Imagine your website is running smoothly on an Azure Virtual Machine. Customers are visiting, orders are flowing, and everything feels great. Then suddenly, something unexpected happens, maybe a bug crashes your system, important files get deleted by mistake, or there’s a power outage. Your site goes down, and just like that, your business takes a hit.
Do you have a backup? Can you restore everything quickly? If the answer is no, you could be in serious trouble.
This is why having a backup and disaster recovery plan is essential. Backups mean you have copies of your data ready to restore. Disaster recovery means you have a plan to get your system back up and running fast, minimizing downtime and data loss.
Azure provides powerful tools to protect your VMs so that even if disaster strikes, you won’t have to start from zero. Let’s explore what Azure VMs are, the difference between backup and disaster recovery, and how to set up these strategies effectively.
What are Azure Virtual Machines?
Azure VMs are one of the central services of Microsoft Azure's cloud platform, which enables users to create virtual computers within the cloud and eliminates the use of on-site physical hardware. Such VMs can be quickly deployed, scaled, and customized to suit various computing needs. Regarding Azure VMs, firms can execute applications, host websites, and process data without making huge investments in hardware. One can choose from among a variety of pre-configured VM sizes and types, and they are optimized for different workloads, such as general-purpose computing, memory-intensive tasks, or high-performance computing.
Finally, Azure VMs support a variety of OS types. For example, Windows and Linux and provide freedom of choice over the environment. They can also be fitted together with other services within Azure, which makes for a solid platform for building sophisticated, distributed applications. Certainly, one of the main abilities and, therefore, advantages of Azure VMs is their auto-scaling and adjustment of resources according to demand, which provides optimal performance at lower costs.
From a security perspective, Azure gives an organization multiple opportunities to secure VMs properly by using network security groups and providing integration with Azure Security Center. Developers can leverage Azure VMs for testing and development by easily spinning up and tearing down environments. Furthermore, the tools needed for monitoring, managing, and maintaining VMs are found in Azure, making IT operations easier.
Backup vs Disaster Recovery
People often confuse backup and disaster recovery, but they are not the same thing. Here is an easy way to understand it:
- Backup is like making a copy of your important files just in case you lose them. If a file gets deleted or damaged, you can bring it back from the backup.
- Disaster recovery is about getting your entire system or service back up and running after something big goes wrong like a power outage, cyberattack, or server crash.
So, backup helps you save your data, and disaster recovery helps you get back to work fast when everything breaks.
The following comparison table help you in understanding this in detailed way:
| Feature | Backup | Disaster Recovery |
|---|
| What it does | Keeps a copy of your data | Gets your system back online |
| Main goal | Protect your data | Restore full services |
| Used when | A file is deleted or corrupted | The whole system fails |
| How fast it works | Slower – you restore files | Faster – whole system is recovered |
| Example | Recover a deleted document | Recover a crashed website or server |
| Azure tool | Azure Backup | Azure Site Recovery |
What are Azure Backup and Disaster Recovery Strategies for Azure VMs?
We all know the importance of data protection and business continuity in case of any eventuality, and it is important to be prepared for such incidents. Similarly, Azure Backup and Disaster Recovery Strategies for Azure VMs the examples of such services.
Azure Backup
Azure Backup is an internal service to the Azure platform that users can leverage to protect VMs, applications, and data by backing them up. It enables scheduling regular backups, keeping them for periods that it specifies, and restoring VMs or single files easily if required. It works for both Windows and Linux VMs and is well-integrated with other Azure services.
Azure Site Recovery
In its strategy on disaster recovery, Azure Site Recovery permits users to replicate VMs to a secondary region in Azure. In other words, we can say that in the case of any issue in a primary region, the workloads can be quickly forwarded to the secondary region in the minimum time possible.
Some of the key features of Azure Backup and Disaster Recovery include:
- Automation and Central management of Backups of Azure VMs
- Application-consistent backups for data integrity
- Flexible retention policies that can meet different compliance requirements.
- Geo-redundant storage options for enhanced protection of data
- Ability to test disaster recovery scenarios without impacting production workloads
These services provide end-to-end protection of Azure VMs against data loss, hardware failure, and regional disasters. They scale to safeguard growing volumes of data and integrate with Azure's security features to ensure that backed-up and replicated data remains protected.
Architecture of Backup and Disaster Recovery Strategies for Azure VMs
- This section applies to all Azure VM backup and disaster recovery strategies, except for basic configurations. Azure Backup and Site Recovery services are deployed for the protection of virtual machines and in support of cross-region replication. Specifically, these services manage data protection and failover capabilities for VMs created in the primary or secondary regions.
