Periodic Table of Elements
Last Updated :
23 Jul, 2025
The Periodic table of elements is a systematic arrangement of 118 known chemical elements. These chemical elements are organized in order of increasing atomic number. The horizontal rows from left to right are called periods while the vertical columns from top to bottom are called groups in a periodic table.
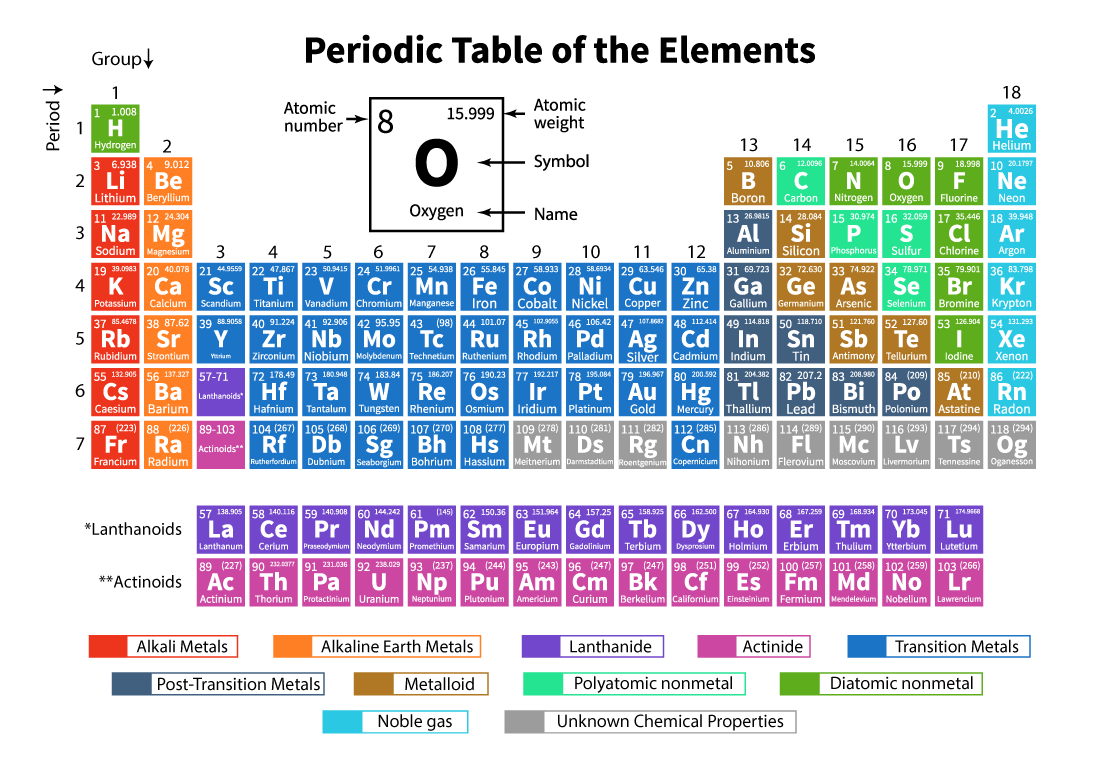
What is Periodic Table ?
A periodic table is a tabular representation in which all the known chemical elements are arranged in horizontal rows called periods and vertical columns called groups based on their atomic number and atomic structure respectively.
It is an arrangement of all the known elements and therefore provides information about the elements such as their mass, electron number, electron configuration, and their unique chemical properties.
List of Periodic Table Elements
Here is the table representing 118 elements of the periodic table. The elements listed are arranged according to the increasing order of atomic number and their respective atomic weight, symbol, density, and electronegativity.
