment using blockchain technology. Unlike traditional authentication systems, which often rely on centralized databases and passwords, blockchain authentication leverages decentralized netw
7 min read
Blockchain and Cryptocurrency
What is Cryptocurrency?
A cryptocurrency is not a type of currency that can be used in the real world. It can be used to perform transactions only in the digital world. So in order to buy/sell using a cryptocurrency, it has to be converted from a digital form to some existing currency that is used in the real world. For ex
12 min read
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cryptocurrency in 2020
Prerequisite - Cryptocurrency With the industrialization and involvement of technology, digital currencies are gaining an upper hand over others. One such currency is bitcoins. Many of us are familiar with this well-known terminology. The only confusing thing is Cryptocurrency. What are its pros and
6 min read
How are Cryptocurrencies Created?
A cryptocurrency is a digital currency, which uses cryptography for secure transactions. It is designed to act as a medium of exchange on a computer network without relying on a central authority such as a government or a bank to manage it. Since cryptocurrencies have no central issuing or regulator
9 min read
What is a Cryptographic Token?
A cryptographic token is a digital unit that has a value and does not have its own native blockchain. Blockchain technology has huge potential to build a secure future internet system and also be able to solve big business problems. A blockchain is a digital, decentralized public ledger that has the
7 min read
What is Cryptoeconomics?
Cryptoeconomics is the study of how economic incentives and cryptographic techniques are used to create secure and decentralized systems, primarily in blockchain technology. It combines principles from economics, game theory, and cryptography to design networks that encourage honest behavior and mai
10 min read
What is an Initial Coin Offering (ICO)?
An Initial Coin Offering (ICO) is a fresh way for businesses to generate funds using cryptocurrency. It is a way to launch a new coin by selling it to investors during a large period. For example, Coinbase is a crypto/fiat-based company that has recently launched its IPO(Initial Public Offering) i.e
11 min read
Generalized Proof-of-Stake Mining in Cryptocurrencies
Generalized Proof-of-Stake (GPoS) is a concept in cryptocurrency mining that builds upon the traditional Proof-of-Stake (PoS) mechanism. While PoS allows users to validate transactions and create new blocks based on the number of coins they hold, GPoS expands on this idea to include a broader range
8 min read
Blockchain - Electronic Cash
eCash is known as Electronic Cash which is a digital currency technique from which transactions can be achieved anywhere through the internet. It is an easier form of payment, it is based on the principles of blockchain technology (Digital Signatures) among the Peer-to-Peer network. All transactions
4 min read
What is Blockchain Wallet?
A blockchain wallet is a software that enables sending and receiving cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, etc. It stores the record of transactions and also public and private keys which are used to perform transactions. A public key is similar to an account number. If A wants to send some mo
10 min read
Smart Contracts and Decentralized Applications (DApps)
What is Ethereum: Working, Types, Features
Ethereum is like a decentralized computing network. It allows developers to create and run applications on its blockchain using smart contracts.Blockchain technology gained public notice with the advent of Bitcoin in 2009. Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency that runs on blockchain technology and is by far,
8 min read
Components of Ethereum Network
The components of the Ethereum network form the foundation of its decentralized platform, enabling the creation and execution of smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps). Key elements include Ethereum nodes, the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), and the consensus mechanism that ensures t
6 min read
Difference Between Bitcoin and Ethereum
Bitcoin is a digital currency that can be transferred on a peer-to-peer (P2P) network without the need for any central authority. It was invented by a person or group of people with the name Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008. All the transactions are stored in an immutable distributed ledger. Bitcoin is crea
4 min read
What are Ethereum Accounts?
Ethereum accounts are essential elements of the Ethereum blockchain, serving as digital identities for users and smart contracts. Two main types of Ethereum Accounts are Externally Owned Accounts (EOAs) and Contract Accounts. This article focuses on discussing Ethereum Accounts in detail.Table of Co
10 min read
What are Nodes and Clients in Ethereum?
In Ethereum, nodes and clients are fundamental to the network's operation. Nodes are individual computers or servers participating in the Ethereum network by maintaining a copy of the blockchain and following the network’s rules. Clients are software applications that nodes run to interact with the
13 min read
What is Ethereum Virtual Machine and How it Works?
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is a crucial component of the Ethereum blockchain that enables the execution of smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps). When developers write smart contracts in languages like Solidity, the EVM processes these contracts, managing state changes and e
12 min read
Ethereum - Gas and Fees
Ethereum Gas is a section that calculates the quantity of calculation action that it takes to perform specific functions. Every function that carries position in Ethereum like transactions and smart contracts etc. performance needs some part of gas. It is essential to the blockchain P2P network beca
8 min read
How to Simply Deploy a Smart Contract on Ethereum?
Smart contracts are blocks of code that reside on the blockchain. It is like an Ethereum account but there is a critical difference between an external account and a smart contract. Unlike a smart contract, an external account can connect to multiple Ethereum networks (Goerli testnet, mainnet, etc.)
7 min read
"Hello World" Smart Contract in Remix-IDE
What do you mean by Smart Contract? Smart contracts are self-executing contracts. The term was coined by Nick in 1994. Smart contracts are very different from traditional software programs. They are immutable once deployed on the blockchain. It was because of Ethereum the term smart contract became
4 min read
What are Decentralized Apps (dApps) in Blockchain
Decentralized apps are digital applications or programs that are based on Blockchain and fundamentally different from normal applications. Unlike normal applications that run on centralized servers that belong to the company that owns them, dApps run on a decentralized peer-to-peer (P2P) network tha
7 min read
Pros, Cons, and Examples of dApp
Dapps are decentralized applications that might feel like regular apps. Behind the scene, it has some special qualities that are discussed in the article. Introduction to dAppDecentralized applications can be accessible to a wide audience and provide a diverse set of functions from business services
5 min read
DAO(Decentralized Autonomous Organization) in Blockchain
DAO stands for Decentralized Autonomous Organization. The concept of a DAO was first proposed by Bit Shares, Steemit, and EOS (Block. one) founder Dan Larimer in the year 2015, and was further refined in the year 2016 by Ethereum’s Vitalik Buterin. A decentralized autonomous organization is decentra
9 min read
Blockchain Applications
Applications of Blockchain in Data Management
As our reliance on data grows, effective management becomes more important than ever. Traditional systems can struggle with issues like security, data integrity, and sharing information across platforms. Blockchain technology offers a promising solution by providing a secure, transparent, and decent
5 min read
Benefits and Applications of Blockchain in Cloud Computing
The various features of Blockchain like decentralization, transparency and security have made it a very important and revolutionary technology for the present generation of several industrial usages. One of those fields is the Cloud of Things which is created by the interlinking of cloud computing a
10 min read
Integration of Artificial Intelligence and BlockChain
Artificial Intelligence and Blockchain are proving to be quite a powerful combination, improving virtually every industry in which they're implemented. These technologies can be combined to upgrade everything from food supply chain logistics and healthcare record sharing to media royalties and finan
8 min read
How Blockchain Can Change the Future of Banking
What is the most important thing for humans? Well, nobody knows for sure but money is definitely one of those! And that’s the reason that the banking sector is one of the most important sectors in the world. This sector includes different institutions such as banks, finance companies, investment fir
6 min read
Blockchain - Into the Future
Accounting, transactions, contracts, and records play a pivotal and defining role in our societal system. They protect assets, and organizational boundaries and uphold the promises between institutions, governments, and corporations. Despite their importance, these have failed to digitize in ways ot
6 min read
Blockchain in Genomics
Blockchain technology is making waves in various industries, and genomics is no exception. By providing a secure and transparent way to manage and share genomic data, blockchain addresses critical challenges such as data privacy, security, and integrity. This integration promises to enhance collabor
9 min read
Integration of Blockchain and AI