- Backup and disaster recovery are basic ways by which you can protect your workloads running in Azure. This would be considered a large risk and is not recommended because it is usually due to regional outage or data loss scenarios. You can mitigate this risk by executing a backup solution coupled with disaster recovery. Such solutions can be designed or configured for business continuity. They also protect data and provide failover capabilities in the primary region for workloads, as well as rapid recovery in the secondary regions.
- By default, geo-redundant storage and cross-region replication are supported for new Azure VM backup and disaster recovery deployments. Previously configured solutions may or may not have these features enabled. Capabilities actually offered are dependent on the chosen service tier and regional availability.
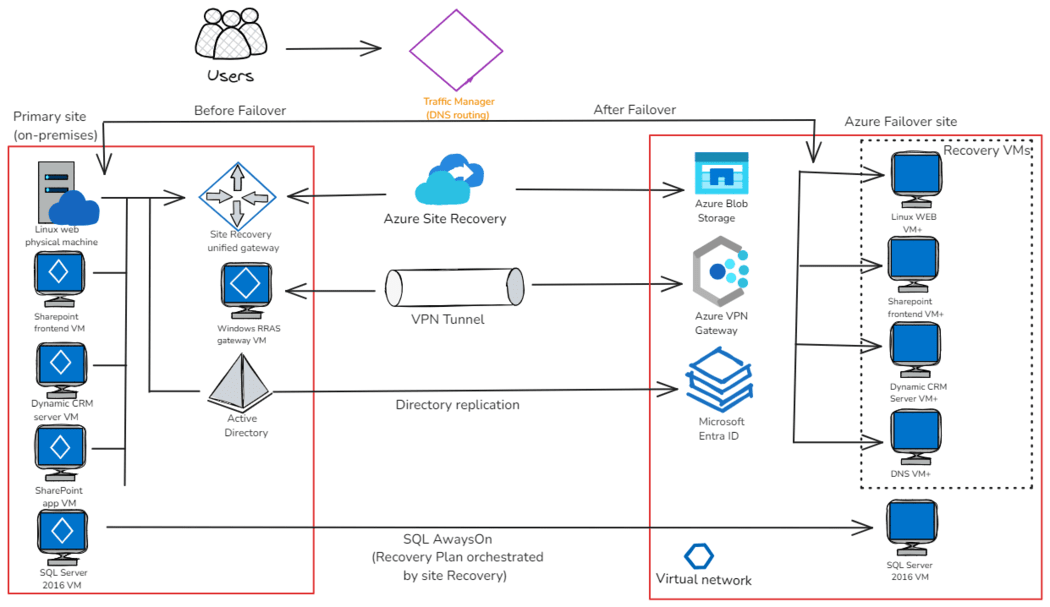 Enterprise-scale disaster recovery
Enterprise-scale disaster recoveryThe Backup and Disaster Recovery Strategies for Azure VMs above is the Architecture of an Enterprise-scale disaster recovery level:
- A unified gateway for site recovery and replication management.
- A VPN tunnel secures communication between two sites.
- Azure Blob Storage to store the replicated data.
- Azure VPN Gateway for network connectivity.
- Identity management is provided by Microsoft Entra ID across both sites.
- Recovery VMs in Azure to match the on-premises environment.
Recovery Objectives in Azure VM Scenarios
When planning for disasters or outages in the cloud, especially with Azure Virtual Machines (VMs), two key terms Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO) help you to decide how prepared you are:
Recovery Time Objective (RTO)
RTO is the maximum acceptable duration to restore services after an incident. In Azure we can say Azure Site Recovery (ASR) facilitates automated failover and continuous replication, supporting low RTO by ensuring rapid workload restoration.
Example: If an application has an RTO of one hour, its disaster recovery plan must enable restoration within that timeframe.
Recovery Point Objective (RPO)
RPO defines the maximum acceptable data loss measured in time. In Azure context Azure Backup allows for customizable backup schedules, helping achieve low RPO with frequent backups.
Example: An RPO of 10 minutes means no more than 10 minutes of data can be lost.
Setting Up Backup and Disaster Recovery Strategies for Azure VMs
Step 1: Sign in to the Azure Portal and Enter the credentials to log in.
Step 2: Create a Recovery Services vault by using the Azure portal search bar, type "Recovery Services vaults". Click on "Recovery Services vaults" in the results. Click "Create" to start the vault creation process
Step 3: Configure the Recovery Services vault and Choose the type of subscription and resource group. Name your vault and Select the region for your vault. Click "Review + create", then "Create"
Step 4: Set up VM backup by using the vault, click "Backup" under "Getting started". For "Where is your workload running?", choose "Azure". For "What do you want to backup?", select "Virtual machine"
Step 5: Create a backup policy by using the Click "Create a new policy". Set backup frequency, retention range, and other parameters
and name the policy and click "OK"
Step 6: Select VMs to backup and choose the VMs you want to backup. Then Click "Enable backup".