Elements in Periodic Table with Atomic Mass
|
|---|
| Atomic Number | Chemical Element Name | Symbol | Atomic Mass (amu) | Density (g/cm3) | Electronegativity |
|---|
| 1 | Hydrogen | H | 1.0079 | 0.00008988 | 2.2 |
| 2 | Helium | He | 4.0026 | 0.0001785 | – |
| 3 | Lithium | Li | 6.941 | 0.534 | 0.98 |
| 4 | Beryllium | Be | 9.0122 | 1.85 | 1.57 |
| 5 | Boron | B | 10.811 | 2.34 | 2.04 |
| 6 | Carbon | C | 12.0107 | 2.267 | 2.55 |
| 7 | Nitrogen | N | 14.0067 | 0.0012506 | 3.04 |
| 8 | Oxygen | O | 15.9994 | 0.001429 | 3.44 |
| 9 | Fluorine | F | 18.9984 | 0.001696 | 3.98 |
| 10 | Neon | Ne | 20.1797 | 0.0009002 | – |
| 11 | Sodium | Na | 22.9897 | 0.968 | 0.93 |
| 12 | Magnesium | Mg | 24.305 | 1.738 | 1.31 |
| 13 | Aluminum | Al | 26.9815 | 2.7 | 1.61 |
| 14 | Silicon | Si | 28.0855 | 2.329 | 1.9 |
| 15 | Phosphorus | P | 30.9738 | 1.823 | 2.19 |
| 16 | Sulfur | S | 32.065 | 2.07 | 2.58 |
| 17 | Chlorine | Cl | 35.453 | 0.0032 | 3.16 |
| 18 | Argon | Ar | 39.948 | 0.001784 | - |
| 19 | Potassium | K | 39.0983 | 0.89 | 0.82 |
| 20 | Calcium | Ca | 40.078 | 1.55 | 1 |
| 21 | Scandium | Sc | 44.9559 | 2.985 | 1.36 |
| 22 | Titanium | Ti | 47.867 | 4.506 | 1.54 |
| 23 | Vanadium | V | 50.9415 | 6.11 | 1.63 |
| 24 | Chromium | Cr | 51.9961 | 7.15 | 1.66 |
| 25 | Manganese | Mn | 54.938 | 7.21 | 1.55 |
| 26 | Iron | Fe | 55.845 | 7.874 | 1.83 |
| 27 | Cobalt | Co | 58.9332 | 8.9 | 1.88 |
| 28 | Nickel | Ni | 58.6934 | 8.908 | 1.91 |
| 29 | Copper | Cu | 63.546 | 1.9 | 60 |
| 30 | Zinc | Zn | 65.39 | 1.65 | 70 |
| 31 | Gallium | Ga | 69.723 | 1.81 | 19 |
| 32 | Germanium | Ge | 72.64 | 2.01 | 1.5 |
| 33 | Arsenic | As | 74.9216 | 2.18 | 1.8 |
| 34 | Selenium | Se | 78.96 | 2.55 | 0.05 |
| 35 | Bromine | Br | 79.904 | 2.96 | 2.4 |
| 36 | Krypton | Kr | 83.798 | 3 | 1×10−4 |
| 37 | Rubidium | Rb | 85.4678 | 0.82 | 90 |
| 38 | Strontium | Sr | 87.62 | 0.95 | 370 |
| 39 | Yttrium | Y | 88.906 | 1.22 | 33 |
| 40 | Zirconium | Zr | 91.224 | 1.33 | 165 |
| 41 | Niobium | Nb | 92.906 | 1.6 | 20 |
| 42 | Molybdenum | Mo | 95.94 | 2.16 | 1.2 |
| 43 | Technetium | Tc | 98 | 1.9 | ~ 3×10−9 |
| 44 | Ruthenium | Ru | 101.07 | 2.2 | 0.001 |
| 45 | Rhodium | Rh | 102.91 | 2.28 | 0.001 |
| 46 | Palladium | Pd | 106.42 | 2.2 | 0.015 |
| 47 | Silver | Ag | 107.87 | 1.93 | 0.075 |
| 48 | Cadmium | Cd | 112.411 | 1.69 | 0.159 |
| 49 | Indium | In | 114.82 | 1.78 | 0.25 |
| 50 | Tin | Sn | 118.71 | 1.96 | 2.3 |
| 51 | Antimony | Sb | 121.76 | 2.05 | 0.2 |
| 52 | Tellurium | Te | 127.6 | 2.1 | 0.001 |
| 53 | Iodine | I | 126.9045 | 2.66 | 0.45 |
| 54 | Xenon | Xe | 131.293 | 2.6 | 3×10−5 |
| 55 | Cesium | Cs | 132.91 | 0.79 | 3 |
| 56 | Barium | Ba | 137.327 | 0.89 | 425 |
| 57 | Lanthanum | La | 138.91 | 1.1 | 39 |
| 58 | Cerium | Ce | 140.12 | 1.12 | 66.5 |
| 59 | Praseodymium | Pr | 140.9077 | 1.13 | 9.2 |
