CRUD Operations using Hibernate
Last Updated :
04 Sep, 2025
Hibernate is a Java Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) framework that simplifies database interactions by mapping Java objects to relational tables. It allows developers to perform CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete) without writing complex SQL queries.
CRUD refers to database operations:
- C -> Insert new records into the database
- R -> Retrieve records from the database
- U -> Modify existing records
- D -> Remove records from the database
Given below are the examples that illustrate the use of Hibernate to perform CRUD operations. All the examples use MySQL for database management and 'student_info' as a sample database.
Project Setup
Step 1: Create a Maven Project
- Open IntelliJ IDEA or Eclipse.
- Create a new Maven Project.
- Add the following dependencies to your pom.xml:
Java
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-crud</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>Hibernate CRUD Example</name>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.3.2</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring Boot Starter Web -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring Boot Starter Data JPA (Hibernate) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- MySQL Driver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Optional: Lombok (for getters/setters) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring Boot DevTools (optional, for live reload) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Testing -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<!-- Spring Boot Maven Plugin -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Project Structure
 Structure
StructureCreate a Hibernate configuration file hibernate.cfg.xml inside src/main/resources.
Java
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"https://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<!-- Automatically update or create tables -->
<property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">update</property>
<!-- Database connection details -->
<property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/student_info?serverTimezone=UTC</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.username">root</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.password">root</property>
<property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL8Dialect</property>
<!-- Mapping class -->
<mapping class="beans.Student"/>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
Note: Make sure your MySQL database student_info exists.
Step 3: Create SessionFactory Provider
Hibernate uses a SessionFactory to create sessions for database operations.
Create a class SessionFactoryProvider.java:
Java
package utilities;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
public class SessionFactoryProvider {
public static SessionFactory provideSessionFactory() {
Configuration config = new Configuration();
config.configure(); // Reads hibernate.cfg.xml
return config.buildSessionFactory();
}
}
Step 4: Create the Entity (POJO) Class
Create a class Student.java in the beans package:
Java
package beans;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
@Entity
public class Student {
@Id
private int id;
private String name;
private int std;
public Student() {}
public Student(int id, String name, int std) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.std = std;
}
// Getters and Setters
public int getId() { return id; }
public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; }
public String getName() { return name; }
public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }
public int getStd() { return std; }
public void setStd(int std) { this.std = std; }
}
Step 5: Create a Record (Create Operation)
Create Create.java:
Java
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import beans.Student;
import utilities.SessionFactoryProvider;
public class Create {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SessionFactory sessionFactory = SessionFactoryProvider.provideSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
// Create a new student
Student s = new Student(101, "John", 10);
session.saveOrUpdate(s);
tx.commit();
session.close();
sessionFactory.close();
System.out.println("Student record created successfully!");
}
}
Run and Verify
- Run Create.java ->This code will insert the new record into the student_info table.
 output
outputStep 6: Retrieve a Record (Read Operation)
Create Retrieve.java: Retrieving data from the database:
Java
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import beans.Student;
import utilities.SessionFactoryProvider;
public class Retrieve {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SessionFactory sessionFactory = SessionFactoryProvider.provideSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Student s = session.get(Student.class, 101); // Fetch by ID
if (s != null) {
System.out.println("Id: " + s.getId());
System.out.println("Name: " + s.getName());
System.out.println("Class: " + s.getStd());
} else {
System.out.println("Student not found.");
}
session.close();
sessionFactory.close();
}
}
The following details will be fetched from the database:

Retrieve.java:
Java
package crudOperations;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import beans.Student;
import utilities.SessionFactoryProvider;
public class Retrieve {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SessionFactory sessionFactory = SessionFactoryProvider.provideSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
// Fetching object using get()
System.out.println("Fetching object using get:");
Student s1 = session.get(Student.class, 102);
if (s1 != null) {
System.out.println("Id: " + s1.getId());
System.out.println("Name: " + s1.getName());
System.out.println("Class: " + s1.getStd());
} else {
System.out.println("Student not found.");
}
sessionFactory.close();
}
}
Output:
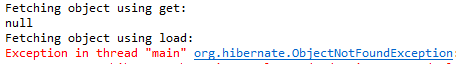
Step 7: Update a Record (Update Operation)
Create Update.java: Updating a record in the database:
Java
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import beans.Student;
import utilities.SessionFactoryProvider;
public class Update {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SessionFactory sessionFactory = SessionFactoryProvider.provideSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
Student s = session.get(Student.class, 101);
s.setStd(11); // Update class
session.saveOrUpdate(s);
tx.commit();
session.close();
sessionFactory.close();
System.out.println("Student record updated successfully!");
}
}
Run and Verify
The following record will be updated:

Step 8: Delete a Record (Delete Operation)
Create Delete.java: To delete an object from the database, the session.delete() method is used.
Java
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import beans.Student;
import utilities.SessionFactoryProvider;
public class Delete {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SessionFactory sessionFactory = SessionFactoryProvider.provideSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
Student s = session.get(Student.class, 101);
if (s != null) {
session.delete(s);
System.out.println("Student record deleted successfully!");
} else {
System.out.println("Student not found.");
}
tx.commit();
session.close();
sessionFactory.close();
}
}
Run and Verify
After run the application check record into database:
 output
output
Explore
Java Enterprise Edition
Multithreading
Concurrency
JDBC (Java Database Connectivity)
Java Frameworks
JUnit