Difference between Flux and MVC
Last Updated :
12 Dec, 2023
In this article, we will see the difference between Flux vs MVC with the working code examples.
1. Flux:
Flux was created by facebook and was initially used by Facebook for building client-side web applications. The Flux application has 3 major parts the dispatcher, the store, and the view.
- The Store: we can think of the Store as a state manager, and it can change the store by listening to actions. It notifies the views to update.
- The View: It renders the user interface and handles user interaction. Container views listen for store changes.
- The dispatcher: It broadcasts actions to all registered stores.
Advantages of using Flux:
- Flux manages complicated interactions between data resources.
- Flux has a unidirectional data flow. Which means it is easier to manage the data flow.
Some popular implementations of flux are Redux, Flummox, and Fluxxor.
Steps to create React Application And Installing Module:
Step 1: Create a React application using the following command:
npx create-react-app foldername
Step 2: After creating your project folder i.e. foldername, move to it using the following command:
cd foldername
Step 3: After creating the ReactJS application, Install the required module using the following command:
npm install redux react-redux
Project Structure:

The updated dependencies in package.json file will look like:
"dependencies": {
"react": "^18.2.0",
"react-dom": "^18.2.0",
"react-redux": "^8.1.3",
"react-scripts": "5.0.1",
"web-vitals": "^2.1.4",
}
Example: This will received all the data passed down by the store in src/index.js file and perform various actions. In this case, we call counter reducer and isLogged reducer using increment, decrement, signing, and logoff actions.
JavaScript
import React from "react";
import './App.css';
import {useSelector,useDispatch} from "react-redux";
import increment,{decrement,signin,logoff} from "./actions";
function App() {
const counter=useSelector(state=>state.counter);
const isLogged=useSelector(state=>state.isLogged);
const dispatch = useDispatch();
function incr(){
dispatch(increment());
}
function dcr(){
dispatch(decrement());
}
function sin(){
dispatch(signin());
}
function sout(){
dispatch(logoff());
}
return (
<div className="App">
<h1>Hello {counter}</h1>
<button onClick={incr}>+</button>
<button onClick={dcr}>-</button>
{isLogged?<h3>Display only if the user is logged</h3>:<h3>User is not logged in</h3>}
{!isLogged?<button onClick={sin}>Login</button>:<button onClick={sout}>Log out</button>}
</div>
);
}
export default App;
src/actions/index.js:
const increment=()=>{
return{
type:"INCREMENT",
}
}
export default increment
const decrement=()=>{
return{
type:"DECREMENT",
}
}
const signin=()=>{
return{
type:"SIGN_IN",
}
}
const logoff=()=>{
return{
type:"LOG_OFF",
}
}
export {decrement,signin,logoff};
//src/index.js
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import './index.css';
import App from './App';
import reportWebVitals from './reportWebVitals';
import {createStore} from "redux";
import allReducers from './reducers';
import {Provider} from "react-redux";
//Creating store
const store=createStore(
allReducers,
window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__ && window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__());
ReactDOM.render(
<React.StrictMode>
//Wrapping our entire app inside the provider so that we can access the store
//from anywhere in our app.
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>
</React.StrictMode>,
document.getElementById('root')
);
// If you want to start measuring performance in your app, pass a function
// to log results (for example: reportWebVitals(console.log))
// or send to an analytics endpoint. Learn more: https://bit.ly/CRA-vitals
reportWebVitals();
//src/reducers/index.js
import counterReducer from "./counter";
import loggedReducer from "./isLogged";
import {combineReducers} from "redux";
const allReducers=combineReducers({
counter:counterReducer,
isLogged:loggedReducer,
});
export default allReducers;
const loggedReducer=(state=false,action)=>{
switch(action.type){
case "SIGN_IN":
return true;
case "LOG_OFF":
return false;
default:
return false;
}
}
//counter.js
const counterReducer=(state=0,action)=>{
switch(action.type){
case "INCREMENT":
return state+1;
case "DECREMENT":
return state-1;
default:
return state;
}
}
export default counterReducer;
Step 4: To get the react server up and running use the following command
npm start
Output:

