Using Azure Durable Functions For Complex Workflows
Last Updated :
23 Jul, 2025
In this tutorial, we will orchestrate a workflow relying 100% on a serverless approach based on Azure Durable Functions. Azure Durable Functions. Azure Durable Functions is an extension of Azure Functions which lets us write stateful and serverless functions using C# or JavaScript programming languages. It gives us the orchestration of a long-running task, error handling, and state management across other functions.
Features of Azure Durable Functions
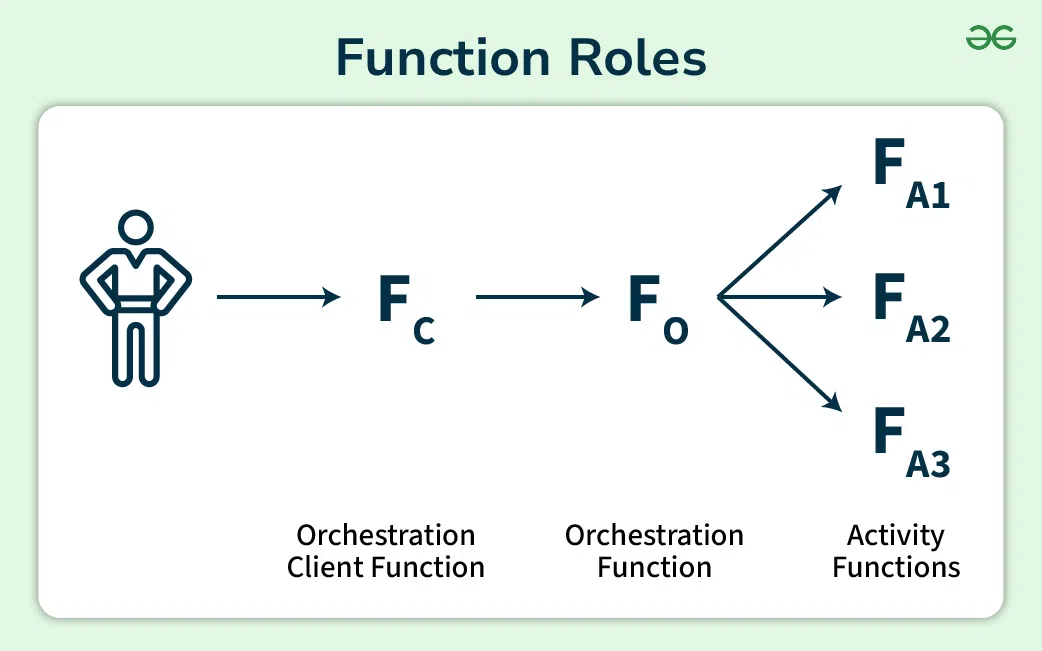
- Orchestration: Durable Functions allow us to write orchestration functions that ensure activities in which other callable service methods run in an expected order.
- Activities: The smallest work units within a workflow are typically written in C# or JavaScript programming languages.
- State Management: The Durable Functions offer stateful management that allows us to store and retrieve data between different functions.
- Error Handling: The Durable Functions have native error handling methods like retries and timeouts to manage the failures within the complex workflow.
- Event-Driven: The Durable Functions are event-driven, allowing us to trigger workflows based on events from various sources like Azure Storage, Azure Service Bus or HTTP requests.
Advantages Of Using Azure Durable Functions For Complex Workflows
In a simplified workflow management the Durable Functions gives us a straightforward way to express long running operations in code as well as avoid the processing on our own.
- Scalability: Durable Functions build on top of Azure Function, so they benefit from the automatic scaling and can be naturally scalable to very large amounts of data/traffic.
- Reliability: Durable Functions automatically handles errors and orchestrates retries to bring increased sensitivity of workflows to faults.
- Lower Cost: Durable Functions utilize a serverless model, meaning you only pay for the compute resources you use, reducing costs and optimizing resource utilization.
Use Cases For Azure Durable Functions
To orchestrate the processing of orders which includes payment, inventory management and shipping with the help of Durable Functions.
- Data Ingress: We ingest the data from diverse sources such as IOT devices and social media API's and we process it in real time using the Durable Functions.
- Machine Learning Pipelines: The Durable Functions is used to orchestrate machine learning pipelines which contains data preparation, model training and model deployment.
Design Patterns For Complex Workflows
- Keep Workflows Simple: If we break down complex workflows into smaller one's the constituent tasks to simplify orchestration. We then use activities to perform specific tasks within the workflow rather than relying on a single function which handles everything.
- Monitor And Debug: Monitor and debug workflows uses the Azure Monitor to use the in built debugging tools for an Azure Function.
Step-by-Step Process for Setting Up Azure Durable Functions
Creating a Durable Function
Step 1: Open Visual Studio
Step 2: Click on "Create a new project" and search for "Azure Function"