| 60 | Neodymium | Nd | 144.24 | 1.14 | 41.5 |
| 61 | Promethium | Pm | 145 | 1.13 | 2×10−19 |
| 62 | Samarium | Sm | 150.36 | 1.17 | 7.05 |
| 63 | Europium | Eu | 151.964 | 1.2 | 2 |
| 64 | Gadolinium | Gd | 157.25 | 1.2 | 6.2 |
| 65 | Terbium | Tb | 158.9253 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| 66 | Dysprosium | Dy | 162.5 | 1.22 | 5.2 |
| 67 | Holmium | Ho | 164.9303 | 1.23 | 1.3 |
| 68 | Erbium | Er | 167.259 | 1.24 | 3.5 |
| 69 | Thulium | Tm | 168.9342 | 1.25 | 0.52 |
| 70 | Ytterbium | Yb | 173.04 | 1.1 | 3.2 |
| 71 | Lutetium | Lu | 174.967 | 1.27 | 0.8 |
| 72 | Hafnium | Hf | 178.49 | 1.3 | 3 |
| 73 | Tantalum | Ta | 180.9479 | 1.5 | 2 |
| 74 | Tungsten | W | 183.84 | 2.36 | 1.3 |
| 75 | Rhenium | Re | 186.207 | 1.9 | 7×10−4 |
| 76 | Osmium | Os | 190.23 | 2.2 | 0.002 |
| 77 | Iridium | Ir | 192.22 | 2.2 | 0.001 |
| 78 | Platinum | Pt | 195.08 | 2.28 | 0.005 |
| 79 | Gold | Au | 196.97 | 2.54 | 0.004 |
| 80 | Mercury | Hg | 200.59 | 2 | 0.085 |
| 81 | Thallium | Tl | 204.3833 | 1.62 | 0.85 |
| 82 | Lead | Pb | 207.2 | 1.87 (2+)
2.33 (4+) | 14 |
| 83 | Bismuth | Bi | 208.9804 | 2.02 | 0.009 |
| 84 | Polonium | Po | 209 | 2 | 2×10−10 |
| 85 | Astatine | At | 210 | 2.2 | 3×10−20 |
| 86 | Radon | Rn | 222 | 2.2 | 4×10−13 |
| 87 | Francium | Fr | 223 | >0.79[6] | ~ 1×10−18 |
| 88 | Radium | Ra | 226 | 0.9 | 9×10−7 |
| 89 | Actinium | Ac | 227 | 1.1 | 5.5×10−10 |
| 90 | Thorium | Th | 232.0381 | 1.3 | 9.6 |
| 91 | Protactinium | Pa | 231.0359 | 1.5 | 1.4×10−6
|
| 92 | Uranium | U | 238.0289 | 1.38 | 2.7 |
| 93 | Neptunium | Np | 237 | 1.36 | ≤ 3×10−12 |
| 94 | Plutonium | Pu | 244 | 1.28 | ≤ 3×10−11 |
| 95 | Americium | Am | 243 | 1.13 | - |
| 96 | Curium | Cm | 247 | 1.28 | - |
| 97 | Berkelium | Bk | 247 | 1.3 | - |
| 98 | Californium | Cf | 251 | 1.3 | - |
| 99 | Einsteinium | Es | 252 | 1.3 | - |
| 100 | Fermium | Fm | 257 | 1.3 | - |
| 101 | Mendelevium | Md | 258 | 1.3 | - |
| 102 | Nobelium | No | 259 | 1.3 | - |
| 103 | Lawrencium | Lr | 262 | 1.3 | - |
| 104 | Rutherfordium | Rf | 267 | - | - |
| 105 | Dubnium | Db | 268 | - | - |
| 106 | Seaborgium | Sg | 269 | - | - |
| 107 | Bohrium | Bh | 270 | - | - |
| 108 | Hassium | Hs | 269 | - | - |
| 109 | Meitnerium | Mt | 277 | - | - |
| 110 | Darmstadtium | Ds | 281 | - | - |
| 111 | Roentgenium | Rg | 282 | - | - |
| 112 | Copernicium | Cn | 285 | - | - |
| 113 | Nihonium | Nh | 286 | - | - |
| 114 | Flerovium | Fl | 290 | - | - |
| 115 | Moscovium | Mc | 290 | - | - |
| 116 | Livermorium | Lv | 293 | - | - |
| 117 | Tennessine | Ts | 294 | - | - |
| 118 | Oganesson | Og | 294 | - | - |
Important Terms in Periodic Table
Terms
| Description
|
|---|
Atomic Number
| The number of protons that constitutes an element's nucleus is called its Atomic Number (Z). e.g. Carbon contains 6 protons then, so its atomic number must be 6 only.