2. MVC:
The MVC is the first web architecture introduced by Trygve Reenskaug in 1979 to build the user interface. The MVC is an acronym for Model View Controller.
- Model: It is a backend that includes all the data logic.
- View: View is basically the frontend or graphical user interface of the application.
- Controller: The brains of the application that controls how data is displayed.
Creating React Application And Installing Module:
Step 1: Create a React application using the following command:
npx create-react-app foldername
Step 2: After creating your project folder i.e. foldername, move to it using the following command:
cd foldername
Step 3: After creating the ReactJS application, Install the required module using the following command:
npm install redux react-redux
Project Structure:

The updated dependencies in package.json file will look like:
"dependencies": {
"react": "^18.2.0",
"react-dom": "^18.2.0",
"react-redux": "^8.1.3",
"react-scripts": "5.0.1",
"web-vitals": "^2.1.4",
}
Example: Below is the code example of the MVC write the below code into app.jsx, code.jsx and view.jsx.
JavaScript
import "./styles.css";
import Code from "./Code"
export default function App() {
return (
<div className="App">
<h1>Hello User</h1>
<h2>Lets see MVC in act</h2>
<Code />
</div>
);
//Code.jsx
import React,{useState} from 'react';
import View from "./View";
function Code(){
const[toggle,setToggle]=useState(false);
function handleClickTrue(){
setToggle(true);
}
function handleClickFalse(){
setToggle(false);
}
return(
<div>
{toggle&&<h1>Hello world</h1>}
//Passing handleClickTrue and handleCLickFalse functions as props to View.
<View isTrue={handleClickTrue} isFalse={handleClickFalse}/>
</div>
);
}
export default Code
//View.jsx
import React from 'react';
function View({isTrue,isFalse}){
return(
<div>
<button onClick={isTrue}>Render Hello World</button>
<button onClick={isFalse}>Remove Hello World </button>
</div>
);
}
export default View
Step 4: To get the react server up and running use the following command
npm start
Output:

Difference between Flux and MVC:
Flux
| MVC
|
| Flux application architecture is designed to build client-side web apps. | MVC application architecture is designed for developing User Interfaces. |
Flux architecture has these main components:

