Binary Search is a searching algorithm that operates on a sorted or monotonic search space, repeatedly dividing it into halves to find a target value or optimal answer in logarithmic time O(log N).
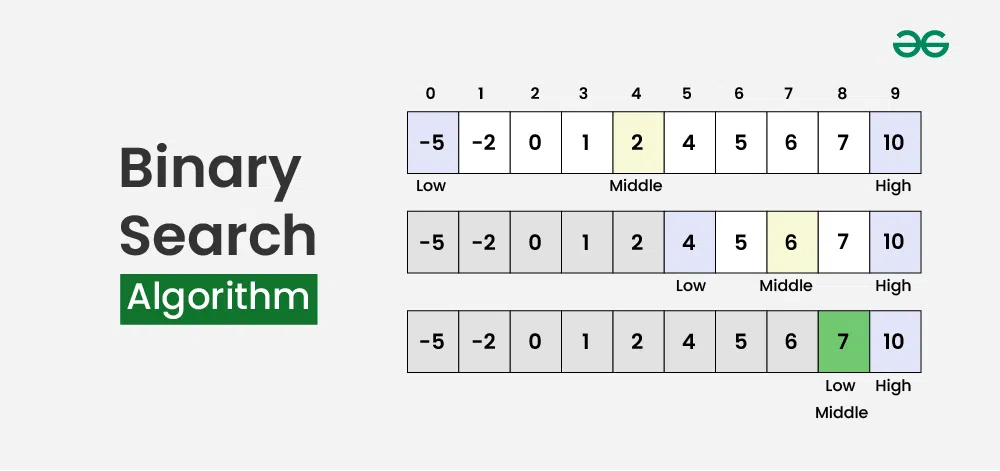 Binary Search Algorithm
Binary Search AlgorithmConditions to apply Binary Search Algorithm in a Data Structure
To apply Binary Search algorithm:
- The data structure must be sorted.
- Access to any element of the data structure should take constant time.
Binary Search Algorithm
Below is the step-by-step algorithm for Binary Search:
- Divide the search space into two halves by finding the middle index "mid".
- Compare the middle element of the search space with the key.
- If the key is found at middle element, the process is terminated.
- If the key is not found at middle element, choose which half will be used as the next search space.
-> If the key is smaller than the middle element, then the left side is used for next search.
-> If the key is larger than the middle element, then the right side is used for next search. - This process is continued until the key is found or the total search space is exhausted.
How does Binary Search Algorithm work?
To understand the working of binary search, consider the following illustration:
Consider an array arr[] = {2, 5, 8, 12, 16, 23, 38, 56, 72, 91}, and the target = 23.
How to Implement Binary Search Algorithm?
The Binary Search Algorithm can be implemented in the following two ways
- Iterative Binary Search Algorithm
- Recursive Binary Search Algorithm
Iterative Binary Search Algorithm: O(log n) Time and O(1) Space
Here we use a while loop to continue the process of comparing the key and splitting the search space in two halves.
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int binarySearch(vector<int> &arr, int x) {
int low = 0;
int high = arr.size() - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
// Check if x is present at mid
if (arr[mid] == x)
return mid;
// If x greater, ignore left half
if (arr[mid] < x)
low = mid + 1;
// If x is smaller, ignore right half
else
high = mid - 1;
}
// If we reach here, then element was not present
return -1;
}
int main() {
vector<int> arr = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int x = 10;
int result = binarySearch(arr, x);
if(result == -1) cout << "Element is not present in array";
else cout << "Element is present at index " << result;
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int binarySearch(int arr[], int n, int x) {
int low = 0;
int high = n-1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
// Check if x is present at mid
if (arr[mid] == x)
return mid;
// If x greater, ignore left half
if (arr[mid] < x)
low = mid + 1;
// If x is smaller, ignore right half
else
high = mid - 1;
}
// If we reach here, then element was not present
return -1;
}
int main() {
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int x = 10;
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int result = binarySearch(arr, n, x);
if(result == -1) printf("Element is not present in array");
else printf("Element is present at index %d",result);
}
class GFG {
static int binarySearch(int arr[], int x) {
int low = 0, high = arr.length - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
// Check if x is present at mid
if (arr[mid] == x)
return mid;
// If x greater, ignore left half
if (arr[mid] < x)
low = mid + 1;
// If x is smaller, ignore right half
else
high = mid - 1;
}
// If we reach here, then element was
// not present
return -1;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int x = 10;
int result = binarySearch(arr, x);
if (result == -1)
System.out.println(
"Element is not present in array");
else
System.out.println("Element is present at "
+ "index " + result);
}
}
def binarySearch(arr, x):
low = 0
high = len(arr) - 1
while low <= high:
mid = low + (high - low) // 2
# Check if x is present at mid
if arr[mid] == x:
return mid
# If x is greater, ignore left half
elif arr[mid] < x:
low = mid + 1
# If x is smaller, ignore right half
else:
high = mid - 1
# If we reach here, then the element
# was not present
return -1
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [2, 3, 4, 10, 40]
x = 10
result = binarySearch(arr, x)
if result != -1:
print("Element is present at index", result)
else:
print("Element is not present in array")
using System;
class GFG {
static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int x) {
int low = 0, high = arr.Length - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
// Check if x is present at mid
if (arr[mid] == x)
return mid;
// If x greater, ignore left half
if (arr[mid] < x)
low = mid + 1;
// If x is smaller, ignore right half
else
high = mid - 1;
}
// If we reach here, then element was
// not present
return -1;
}
public static void Main() {
int[] arr = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int n = arr.Length;
int x = 10;
int result = binarySearch(arr, x);
if (result == -1)