Step 3: Give your project a name and a path , click on create

Step 4: Select "Durable Functions Orchestration", click on create

Step 5: After creating you will be able to see a code format
- The code format will have the name of your project and many functions under it like Orchestrator Function responsible for the overall workflow , Activity Function, Http Trigger , Error Handling and other.
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.Azure.WebJobs;
using Microsoft.Azure.WebJobs.Extensions.Http;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Newtonsoft.Json;
namespace DurableDemoFn
{
public static class Function1
{
[FunctionName("OrchestratorFunction")]
public static async Task<List<string>> RunOrchestrator(
[OrchestrationTrigger] IDurableOrchestrationContext context)
{
var outputs = new List<string>();
// Calling activity functions in sequence.
outputs.Add(await context.CallActivityAsync<string>("ATM", "200"));
outputs.Add(await context.CallActivityAsync<string>("BuyGrocery", "Potato"));
outputs.Add(await context.CallActivityAsync<string>("DepositMoney", "Citibank"));
// returns ["Hello Tokyo!", "Hello London!", "Hello Seattle!"]
return outputs;
}
[FunctionName("ATM")]
public static string GetCash([ActivityTrigger] string name, ILogger log)
{
log.LogInformation($"Saying hello to {name}.");
return $"Cash {name} withdrawn!";
}
[FunctionName("BuyGrocery")]
public static string GetItems([ActivityTrigger] string name, ILogger log)
{
log.LogInformation($"Saying hello to {name}.");
return $"Bought {name}!";
}
[FunctionName("DepositMoney")]
public static string SaveCash([ActivityTrigger] string name, ILogger log)
{
log.LogInformation($"Saying hello to {name}.");
return $"Deposited money in {name}!";
}
[FunctionName("HttpStart")]
public static async Task<IActionResult> HttpStart(
[HttpTrigger(AuthorizationLevel.Function, "get", "post")] HttpRequest req,
[DurableClient] IDurableOrchestrationClient starter,
ILogger log)
{
// Function input comes from the request content.
string instanceId = await starter.StartNewAsync("OrchestratorFunction", null);
log.LogInformation($"Started orchestration with ID = '{instanceId}'.");
return starter.CreateCheckStatusResponse(req, instanceId);
}
}
Running The Function Locally
Step 6: Click on Build and after that Run it.

Step 7: Copy the URL show in the terminal window.

Step 8: Open Postman and paste the URL and Click on send

Step 9: To get the status workflow , Copy the StatusQueryURL and paste it in a new tab in postman.

Deploying it to Azure
Step 10: Stop the RUN and Click on Publish

Step 11: Click on Azure > Next then Click on Azure Function App (Windows) > Next
Step 12: Click on the Plus sign and Click on create > Finish

Step 13: Copy the Site URL and Click on Publish

Step 14: Open your Azure account and under Resource Groups find the published project , Now copy the base URL

Step 15: To verify if the Function is running copy the base url from the azure account and replace it with "http://localhost:7071" and click on send.

Troubleshooting And Optimizing Azure Durable Functions For Performance
Here are some best practices for optimizing the performance of Azure Durable Functions:
Monitoring And Diagnostics
- Enable Application Insights to collect telemetry data, track execution times, monitor failures, and gather performance metrics.
- Analyse telemetry data to identify performance issues and set up alerts for anomalies.

Performance Bottlenecks And Solutions
- Manage complexity by breaking down long workflows using patterns like Fan-out/Fan-in or Chaining.
- Use Durable Entities for workload distribution and scaling
- Optimize data storage and clean up old data regularly.
- Improve activity function efficiency by reducing complexity and using asynchronous operations.
Scaling And Performance Tuning
- Adjust resources and plans based on performance requirements.
- Utilize Auto-Scaling for dynamic resource adjustments based on metrics.
- Establish appropriate timeout configurations to balance performance and cost.
Conclusion
Azure Durable Functions simplify the management of long-running tasks in a serverless environment by providing state management, error handling, and automatic scaling.
Explore
DevOps Basics
Version Control
CI & CD
Containerization
Orchestration
Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Monitoring and Logging
Security in DevOps