| MVC architecture has these main components:
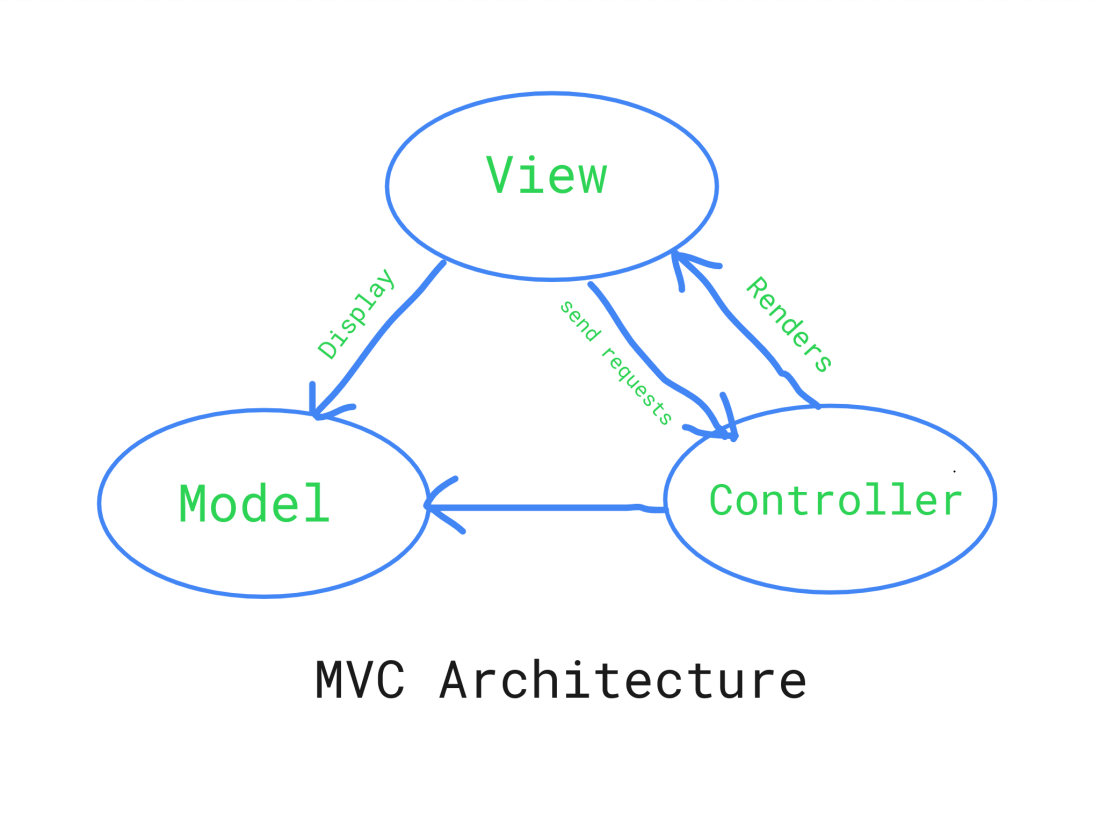
|
| In the flux the data flow direction is Unidirectional. | In the MVC the data flow direction is Bidirectional |
| There is Multiple Store in Flux. | There is no concept of Store in MVC. |
| In Flux the Store handles all the logic | In MVC the Controller handles the entire logic. |
| It supports client-side frameworks. | It supports both client-side and server-side frameworks. |
| It supports front-end frameworks like React, AngularJS, Vue.js. | It supports both front-end and back-end frameworks. |
Similar Reads
Differences between Web API and MVC
In this article, we will see what is Web API & MVC, their features & components, along with knowing their advantages & disadvantages, finally, will see the difference between them.The Model View Controller (MVC) is part of an architecture pattern that separates the application into 3 maj
5 min read
Difference between Falcon and Flask
The choice between Falcon and Flask is determined by your specific project requirements. Falcon is an excellent choice for developing high-performance APIs, particularly in situations where low latency and Async support are critical. Flask, on the other hand, is a more adaptable and beginner-friendl
5 min read
Difference between GWT and React
GWT (Google Web Toolkit ) is a development toolkit that compiles Java code into JavaScript for building the web applications, while React is a JavaScript library used to create modern, component-based user interfaces directly in the browsers.GWTGWT is a development toolkit for building and optimizin
2 min read
Difference between Maven and Ant
1. Maven :Maven is a powerful project management tool based on the Project Object Model. It helps in managing project builds, documentation, dependency, releases, etc.2. Ant :Ant is a command-line toolbox without any coding conventions or project structures, making it flexible and more manageable to
2 min read
Difference between Flow and TypeScript
1. Flow : Flow is developed and maintained by Facebook. It is a static type checker, designed to quickly find errors in JavaScript applications. Nothing more, nothing less. It's not a compiler, but a checker. It can work without any type of annotations and it is very good at inferring types. To enab
2 min read
Difference between MERCURIAL and GIT
Version control systems (VCS) are important tools in modern software development, allowing teams to track changes, collaborate efficiently, and maintain project history. Among the most popular VCS tools are Mercurial and Git. Both are distributed version control systems, but they have distinct featu
4 min read
Difference between ReactJS and Vue.js
ReactJS: ReactJS is an open-source JavaScript library created by Facebook which is used to deal with the view layer for both Web and Mobile applications. It can be provided on the server-side along with working on the client-side. Features of ReactJS: Scalability: It is reasonable for enormous scale
2 min read
Difference Between Struts and Spring MVC
When developing Java-based web applications, choosing between Struts and Spring MVC is crucial for ensuring scalability and maintainability. Both frameworks follow the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture, but they differ in their approach and flexibility. Struts, an older and once-dominant fram
5 min read
Difference Between JSON and AJAX
AJAXAjax is an acronym for Asynchronous Javascript and XML. It is used to communicate with the server without refreshing the web page and thus increasing the user experience and better performance. There are two types of requests synchronous as well as asynchronous. Synchronous requests are the one
5 min read
Difference between LAMP, MAMP and WAMP Stack
A web stack, also known as a web application stack is an assembly of software tools used in the development of online pages and web apps. An operating system, web server, database, and script interpreter are usually included. The web stacks such as LAMP, WAMP, and MAMP, which are mostly differentiat
6 min read