|
|---|
Atomic Mass
| It is defined as the average mass of the atoms of an element. It is measured on the basis of the relative natural abundance of the isotopes of the element. Atomic mass is also termed Atomic Weight (A). It is measured in the atomic mass unit (amu).
|
|---|
Period
| The horizontal rows from left to right in a periodic table are called Periods. There are a total of 7 periods in the periodic table. The elements are arranged horizontally due to their similarities in properties, like the same atomic orbitals and so on.
|
|---|
Group
| The vertical columns from top to bottom in a periodic table are called Groups. There is a total of 18 groups in the periodic table. The elements are arranged vertically due to their similarities in properties, as they have the same number of valence electrons in them.
|
|---|
Symbol of an Element
| A symbol is a notion that is used to represent a chemical element using a letter or a combination of two to three letters. e.g. The chemical symbol of Carbon is C, while Fe is used for Iron and so on.
|
|---|
Classification of Elements in Periodic Table
The 118 elements are arranged in 7 periods and 18 groups as shown above. Further, the elements are divided into different blocks.
| Block | Elements Included | Last Electron Subshell Filled |
|---|
| s-block | Group 1 (Alkali Metals) | s-subshell |
| Group 2 (Alkaline Earth Metals) |
| p-block | Group 13 (Boron Family) | p-subshell |
| Group 14 (Carbon Family) |
| Group 15 (Nitrogen Family) |
| Group 16 (Oxygen Family) |
| Group 17 (Fluorine Family) |
| d-block | Groups 3 to 12 (Transition Elements) | d-subshell |
| f-block | Lanthanides (Rare Earth Elements) | f-subshell |
| Actinides |
Mendeleev Periodic Table
In order to represent similarities and trends in the behavior of elements, Mendeleev developed the periodic table, which is an arrangement of elements in an increasing atomic mass order in tabular form.

According to Mendeleev's Periodic Table, elements were arranged as per their fundamental property, atomic mass, and chemical characteristics. Only 63 elements were known at the time of Mendeleev's work. In the Mendeleev periodic table, the horizontal row and vertical columns were referred to as groups and periods, respectively.
However, Mendeleev's Periodic Table fails due to many flaws in it. Some of them are, that it failed to designate Hydrogen and Noble gases in it. Also, the increasing order of the atomic mass of the elements wasn't regular throughout the table. Even, the discovery of isotopes violates the Mendeleev Periodic Law.
Read More:
Explore
Basic Concepts
Structure of Atom
Classification of Periodicity
Bonding and Molecular Structure
Thermodynamics
Equilibrium
Redox Reactions
Basic Principles and Techniques
Hydrocarbons