Console.WriteLine(
"Element is not present in array");
else
Console.WriteLine("Element is present at "
+ "index " + result);
}
}
function binarySearch(arr, x) {
let low = 0;
let high = arr.length - 1;
let mid;
while (high >= low) {
mid = low + Math.floor((high - low) / 2);
// If the element is present at the middle
// itself
if (arr[mid] == x)
return mid;
// If element is smaller than mid, then
// it can only be present in left subarray
if (arr[mid] > x)
high = mid - 1;
// Else the element can only be present
// in right subarray
else
low = mid + 1;
}
// We reach here when element is not
// present in array
return -1;
}
// Driver Code
arr = new Array(2, 3, 4, 10, 40);
x = 10;
result = binarySearch(arr, x);
if (result == -1)
console.log("Element is not present in array")
else
console.log("Element is present at index "
+ result);
<?php
function binarySearch($arr, $x) {
$low = 0;
$high = sizeof($arr) - 1;
while ($low <= $high) {
$mid = $low + ($high - $low) / 2;
// Check if x is present at mid
if ($arr[$mid] == $x)
return floor($mid);
// If x greater, ignore
// left half
if ($arr[$mid] < $x)
$low = $mid + 1;
// If x is smaller,
// ignore right half
else
$high = $mid - 1;
}
// If we reach here, then
// element was not present
return -1;
}
// Driver Code
$arr = array(2, 3, 4, 10, 40);
$x = 10;
$result = binarySearch($arr, $x);
if(($result == -1))
echo "Element is not present in array";
else
echo "Element is present at index ",
$result;
?>
OutputElement is present at index 3
Recursive Binary Search Algorithm:
Create a recursive function and compare the mid of the search space with the key. And based on the result either return the index where the key is found or call the recursive function for the next search space.
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// A recursive binary search function. It returns
// location of x in given array arr[low..high] is present,
// otherwise -1
int binarySearch(vector<int> &arr, int low, int high, int x) {
if (high >= low) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
// If the element is present at the middle
// itself
if (arr[mid] == x)
return mid;
// If element is smaller than mid, then
// it can only be present in left subarray
if (arr[mid] > x)
return binarySearch(arr, low, mid - 1, x);
// Else the element can only be present
// in right subarray
return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, high, x);
}
return -1;
}
int main() {
vector<int> arr = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int query = 10;
int n = arr.size();
int result = binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, query);
if (result == -1) cout << "Element is not present in array";
else cout << "Element is present at index " << result;
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
// A recursive binary search function. It returns
// location of x in given array arr[low..high] is present,
// otherwise -1
int binarySearch(int arr[], int low, int high, int x) {
if (high >= low) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
// If the element is present at the middle
// itself
if (arr[mid] == x)
return mid;
// If element is smaller than mid, then
// it can only be present in left subarray
if (arr[mid] > x)
return binarySearch(arr, low, mid - 1, x);
// Else the element can only be present
// in right subarray
return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, high, x);
}
// We reach here when element is not
// present in array
return -1;
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int x = 10;
int result = binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);
if (result == -1) printf("Element is not present in array");
else printf("Element is present at index %d", result);
return 0;
}
class GFG {
// A recursive binary search function. It returns
// location of x in given array arr[low..high] is present,
// otherwise -1
static int binarySearch(int arr[], int low, int high, int x) {
if (high >= low) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
// If the element is present at the
// middle itself
if (arr[mid] == x)
return mid;
// If element is smaller than mid, then
// it can only be present in left subarray
if (arr[mid] > x)
return binarySearch(arr, low, mid - 1, x);
// Else the element can only be present
// in right subarray
return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, high, x);
}
// We reach here when element is not present
// in array
return -1;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int n = arr.length;
int x = 10;
int result = binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);
if (result == -1)
System.out.println(
"Element is not present in array");
else
System.out.println(
"Element is present at index " + result);
}
}
# A recursive binary search function. It returns
# location of x in given array arr[low..high] is present,
# otherwise -1
def binarySearch(arr, low, high, x):
# Check base case
if high >= low:
mid = low + (high - low) // 2
