What is Network Access Control?
Last Updated :
09 Dec, 2025
Network Access Control (NAC) secures a network by ensuring only authenticated, compliant users and devices can connect. It strengthens protection by enforcing security policies, controlling device access, and preventing unauthorized or unsafe systems from entering the network.
- Blocks unauthorized users and non-compliant devices
- Grants restricted access based on device health and user identity
- Ensures policy enforcement across wired and wireless networks
- Limits the spread of threats by controlling lateral movement
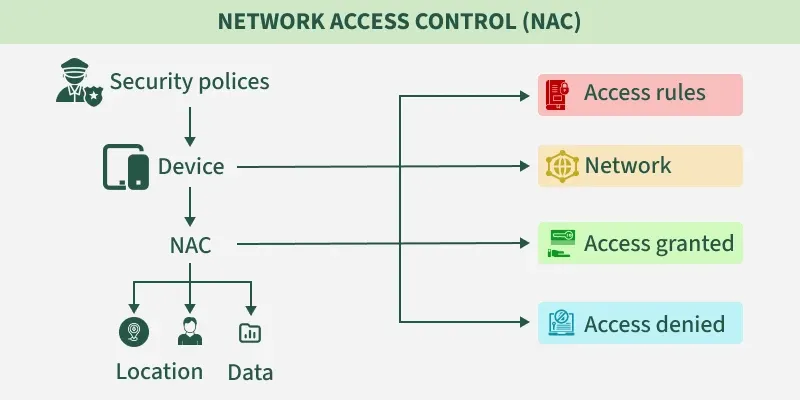
How NAC Works
- Identifies devices attempting to connect
- Evaluates device compliance with security policies
- Authenticates users and devices
- Authorizes access based on identity, role, and device posture
- Grants full, limited, or no access depending on compliance
Types of Network Access Control
Different types of network access control are:
1. Pre-Admission NAC
- Occurs before a device joins the network
- Evaluates compliance and identity during connection request
- Only allows access if the device meets required security standards
- Prevents unauthorized or risky devices from entering the network
2. Post-Admission NAC
- Applies after the device is on the network
- Restricts lateral movement by requiring re-authentication for sensitive areas
- Monitors device behavior and enforces access rules across segments
- Ideal for preventing internal spread of compromised devices
Steps to Implement NAC Solutions
Following are the steps to implement NAC solutions:
 Implement NAC Solutions
Implement NAC Solutions1. Gather Data
- Identify all devices, users, and systems interacting with network resources
- Document device types, OS versions, ownership, and usage
2. Manage Identities
- Authenticate and authorize every user or device
- Integrate with directory services (Active Directory, LDAP, etc.)
3. Determine Permissions
- Define access levels for different user/device groups
- Apply least-privilege principles
4. Apply Permissions
- Enforce access control policies on each group
- Register users/devices in the NAC system for tracking
5. Update and Monitor
- Continuously monitor network activity
- Modify access rules as organizational needs evolve
- Regularly review logs, compliance status, and device posture
Importance of Network Access Control
Given below the importance of Network Access Control:
- The surge in mobile and personal devices has increased security risks
- Modern networks require tools that provide visibility, control, and compliance
- NAC strengthens enterprise security by ensuring only trusted devices connect
NAC systems can:
- Deny access to unauthorized or non-compliant devices
- Grant restricted access to partially compliant devices
- Prevent vulnerable devices from infecting the network
- Scale across large enterprise networks with diverse device types
- Modern networks require tools that provide visibility, control, and compliance
- NAC strengthens enterprise security by ensuring only trusted devices connect
Principal Elements of NAC
There are mainly three Principal Elements of NAC which are:

1. Access Requestor (AR)
- Any device, user, or process requesting network access
- Includes laptops, servers, IP cameras, printers, IoT devices
- Must comply with organizational security policies
2. Policy Server
- Determines access level based on identity, permissions, device posture, and request type
- Integrates with back-end systems such as antivirus tools, patch management, and directory services
- Authorizes, restricts, or denies network access accordingly
3. Network Access Server (NAS)
- Access control point for users connecting remotely
- Often integrated with VPN gateways
- Provides secure entry to internal networks for remote employees
Key Responsibilities of Network Access Control
Here are the key responsibilities of Network Access Control systems, organized clearly for understanding:
- It allows only compliant, authenticated devices to access network resources and infrastructure.
- It controls and monitors the activity of connected devices on the network.
- It restricts the availability of network resources of private organizations to devices that follow their security policy.
- It regulates the access of network resources to the users.
- It mitigates network threats by enforcing security policies that block, isolate, and repair non-compliant machines without administrator attention.
Real-Life NAC Examples
Here are some real-life Network Access Control (NAC) examples to help you understand how it's used in enterprise environments:
- Corporate Office : NAC ensures only company-issued, secure laptops can access internal systems. Unapproved or non-compliant devices are blocked or sent to a restricted network.
- Hospital / Healthcare : NAC verifies that medical devices and staff computers meet security standards before accessing patient data. Non-compliant devices are denied or limited in access.
- Retail Store : It restricts access so only authorized point-of-sale systems connect to the network. Customer and staff devices are placed on a separate guest Wi-Fi.
- Smart Home : It checks smart devices before letting them connect. Guests get internet access only, keeping home automation systems secure.
Limitations of Network Access Control (NAC)
Here are the Limitations of NAC systems that are important to understand, especially in real-world deployments:
- Limited Visibility for IoT Devices: NAC has low visibility and control over IoT devices or endpoints without specific user identities.
- No Internal Threat Protection: NAC does not protect against threats that originate within the network, such as insider attacks or compromised internal devices.
- Compatibility Issues: NAC solutions may not function effectively if they are incompatible with existing security tools or infrastructure within the organization.
Explore
Computer Network Basics
Physical Layer
Data Link Layer
Network Layer
Transport Layer
Session Layer & Presentation Layer
Application Layer
Advanced Topics
Practice