Difference Between FDM,TDM and WDM
Last Updated :
23 Apr, 2025
Multiplexing is the set of techniques that allows the simultaneous transmission of multiple signals across a single data link. In a multiplexed system, n lines share the bandwidth of one link. The lines direct their transmission streams to a multiplexer (MUX), which combines them into a single stream .
- TDM uses a shared channel to transmit two or more digital or analog signals. It can be used when the transmission media's bit rate exceeds that of the signal to be delivered. Simply divide the available bandwidth into channels, each with a specified bandwidth.
- FDM allows independent signals to use the same transmission channel, such as a cable or optical fiber.
- WDM uses many lasers, each generating a unique color of light, to transfer data over a single fiber optic line.
FDM(Frequency Division Multiplexing)
Frequency-division multiplexing (FDM) is an analog technique that can be applied when the bandwidth of a link is greater than the combined bandwidths of the signals to be transmitted. In FDM, signals generated by each sending device modulate different carrier frequencies.
These modulated signals are then combined into a single composite signal that can be transported by the link. Carrier frequencies are separated by sufficient bandwidth to accommodate the modulated signal. These bandwidth ranges are the channels through which the various signals travel.
 FDM
FDMTDM(Time Division Multiplexing)
TDM (Time Division Multiplexing) is a multiplexing technology and has low conflict. It works with both digital and analog signals. TDM shares the timeframe of the multiple signals. TDM and synchronous time division multiplexing (sync TDM).
TDM is utilized for long-distance communication networks and can handle high data traffic demands from end users. TDM splits the available time on the channel into discrete time slots, each allocated to a distinct signal or data stream.
 TDM
TDMWDM(Wavelength Division Multiplexing)
WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing) is generally utilized for multiplexing numerous optical carrier signals into a single optical fiber channel. WDM permits communication in both directions via the fiber connection.
Two or more colors of light can flow through a single fiber, and an optical waveguide can transport multiple signals at different wavelengths or frequencies on the optical spectrum.
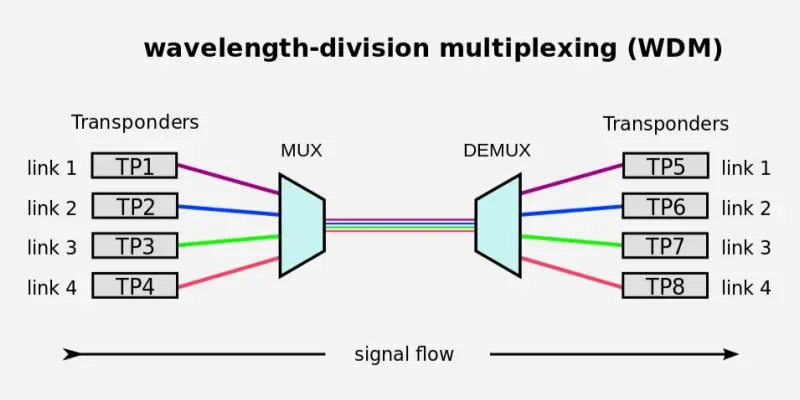 WDM(Wavelength Division Multiplexing)
WDM(Wavelength Division Multiplexing)Difference Between FDM, TDM, and WDM
FDM | TDM | WDM |
|---|
FDM is a multiplexing method used in analog systems that requires a guard band to prevent signals from overlapping. | TDM (Time Division Multiplexing) is a multiplexing technology and has low conflict, working with both digital and analog signals. | Wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) is often used for multiplexing numerous optical carrier signals into a single optical fiber channel. |
FDM divides the bandwidth into smaller frequency ranges, and transmitters broadcast data concurrently across a shared channel inside each frequency range. | TDM provides each user a defined time slot to deliver signals across a shared channel. The user receives the complete bandwidth during that time frame. | WDM combines numerous light beams from different channels into a single light beam and delivers it over a fiber optic thread similar to FDM. |
FDM refers to Frequency Division Multiplexing. | TDM refers to Time Division Multiplexing. | WDM refers to Wave Length Multiplexing. |
FDM is used in a communications network to send and receive input signals at maximum speed at all times. | This technology is used in GSM and also in SDH Transmission. | It is used in ultra-long-distance and high-capacity fiber systems. |
Conclusion
In this article, we have learned about FDM, TDM, and WDM. FDM divides the bandwidth into smaller frequency ranges, TDM provides each user a defined time slot to deliver signals across a shared channel and WDM combines numerous light beams from different channels into a single light beam and delivers it over a fiber optic thread similar to FDM.