# If element is present at the middle itself
if arr[mid] == x:
return mid
# If element is smaller than mid, then it
# can only be present in left subarray
elif arr[mid] > x:
return binarySearch(arr, low, mid-1, x)
# Else the element can only be present
# in right subarray
else:
return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, high, x)
# Element is not present in the array
else:
return -1
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [2, 3, 4, 10, 40]
x = 10
result = binarySearch(arr, 0, len(arr)-1, x)
if result != -1:
print("Element is present at index", result)
else:
print("Element is not present in array")
using System;
class GFG {
// Returns index of x if it is present in
// arr[low..high], else return -1
static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int low, int high, int x) {
if (high >= low) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
// If the element is present at the
// middle itself
if (arr[mid] == x)
return mid;
// If element is smaller than mid, then
// it can only be present in left subarray
if (arr[mid] > x)
return binarySearch(arr, low, mid - 1, x);
// Else the element can only be present
// in right subarray
return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, high, x);
}
// We reach here when element is not present
// in array
return -1;
}
public static void Main() {
int[] arr = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int n = arr.Length;
int x = 10;
int result = binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);
if (result == -1)
Console.WriteLine(
"Element is not present in arrau");
else
Console.WriteLine("Element is present at index "
+ result);
}
}
// A recursive binary search function. It returns
// location of x in given array arr[low..high] is present,
// otherwise -1
function binarySearch(arr, low, high, x) {
if (high >= low) {
let mid = low + Math.floor((high - low) / 2);
// If the element is present at the middle
// itself
if (arr[mid] == x)
return mid;
// If element is smaller than mid, then
// it can only be present in left subarray
if (arr[mid] > x)
return binarySearch(arr, low, mid - 1, x);
// Else the element can only be present
// in right subarray
return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, high, x);
}
// We reach here when element is not
// present in array
return -1;
}
// Driver Code
let arr = [ 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 ];
let x = 10;
let n = arr.length
let result = binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);
if (result == -1)
console.log("Element is not present in array");
else
console.log("Element is present at index " + result);
<?php
// A recursive binary search function. It returns
// location of x in given array arr[low..high] is present,
// otherwise -1
function binarySearch($arr, $low, $high, $x) {
if ($high >= $low) {
$mid = ceil($low + ($high - $low) / 2);
// If the element is present
// at the middle itself
if ($arr[$mid] == $x)
return floor($mid);
// If element is smaller than
// mid, then it can only be
// present in left subarray
if ($arr[$mid] > $x)
return binarySearch($arr, $low,
$mid - 1, $x);
// Else the element can only
// be present in right subarray
return binarySearch($arr, $mid + 1,
$high, $x);
}
// We reach here when element
// is not present in array
return -1;
}
$arr = array(2, 3, 4, 10, 40);
$n = count($arr);
$x = 10;
$result = binarySearch($arr, 0, $n - 1, $x);
if(($result == -1))
echo "Element is not present in array";
else
echo "Element is present at index ",
$result;
?>
OutputElement is present at index 3
Complexity Analysis of Binary Search Algorithm
- Time Complexity:
-> Best Case: O(1)
-> Average Case: O(log N)
-> Worst Case: O(log N) - Auxiliary Space: O(1), If the recursive call stack is considered then the auxiliary space will be O(log N).
Please refer Time and Space Complexity Analysis of Binary Search for more details.
Binary Search Visualizer
Applications of Binary Search Algorithm
- Searching in sorted arrays
- Finding first/last occurrence or closest match in a sorted array
- Database indexing — Used in B-trees and similar structures for fast data lookup.
- Debugging in version control — Tools like
git bisect use binary search to isolate faulty commits. - Network routing & IP lookup — Efficiently find routing entries in tables sorted by address ranges.
- File systems & libraries — Fast search through sorted directories or symbol tables.
- Gaming/graphics — Collision detection or ray tracing using sorted spatial data.
- Machine learning tuning — Efficient hyperparameter search (e.g., learning rate, thresholds).
- Optimization problems & competitive programming — Solve boundary-value challenges by narrowing search space.
- Advanced data structures — Binary search trees, self-balancing BSTs, and fractional cascading rely on search logic.
Iterative Binary Search Tree
Problems Based on Binary Search
Related Links
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem