RESTful Web Services are a way of designing and developing web services that use REST (Representational State Transfer) principles. They enable applications to communicate over the web using standard HTTP methods, such as GET, POST, PUT and DELETE. REST is lightweight, stateless and widely used in modern web and mobile applications.
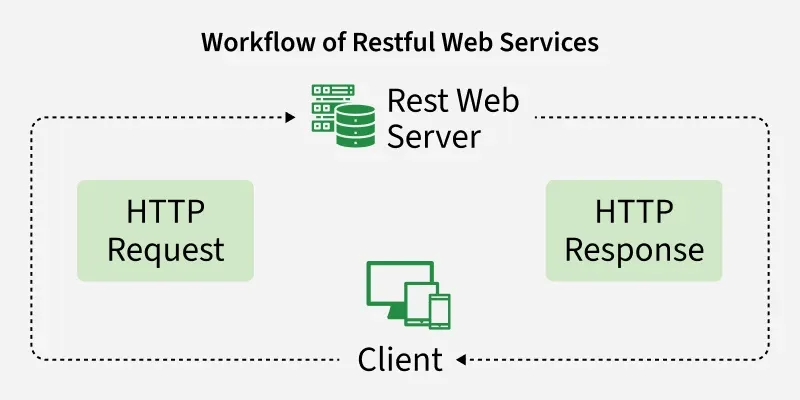 workflow
workflowWhat is REST
REST or Representational State Transfer is an architectural style that can be applied to web services to create and enhance properties like performance, scalability and modifiability.
REST became popular due to its simplicity and adaptability
- Cross-Platform Communication: Applications built in different languages and environments can easily talk to each other.
- Mobile-Friendly: REST works smoothly on mobile devices without extra effort.
- Cloud Compatibility: Most modern cloud platforms and architectures are based on REST principles.
RESTful Architecture
- Resources via HTTP: Every resource is accessed using standard HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE).
- Stateless: Each request is independent; the server doesn’t store client session data.
- Client/Server: The client (browser/app) sends requests and the server responds with data.
- Layered: Requests may pass through intermediaries like load balancers or security layers.
- Caching: Responses can be cached for faster performance.
Principles of RESTful Applications
1. URI Resource Identification
- Each resource (user, product, file) should have a unique URI (e.g., /users/1).
- URIs help with easy discovery and access.
2. Uniform Interface
- REST uses a fixed set of operations: GET, POST, PUT, DELETE.
- This makes REST simple and consistent.
3. Self-Descriptive Messages
- Data can be sent/received in formats like JSON, XML, HTML, PDF or plain text.
- Metadata helps with caching, error handling, authentication, etc.
4. Hyperlinks for State Interactions (HATEOAS)
- RESTful responses can include links that guide clients on what they can do next.
- Example: A response for /users/1 may also include a link to /users/1/orders.
Example
Here is an example of a simple RESTful service that allows a client to create, read, update and delete (CRUD) a resource :
Java
// GET /resource/123 Returns the state of the resource with ID 123
app.get('/resource/:id', function(req, res) {
var id = req.params.id;
var resource = findResourceById(id);
res.json(resource);
});
// POST /resource Creates a new resource with the state specified in the request body
app.post('/resource', function(req, res) {
var resource = req.body;
var id = createResource(resource);
res.json({ id: id });
});
// PUT /resource/123 Updates the state of the resource with ID 123 with the state specified in the request body
app.put('/resource/:id', function(req, res) {
var id = req.params.id;
var resource = req.body;
updateResource(id, resource);
res.sendStatus(200);
});
// DELETE /resource/123 Deletes the resource with ID 123
app.delete('/resource/:id', function(req, res) {
var id = req.params.id;
deleteResource(id);
res.sendStatus(200);
});
In this example:
- GET retrieves a resource.
- POST creates a new one.
- PUT updates an existing one.
- DELETE removes it.
Advantages of RESTful web services
- Speed: As there is no strict specification, RESTful web services are faster as compared to SOAP. It also consumes fewer resources and bandwidth.
- Compatible with SOAP: RESTful web services are compatible with SOAP, which can be used as the implementation.
- Language and Platform Independency: RESTful web services can be written in any programming language and can be used on any platform.
- Supports Various Data Formats: It permits the use of several data formats like HTML, XML, Plain Text, JSON, etc.
Explore
Computer Network Basics
Physical Layer
Data Link Layer
Network Layer
Transport Layer
Session Layer & Presentation Layer
Application Layer
Advanced Topics
Practice