Step 7: Configure Azure Site Recovery (for disaster recovery). In your Recovery Services vault, click "Site Recovery" and click "Enable Site Recovery". Follow the wizard to set up replication for your VMs
Step 8: Create a recovery plan by using in Site Recovery, click "Recovery Plans" then "Create". Name your plan and select source and target locations. Add VMs to the plan and configure recovery settings
Step 9: Test your backup and recovery. For backup, select a VM and click "Backup now". For disaster recovery, run a test failover of your recovery plan
Step 10: Monitor and maintain. Regularly check the "Backup Jobs" and "Site Recovery Jobs" in your vault. Review alerts and resolve any issues promptly
Advantages of Backup and Disaster Recovery Strategies for Azure VMs
There are several benefits we have to opt the for the Backup and Disaster Recovery Strategies. Following table illustrates some main key benefits of using the same:
Benefit | Description |
|---|
Data Protection | Safeguards critical data against accidental deletion, corruption, or hardware failures. |
|---|
Business Continuity | Ensures minimal downtime and continuous operation of essential services during disasters. |
|---|
Compliance | Helps meet regulatory requirements for data retention and disaster recovery. |
|---|
Cost-Effective | Eliminates the need for secondary physical data centers, reducing infrastructure costs. |
|---|
Scalability | Easily scales to accommodate growing data volumes and changing business needs. |
|---|
Geo-Redundancy | Offers the ability to store backups in geographically distant locations for added protection. |
|---|
Automated Backups | Provides scheduled, automatic backups, reducing manual effort and human error. |
|---|
Flexible Recovery Options | Allows for granular recovery of files, folders, or entire VMs as needed. |
|---|
Centralized Management | Offers a unified interface to manage backups and recovery across multiple VMs. |
|---|
Security | Provides encryption for data at rest and in transit, enhancing overall security. |
|---|
Disadvantages of Backup and Disaster Recovery Strategies for Azure VMs
The following are the disadvantages of Backup and Disaster Recovery Strategies for Azure VMs:
- The backup and recovery processes may steal some resources from the VM itself, thereby impacting performance.
- Complex configurations often require specialized skills and hence add to management overhead.
- Backups and recoveries at scale incur a significant cost of data egress.
- Network latency will impact recovery time, especially on large VMs datasets.
- Some specific industry compliance may require more than what is offered by Azure out-of-the-box.
- Costs for backup storage add up quick, especially on those VMs under heavy change rates.
- Testing of disaster recovery scenarios can be time-consuming and possibly disruptive. Dependency management between interdependent VMs complicates the recovery processes.
Security for Backup and Disaster Recovery Data in Azure
Securing your backup and disaster recovery (DR) data in Azure is important to protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and ensure compliance. Let's try to understand how Azure helps you achieve this:
- Encryption: Data is encrypted at rest and in transit. You can use Microsoft-managed keys or customer-managed keys stored in Azure Key Vault.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assign granular permissions (Backup Contributor, Operator, Reader) to restrict who can perform backup and recovery operations.
- Managed Identities: Enable secure, credential-free authentication for Azure services involved in backup and recovery.
- Soft Delete: Protect against accidental backup deletions.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adds security for accessing backup data.
- Alerts and Monitoring: Configure to detect failures or suspicious activity promptly.
Cost Optimization Tips for Backup and DR in Azure
The following are some cost optimization tips for using Backup and DR in Azure:
- Use Locally Redundant Storage (LRS) when geo-redundancy (GRS) is not required to save costs.
- Implement Lifecycle Management to automatically delete old backups.
- Use Auto-Shutdown for disaster recovery VMs to reduce compute charges during off-hours.
- Regularly review usage and delete unnecessary backups.
Best Practices for Azure VM Backup and Disaster Recovery
The following are some key best practices for Azure VM Backup and Disaster Recovery, explained in simple terms:
- Test failovers regularly to ensure your recovery plan works.
- Tag backup resources for cost tracking.
- Enable Soft Delete for extra protection.
- Implement RBAC to restrict backup access.
- Monitor backup health and recovery points continuously.
Conclusion
Backup and disaster recovery strategies for Azure VMs are important to protect your data and keep your business running smoothly during unexpected problems. Azure makes it easy to back up your virtual machines regularly and quickly recover them if something goes wrong. These strategies help you save money, meet compliance rules, and handle growing data without stress.
It is important to consider your specific needs, such as how important your data is, your budget, and the skills required to manage backups and recovery. While there can be challenges like costs and complexity, having a solid backup and disaster recovery plan keep your business safe from downtime and data loss.
Explore
DevOps Basics
Version Control
CI & CD
Containerization
Orchestration
Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Monitoring and Logging
Security in DevOps