Diameter of a Binary Tree
Last Updated :
08 Oct, 2025
Given the root of a binary tree, Find the diameter of the tree. The diameter of a tree is defined as the number of edges on the longest path between any two nodes.
Examples:
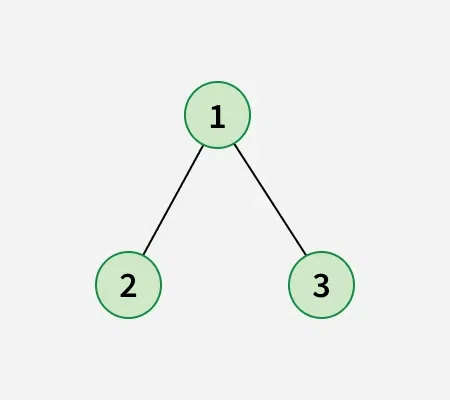
Input:

Output: 2
Explanation: The longest path has 2 edges (from node 1 to node 3).
Input:
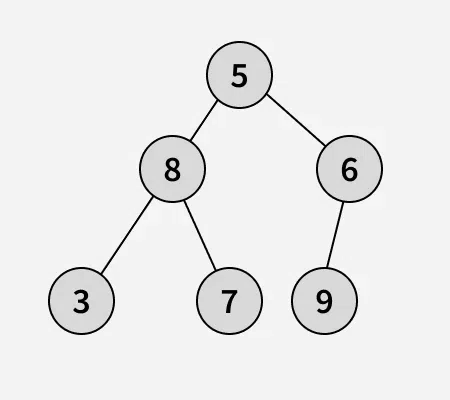
Output: 4
Explanation: The longest path has 4 edges (from node 3 to node 9).

[Naive Approach] By Calculating Height For Each Node - O(n2) Time and O(h) Space
Intuition:
The diameter of a binary tree is the number of edges in the longest path between any two nodes. For any node, the longest path passing through it goes from the deepest leaf in its left subtree to the deepest leaf in its right subtree. The height of a subtree is the number of edges from the node to its deepest leaf. So, adding the left and right subtree heights gives the number of edges in the path through that node. The diameter of the tree is the maximum such sum across all nodes.
The idea is to recursively traverse the tree. For each node, find the height of left subtree and right subtree and maintain the maximum diameter (sum of height of left subtree + height of right subtree).
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
// Node Structure
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node *left, *right;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = nullptr;
right = nullptr;
}
};
// Function to compute the height of a tree.
int height(Node* root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
// If tree is not empty then height = 1 +
// max of left height and right heights
return 1 + max(height(root->left),
height(root->right));
}
// Function to get diameter of a binary tree
int diameter(Node* root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
// Get the height of left and right
// sub-trees
int lheight = height(root->left);
int rheight = height(root->right);
// Get the diameter of left and right
// sub-trees
int ldiameter = diameter(root->left);
int rdiameter = diameter(root->right);
return max({lheight + rheight, ldiameter, rdiameter});
}
int main() {
// Constructed binary tree is
// 5
// / \
// 8 6
// / \ /
// 3 7 9
Node* root = new Node(5);
root->left = new Node(8);
root->right = new Node(6);
root->left->left = new Node(3);
root->left->right = new Node(7);
root->right->left = new Node(9);
cout << diameter(root) << endl;
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Node Structure
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* left;
struct Node* right;
};
// Function to compute the height of a tree.
int height(struct Node* root) {
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
// If tree is not empty then height = 1 +
// max of left height and right heights
int leftHeight = height(root->left);
int rightHeight = height(root->right);
return 1 +
(leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight : rightHeight);
}
// Function to get diameter of a binary tree
int diameter(struct Node* root) {
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
// Get the height of left and right sub-trees
int lheight = height(root->left);
int rheight = height(root->right);
// Get the diameter of left and right sub-trees
int ldiameter = diameter(root->left);
int rdiameter = diameter(root->right);
// Diameter of current subtree
int curr = lheight+rheight;
if (ldiameter > rdiameter && ldiameter > curr)
return ldiameter;
else if (rdiameter > ldiameter && rdiameter > curr)
return rdiameter;
return curr;
}
struct Node* createNode(int x) {
struct Node* newNode =
(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->data = x;
newNode->left = NULL;
newNode->right = NULL;
return newNode;
}
int main() {
// Constructed binary tree is
// 5
// / \
// 8 6
// / \ /
// 3 7 9
struct Node* root = createNode(5);
root->left = createNode(8);
root->right = createNode(6);
root->left->left = createNode(3);
root->left->right = createNode(7);
root->right->left = createNode(9);
printf("%d\n", diameter(root));
return 0;
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
// Node Structure
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
class GFG {
// Function to compute the height of a tree.