AI and blockchain are proving to be quite a powerful combination, improving virtually every industry in which they’re implemented. Blockchain and artificial intelligence are combining to upgrade everything from food supply chain logistics and healthcare record sharing to media royalties and financia
8 min read
Use Cases of BlockChain in different fields
Blockchain : Blockchain is a system of recording data that makes it troublesome or not possible to vary, hack, or cheat the system. Blockchain is truly a digital ledger of duplicated transactions and distributed across the total network of laptop systems on the blockchain. Every block among the chai
2 min read
Role of Blockchain in Sustainable Development
The Blockchain is a decentralized database, which means authority is not associated with one person; it will be shared among the people. Hence, changing and modifying the data is nearly impossible in the blockchain database. That's why it's the most trustworthy. It came in the 1990s when the researc
9 min read
Applications and Uses of Blockchain
A blockchain is actually a digital ledger of transactions that is copied and distributed across the network of computer systems. Each of the blocks generated after every transaction holds various information about the transaction and gets itself updated in every participant's ledger which once writt
9 min read
Benefits of Blockchain in Healthcare
A blockchain is a chain of blocks linked together using hashing technique. Each block consists of some timestamped records of information such as financial, healthcare, confidential data, etc. The Blockchain network is managed by a group of users on a decentralized network. All the information is av
6 min read
Decentralized Voting System using Blockchain
Blockchain is a technology that is rapidly gaining momentum in era of industry 4.0. With high security and transparency provisions, it is being widely used in supply chain management systems, healthcare, payments, business, IoT, voting systems, etc. Why do we need it? Current voting systems like bal
4 min read
Blockchain Implementation
Create simple Blockchain using Python
Blockchain is a time-stamped decentralized series of fixed records that contains data of any size and it is controlled by a large network of computers that are scattered around the globe and not owned by a single organization. Every block is secured and connected with each other using hashing techno
8 min read
Implementation of Blockchain in Java
Blockchain is the backbone Technology of Digital CryptoCurrency BitCoin. A Blockchain is a list of records called blocks that are linked together using linked lists and use the cryptographic technique.Each block contains its own digital fingerprint called Hash, the hash of the previous block, a tim
5 min read
Build a To-do List Web Application Powered by Blockchain
Here, we are going to build a to-do list application that will save the data in the blockchain. The blockchain part of this application can also be understood as a database. First, we'll create a smart contract and subsequently the web application itself. We'll use Bloc as the application name but f
15 min read
Flutter and Blockchain - Hello World Dapp
Flutter and Blockchain This tutorial will take you through the process of building your first mobile dapp - Hello World Dapp! This tutorial is meant for those with a basic knowledge of Ethereum and smart contracts, who have some knowledge of the Flutter framework but are new to mobile dapps. In this
9 min read
Blockchain Gaming : Part 1 (Introduction)
Blockchain Gaming. It’s a world of it’s own. It’s ‘Ready Player One’ incorporated into gaming. Before reading this article, it is recommended to read: Introduction to Blockchain to get well versed with the concept of blockchain. Part-1: Transparency, Proven Rarity and True Ownership Transparency: Wh
4 min read
How to use GANACHE Truffle Suite to Deploy a Smart Contract in Solidity (Blockchain)?
There are various processes involved in deploying a smart contract using Ganache and Truffle Suite: 1. Install Ganache first. Ganache is a personal blockchain for Ethereum development. You must first download and install it. It is available for download from https://www.trufflesuite.com/ganache, the
4 min read
How to use MetaMask to Deploy a Smart contract in Solidity (Blockchain)?
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts. They were first proposed by Nick Szabo in the 90s. They are set of rules and protocols which two parties agree upon and have to follow. One of the main features is that they are immutable once deployed on the blockchain. It is widely used in the Ethereum
3 min read
Build a Authentication Using Blockchain
Normally authentication is seen using databases like MYSQL, Firebase, MongoDB, etc. One of the biggest drawbacks is the chance of the data getting corrupted. The data can be modified by anyone who is in control of the database itself.To overcome the above problem here a web app authentication using
9 min read