USB Full Form | About USB
Last Updated :
12 Jul, 2025
Universal Serial Bus (USB) has revolutionized the way we connect and interact with electronic devices, becoming an indispensable standard in the tech industry. With its widespread adoption, USB technology has simplified data transfer, device charging, and peripheral connectivity. From USB 2.0 to the latest USB 4.0, this versatile interface offers speed, convenience, and reliability.
USB stands for Universal Serial Bus. USB was designed to standardize the connection of peripherals like pointing devices, keyboards, digital still, and video cameras. But soon devices such as printers, portable media players, disk drives, and network adaptors to personal computers used USB to communicate and to supply electric power.
In this article, we will explore the evolution, types, and benefits of USB, highlighting why it remains a critical component in modern computing and electronics.
What is the Full Form of USB?
USB full form is Universal Serial Bus. It is used as a device for communication between connectors and cables. USB is also used for connection and power supply between computers, laptops, and electronic devices. USB reduces the workload to serve the function of transferring data, Data transfer and electricity supply between peripheral devices such as keyboards, mouse, printers, portable media players, disk drives, etc was the main motive behind designing a USB. USB is an industry-standard that establishes specifications for connectors, cables, and protocols for communication, connection, and power supply between personal computers and their peripheral devices.
History of Universal Serial Bus (USB)
Universal Serial Bus (USB) was developed by a group of seven companies named Microsoft, IBM, Compaq, DEC, Intel, NEC, and Nortel in 1994. USB was developed for an easy connection with external devices. It is very simple to connect USB devices with laptops and computers. Before the use of USBs, the ports were used to plug into devices and computers for data transfer. Each of the peripheral devices like the Keyboard, mouse, printer, etc. used its own individual port to connect with the computer. Data transfer between serial and parallel ports was very slow and ranged between 100 to 450 kbs per second. Because of these greater levels of incompatibility and problems in using multiple interfaces, the need for a technology like USB emerged.
Versions of USB and Their Key Features
| USB Version | Release Year | Max Data Transfer Rate | Key Features |
|---|
| USB 1.0 | 1996 | 1.5 Mbps (Low-Speed), 12 Mbps (Full-Speed) | Initial version, basic connectivity |
| USB 1.1 | 1998 | 12 Mbps | Improved compatibility and performance |
| USB 2.0 | 2000 | 480 Mbps | High-Speed support, widespread adoption |
| USB 3.0 | 2008 | 5 Gbps | SuperSpeed, improved power efficiency, backward compatible with USB 2.0 |
| USB 3.1 | 2013 | 10 Gbps | SuperSpeed+, better data handling, USB Type-C support |
| USB 3.2 | 2017 | 20 Gbps | Enhanced SuperSpeed+, dual-lane operation |
| USB4 | 2019 | 40 Gbps | Thunderbolt 3 compatibility, improved bandwidth management, USB Type-C connector |
Each version of USB has brought significant improvements in speed, power efficiency, and connectivity, making USB a crucial standard in modern electronics.
Connection of USB in Computer
To connect a Universal Serial Bus (USB) device to your computer, just insert the USB device into the computer in the port. The computer will automatically detect and connect to the device. If this way is not working for you, then just reboot your computer and then connect the USB.
Basic USB connectors come in different sizes :
- Standard size USB
- Mini size USB
- Micro size USB
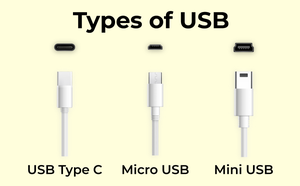 Types of USB
Types of USBFeatures of Universal Serial Bus (USB)
- A maximum of 127 peripherals can be connected to a single USB host controller.
- USB device has a maximum speed of up to 480 Mbps (for USB 2.0).
- The length of the individual USB cable can reach up to 5 meters without a hub and 40 meters with a hub.
- USB acts as a plug and play device.
- USB can draw power from its own supply or from a computer.
- If a computer turns into power-saving mode, some USB devices will automatically convert themselves into sleep mode.
Advantages of Universal Serial Bus (USB)
- USB is ease of use.
- The acceptable data rate for many applications
- Robust connector system.
- A variety of connector types/sizes are available
- USB has true plug and play nature.
- USB has very low cost.
Disadvantages of USB
- USB cables are limited in length.
- Some very high-speed peripheral devices require sustained speeds not available in the USB standard.
- The use of the USB logos on the product requires annual fees and membership in the organization.
 USB- Universal Serial Bus
USB- Universal Serial BusConclusion
Universal Serial Bus (USB) has become a cornerstone of modern technology, facilitating seamless connectivity and efficient data transfer across a multitude of devices. Its evolution from USB 1.0 to USB 4.0 has consistently brought faster speeds, greater versatility, and enhanced user convenience. As technology continues to advance, USB remains a vital interface, driving innovation and improving our digital experiences. Whether for personal use, professional applications, or advanced computing, the enduring importance of USB is undeniable, making it an essential component in the ever-evolving landscape of electronics and computing.
Explore
Computer Network Basics
Physical Layer
Data Link Layer
Network Layer
Transport Layer
Session Layer & Presentation Layer
Application Layer
Advanced Topics
Practice