static int height(Node root) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
// If tree is not empty then height = 1 +
// max of left height and right heights
return 1 + Math.max(height(root.left), height(root.right));
}
// Function to get diameter of a binary tree
static int diameter(Node root) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Get the height of left and right sub-trees
int lheight = height(root.left);
int rheight = height(root.right);
// Get the diameter of left and right sub-trees
int ldiameter = diameter(root.left);
int rdiameter = diameter(root.right);
return Math.max(lheight + rheight,
Math.max(ldiameter, rdiameter));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Constructed binary tree is
// 5
// / \
// 8 6
// / \ /
// 3 7 9
Node root = new Node(5);
root.left = new Node(8);
root.right = new Node(6);
root.left.left = new Node(3);
root.left.right = new Node(7);
root.right.left = new Node(9);
System.out.println(diameter(root));
}
}
# Node Structure
class Node:
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Function to compute the height
# of a tree
def height(root):
if root is None:
return 0
# If tree is not empty then height = 1 +
# max of left height and right heights
return 1 + max(height(root.left), height(root.right))
# Function to get diameter of a binary tree
def diameter(root):
if root is None:
return 0
# Get the height of left and
# right sub-trees
lheight = height(root.left)
rheight = height(root.right)
# Get the diameter of left and
# right sub-trees
ldiameter = diameter(root.left)
rdiameter = diameter(root.right)
return max(lheight + rheight, ldiameter, rdiameter)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Constructed binary tree is
# 5
# / \
# 8 6
# / \ /
# 3 7 9
root = Node(5)
root.left = Node(8)
root.right = Node(6)
root.left.left = Node(3)
root.left.right = Node(7)
root.right.left = Node(9)
print(diameter(root))
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// Node Structure
class Node {
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
class GFG {
// Function to compute the
// height of a tree
static int height(Node root) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
// If tree is not empty then height = 1 +
// max of left height and right heights
return 1 + Math.Max(height(root.left), height(root.right));
}
// Function to get diameter of
// a binary tree
static int diameter(Node root) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Get the height of left and
// right sub-trees
int lheight = height(root.left);
int rheight = height(root.right);
// Get the diameter of left and right sub-trees
int ldiameter = diameter(root.left);
int rdiameter = diameter(root.right);
return Math.Max(lheight + rheight,
Math.Max(ldiameter, rdiameter));
}
static void Main(string[] args) {
// Constructed binary tree is
// 5
// / \
// 8 6
// / \ /
// 3 7 9
Node root = new Node(5);
root.left = new Node(8);
root.right = new Node(6);
root.left.left = new Node(3);
root.left.right = new Node(7);
root.right.left = new Node(9);
Console.WriteLine(diameter(root));
}
}
// Node Structure
class Node {
constructor(x) {
this.data = x;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
// Function to compute the height of a tree.
function height(root) {
if (root === null)
return 0;
// If tree is not empty then height = 1 +
// max of left height and right heights
return 1 + Math.max(height(root.left), height(root.right));
}
// Function to get diameter of a binary tree
function diameter(root) {
if (root === null)
return 0;
// Get the height of left and right sub-trees
const lheight = height(root.left);
const rheight = height(root.right);
// Get the diameter of left and right sub-trees
const ldiameter = diameter(root.left);
const rdiameter = diameter(root.right);
return Math.max(lheight + rheight, ldiameter, rdiameter);
}
// Driver Code
// Constructed binary tree is
// 5
// / \
// 8 6
// / \ /
// 3 7 9
let root = new Node(5);
root.left = new Node(8);
root.right = new Node(6);
root.left.left = new Node(3);
root.left.right = new Node(7);
root.right.left = new Node(9);
console.log(diameter(root));
[Expected Approach] Using Single Traversal - O(n) Time and O(h) Space
The idea is to calculate the diameter efficiently without recomputing the heights of the left and right subtrees for every node. Using recursion, we compute both the height and the diameter in a single traversal. For each node, the longest path passing through it is the sum of the heights of its left and right subtrees. Among all the subtrees, maintain the maximum diameter to represent the longest path in the entire tree.
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Node Structure
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = nullptr;
right = nullptr;
}
};
// Global variable to store the maximum diameter
int maxDiameter = 0;
int diameterRecur(Node* root) {
if (!root)
return 0;
// Find the height of left and right subtree
int lHeight = diameterRecur(root->left);
int rHeight = diameterRecur(root->right);
// Update the global max diameter if this node gives a longer path
if (lHeight + rHeight > maxDiameter)
maxDiameter = lHeight + rHeight;
// Return height of current subtree
return 1 + max(lHeight, rHeight);
}
// Function to get diameter of a binary tree
int diameter(Node* root) {
maxDiameter = 0;
diameterRecur(root);
return maxDiameter;
}
int main() {
// Constructed binary tree:
// 5
// / \
// 8 6
// / \ /
// 3 7 9
Node* root = new Node(5);
root->left = new Node(8);
root->right = new Node(6);
root->left->left = new Node(3);
root->left->right = new Node(7);
root->right->left = new Node(9);
cout << diameter(root) << endl;
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Node Structure
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* left;
struct Node* right;
};
// Function to create a new Node
struct Node* newNode(int x) {
struct Node* node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
node->data = x;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
int max(int a, int b) {
return a > b ? a : b;
}
// Global variable to store the maximum diameter
int maxDiameter = 0;
int diameterRecur(struct Node* root) {
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
// Find the height of left and right subtree
int lHeight = diameterRecur(root->left);
int rHeight = diameterRecur(root->right);
// Update the global max diameter if this node gives a longer path
if (lHeight + rHeight > maxDiameter)
maxDiameter = lHeight + rHeight;
// Return height of current subtree
return 1 + max(lHeight, rHeight);
}
// Function to get diameter of a binary tree
int diameter(struct Node* root) {
maxDiameter = 0;
diameterRecur(root);
return maxDiameter;
}
int main() {
// Constructed binary tree:
// 5
// / \
// 8 6
// / \ /
// 3 7 9
struct Node* root = newNode(5);
root->left = newNode(8);
root->right = newNode(6);
root->left->left = newNode(3);
root->left->right = newNode(7);
root->right->left = newNode(9);
printf("%d\n", diameter(root));
return 0;
}
// Node Structure
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
class GFG {
// Static variable to store maximum diameter
static int maxDiameter = 0;
// Recursive function to calculate height and update diameter
static int diameterRecur(Node root) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Find the height of left and right subtree
int lHeight = diameterRecur(root.left);
int rHeight = diameterRecur(root.right);
// Update the global max diameter if this node gives a longer path
if (lHeight + rHeight > maxDiameter)
maxDiameter = lHeight + rHeight;
// Return height of current subtree
return 1 + Math.max(lHeight, rHeight);
}
// Function to get diameter of a binary tree
static int diameter(Node root) {
maxDiameter = 0;
diameterRecur(root);
return maxDiameter;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Constructed binary tree:
// 5
// / \
// 8 6
// / \ /
// 3 7 9
Node root = new Node(5);
root.left = new Node(8);
root.right = new Node(6);
root.left.left = new Node(3);
root.left.right = new Node(7);
root.right.left = new Node(9);
System.out.println(diameter(root));
}
}
# Node Structure
class Node:
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Global variable to store the maximum diameter
maxDiameter = 0
# Recursive function to calculate height and update diameter
def diameterRecur(root):
global maxDiameter
if root is None:
return 0
# Find the height of left and right subtree
lHeight = diameterRecur(root.left)
rHeight = diameterRecur(root.right)
# Update the global max diameter if this node gives a longer path
maxDiameter = max(maxDiameter, lHeight + rHeight)
# Return height of current subtree
return 1 + max(lHeight, rHeight)
# Function to get diameter of a binary tree
def diameter(root):
global maxDiameter
maxDiameter = 0
diameterRecur(root)
return maxDiameter
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = Node(5)
root.left = Node(8)
root.right = Node(6)
root.left.left = Node(3)
root.left.right = Node(7)
root.right.left = Node(9)
print(diameter(root))
using System;
// Node Structure
class Node {
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
class GFG {
// global variable to store maximum diameter
static int maxDiameter = 0;
// Recursive function which finds the
// the diameter of the tree.
static int diameterRecur(Node root) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
// find the height of left and right subtree
int lHeight = diameterRecur(root.left);
int rHeight = diameterRecur(root.right);
// Check if diameter of root is greater
// than maxDiameter.
maxDiameter = Math.Max(maxDiameter, lHeight + rHeight);
// return the height of current subtree.
return 1 + Math.Max(lHeight, rHeight);
}
// Function to get diameter of a binary tree
static int diameter(Node root) {
maxDiameter = 0;
diameterRecur(root);
return maxDiameter;
}
static void Main(string[] args) {
// Constructed binary tree is
// 5
// / \
// 8 6
// / \ /
// 3 7 9
Node root = new Node(5);
root.left = new Node(8);
root.right = new Node(6);
root.left.left = new Node(3);
root.left.right = new Node(7);
root.right.left = new Node(9);
Console.WriteLine(diameter(root));
}
}
// Node Structure
class Node {
constructor(x) {
this.data = x;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
// global variable to store the maximum diameter
let maxDiameter = 0;
// Recursive function which finds
// the diameter of the tree.
function diameterRecur(root) {
if (root === null)
return 0;
// find the height of left and right subtree
let lHeight = diameterRecur(root.left);
let rHeight = diameterRecur(root.right);
// Check if diameter of root is greater
// than maxDiameter.
maxDiameter = Math.max(maxDiameter, lHeight + rHeight);
// return the height of current subtree.
return 1 + Math.max(lHeight, rHeight);
}
// Function to get diameter of a binary tree
function diameter(root) {
maxDiameter = 0;
diameterRecur(root);
return maxDiameter;
}
// Driver Code
// Constructed binary tree is
// 5
// / \
// 8 6
// / \ /
// 3 7 9
let root = new Node(5);
root.left = new Node(8);
root.right = new Node(6);
root.left.left = new Node(3);
root.left.right = new Node(7);
root.right.left = new Node(9);
console.log(diameter(root));
Related article:
Diameter of a Binary Tree.
Find the Diameter of a Binary Tree
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem