Find if there is a path between two vertices
Last Updated :
27 Oct, 2025
Given a graph represented by its adjacency list adj[][] and two vertices u and v, determine whether a path exists from vertex u to vertex v.
Examples:
Input: adj[][]= [[2, 3], [2], [0, 1], [0], [5], [4]], u = 0, v = 5

Output: false
Explanation: There is no path from vertex 1 to vertex 5.
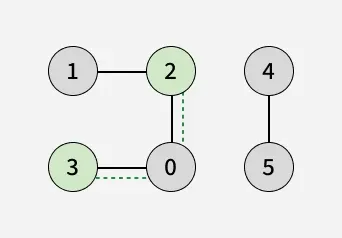
Input: adj[][]= [[2, 3], [2], [0, 1], [0], [5], [4]], u = 2, v= 3

Output: true
Explanation: We can reach vertex 3 from vertex 2 via vertex 0.
[Expected Approach - 1] Using DFS - O(V+E) Time and O(V+E) Auxiliary Space
The idea is to explore all the vertices reachable from the starting vertex u using the Depth First Search (DFS) algorithm. During the traversal, if the target vertex v is found, we can conclude that a path exists between u and v; otherwise, no path exists.
C++
//Driver Code Starts
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
//Driver Code Ends
// DFS to check if a path exists from curr to dest
bool dfs(int curr, int dest, vector<vector<int>>& adj, vector<bool>& visited) {
// already explored
if (visited[curr]) return false;
// destination reached
if (curr == dest) return true;
visited[curr] = true;
for (int neighbor : adj[curr]) {
if (!visited[neighbor] && dfs(neighbor, dest, adj, visited)) {
// path found
return true;
}
}
// no path found
return false;
}
// Function to check if a path exists between u and v
bool checkPath(vector<vector<int>>& adj, int u, int v) {
vector<bool> visited(adj.size(), false);
return dfs(u, v, adj, visited);
}
//Driver Code Starts
int main() {
vector<vector<int>> adj = {{2, 3},{2},{0, 1},{0},{5},{4}};
int u = 2, v = 3;
cout << (checkPath(adj, u, v) ? "true" : "false");
return 0;
}
//Driver Code Ends
//Driver Code Starts
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class GFG {
//Driver Code Ends
// DFS to check if path exists from curr to dest
static boolean dfs(int curr, int dest, ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj,
boolean[] visited) {
// already explored
if (visited[curr]) return false;
// destination reached
if (curr == dest) return true;
visited[curr] = true;
for (int neighbor : adj.get(curr)) {
if (!visited[neighbor] && dfs(neighbor, dest, adj, visited)) {
// path found
return true;
}
}
// no path found
return false;
}
// Function to check path between u and v
static boolean checkPath(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj, int u, int v) {
boolean[] visited = new boolean[adj.size()];
return dfs(u, v, adj, visited);
}
//Driver Code Starts
// Function to add undirected edge
static void addEdge(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj, int u, int v) {
adj.get(u).add(v);
adj.get(v).add(u);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int V = 6;
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
addEdge(adj, 0, 2);
addEdge(adj, 0, 3);
addEdge(adj, 1, 2);
addEdge(adj, 4, 5);
int u = 2, v = 3;
System.out.println(checkPath(adj, u, v) ? "true" : "false");
}
}
//Driver Code Ends
def dfs(curr, dest, adj, visited):
# already explored
if visited[curr]:
return False
# destination reached
if curr == dest:
return True
visited[curr] = True
for neighbor in adj[curr]:
if not visited[neighbor] and dfs(neighbor, dest, adj, visited):
# path found
return True
# no path found
return False
def checkPath(adj, u, v):
visited = [False] * len(adj)
return dfs(u, v, adj, visited)
#Driver Code Starts
if __name__ == "__main__":
adj = [[2, 3],[2],[0, 1],[0],[5],[4]]
u, v = 2, 3
print("true" if checkPath(adj, u, v) else "false")
#Driver Code Ends
//Driver Code Starts
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
//Driver Code Ends
// DFS to check if path exists from curr to dest
static bool dfs(int curr, int dest, List<List<int>> adj, bool[] visited)
{
// already explored
if (visited[curr]) return false;
// destination reached
if (curr == dest) return true;
visited[curr] = true;
foreach (int neighbor in adj[curr])
{
if (!visited[neighbor] && dfs(neighbor, dest, adj, visited))
{
// path found
return true;
}
}
// no path found
return false;
}
// Function to check path between u and v
static bool checkPath(List<List<int>> adj, int u, int v)
{
bool[] visited = new bool[adj.Count];
return dfs(u, v, adj, visited);
}
//Driver Code Starts
// Function to add undirected edge
static void addEdge(List<List<int>> adj, int u, int v)
{
adj[u].Add(v);
adj[v].Add(u);
}
static void Main()
{
int V = 6;
List<List<int>> adj = new List<List<int>>();
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) adj.Add(new List<int>());
addEdge(adj, 0, 2);
addEdge(adj, 0, 3);
addEdge(adj, 1, 2);
addEdge(adj, 4, 5);
int u = 2, v = 3;
Console.WriteLine(checkPath(adj, u, v) ? "true" : "false");
}
}
//Driver Code Ends
function dfs(curr, dest, adj, visited) {
// already explored
if (visited[curr]) return false;
// destination reached
if (curr === dest) return true;
visited[curr] = true;
for (let neighbor of adj[curr]) {
if (!visited[neighbor] && dfs(neighbor, dest, adj, visited)) {
// path found
return true;
}
}
// no path found
return false;
}
function checkPath(adj, u, v) {
let visited = new Array(adj.length).fill(false);
return dfs(u, v, adj, visited);
}
//Driver Code Starts
// Driver Code
const adj = [[2, 3],[2],[0, 1],[0],[5],[4]];
const u = 2, v = 3;
console.log(checkPath(adj, u, v) ? "true" : "false");
//Driver Code Ends
[Expected Approach - 2] Using BFS - O(V+E) Time and O(V) Auxiliary Space
The idea is to explore all the vertices reachable from the starting vertex u using the Breadth First Search (BFS) algorithm. During the traversal, if the target vertex v is encountered, we can conclude that a path exists between u and v; otherwise, no path exists.
C++
//Driver Code Starts
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
//Driver Code Ends
// BFS to check if a path exists from src to dest
bool bfs(int src, int dest, vector<vector<int>>& adj) {
vector<bool> visited(adj.size(), false);
queue<int> q;
visited[src] = true;
q.push(src);
while (!q.empty()) {
int curr = q.front();
q.pop();
// destination reached
if (curr == dest) return true;
// visit all unvisited neighbors
for (int neighbor : adj[curr]) {
if (!visited[neighbor]) {
visited[neighbor] = true;
q.push(neighbor);
}
}
}
// no path found
return false;
}
// Function to check if a path exists between u and v
bool checkPath(vector<vector<int>>& adj, int u, int v) {
return bfs(u, v, adj);
}
//Driver Code Starts
int main() {
vector<vector<int>> adj = {{2, 3},{2},{0, 1},{0},{5},{4}};
int u = 2, v = 3;
cout << (checkPath(adj, u, v) ? "true" : "false") << endl;
return 0;
}
//Driver Code Ends
//Driver Code Starts
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class GFG {
//Driver Code Ends
// BFS to check if a path exists from src to dest
static boolean bfs(int src, int dest, ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj) {
boolean[] visited = new boolean[adj.size()];
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
visited[src] = true;
q.offer(src);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
// remove the front vertex
int curr = q.poll();
// destination reached
if (curr == dest) return true;
// visit all unvisited neighbors
for (int neighbor : adj.get(curr)) {
if (!visited[neighbor]) {
visited[neighbor] = true;
q.offer(neighbor);
}
}
}
// no path found
return false;
}
// Function to check if a path exists between u and v
static boolean checkPath(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj, int u, int v) {
return bfs(u, v, adj);
}
//Driver Code Starts
// Function to add undirected edge
static void addEdge(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj, int u, int v) {
adj.get(u).add(v);
adj.get(v).add(u);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int V = 6;
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
addEdge(adj, 0, 2);
addEdge(adj, 0, 3);
addEdge(adj, 1, 2);
addEdge(adj, 4, 5);
int u = 2, v = 3;
System.out.println(checkPath(adj, u, v) ? "true" : "false");
}
}
//Driver Code Ends
#Driver Code Starts
from collections import deque
#Driver Code Ends
# BFS to check if a path exists from src to dest
def bfs(src, dest, adj):
visited = [False] * len(adj)
q = deque()
visited[src] = True
q.append(src)
while q:
curr = q.popleft()
# destination reached
if curr == dest:
return True
# visit all unvisited neighbors
for neighbor in adj[curr]:
if not visited[neighbor]:
visited[neighbor] = True
q.append(neighbor)
# no path found
return False
# Function to check if a path exists between u and v
def checkPath(adj, u, v):
return bfs(u, v, adj)
#Driver Code Starts
if __name__ == "__main__":
adj = [[2, 3],[2],[0, 1],[0],[5],[4]]
u, v = 2, 3
print("true" if checkPath(adj, u, v) else "false")
#Driver Code Ends
//Driver Code Starts
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
//Driver Code Ends
// BFS to check if a path exists from src to dest
static bool bfs(int src, int dest, List<List<int>> adj)
{
bool[] visited = new bool[adj.Count];
Queue<int> q = new Queue<int>();
visited[src] = true;
q.Enqueue(src);
while (q.Count > 0)
{
// remove the front vertex
int curr = q.Dequeue();
// destination reached
if (curr == dest) return true;
// visit all unvisited neighbors
foreach (int neighbor in adj[curr])
{
if (!visited[neighbor])
{
visited[neighbor] = true;
q.Enqueue(neighbor);
}
}
}
// no path found
return false;
}
// Function to check if a path exists between u and v
static bool checkPath(List<List<int>> adj, int u, int v)
{
return bfs(u, v, adj);
}
//Driver Code Starts
// Function to add undirected edge
static void addEdge(List<List<int>> adj, int u, int v)
{
adj[u].Add(v);
adj[v].Add(u);
}
static void Main()
{
int V = 6;
List<List<int>> adj = new List<List<int>>();
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
adj.Add(new List<int>());
addEdge(adj, 0, 2);
addEdge(adj, 0, 3);
addEdge(adj, 1, 2);
addEdge(adj, 4, 5);
int u = 2, v = 3;
Console.WriteLine(checkPath(adj, u, v) ? "true" : "false");
}
}
//Driver Code Ends
//Driver Code Starts
const Denque = require("denque");
//Driver Code Ends
// BFS to check if a path exists from src to dest
function bfs(adj, src, dest) {
const visited = new Array(adj.length).fill(false);
const q = new Denque();
visited[src] = true;
q.push(src);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
// remove the front vertex
const curr = q.shift();
// destination reached
if (curr === dest) return true;
// Visit all unvisited
// neighbours of current node
for (let neighbor of adj[curr]) {
if (!visited[neighbor]) {
visited[neighbor] = true;
q.push(neighbor);
}
}
}
// no path found
return false;
}
// Function to check if a path exists between u and v
function checkPath(adj, u, v) {
return bfs(adj, u, v);
}
//Driver Code Starts
// Driver code
const adj = [[2, 3],[2],[0, 1],[0],[5],[4]];
const u = 2, v = 3;
const pathExists = checkPath(adj, u, v);
console.log(pathExists ? "true" : "false");
//Driver Code Ends
[Alternate Approach] Using DSU - O(V) Time and O(V) Space
In this approach, we check if both vertices exists in the same component. If both of the vertices are in the same component, then there is always a path between them, otherwise there is no path between them.
To implement this approach, we are using DSU algorithm. To read more about DSU, refer to this article.
C++
//Driver Code Starts
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
//Driver Code Ends
// DSU class
class DSU {
vector<int> parent;
public:
DSU(int n) {
parent.resize(n);
// Each node is its own parent initially
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
}
// Find with path compression
int findParent(int u) {
if (u == parent[u]) return u;
return parent[u] = findParent(parent[u]);
}
// Union the sets of u and v
void unite(int u, int v) {
int pu = findParent(u);
int pv = findParent(v);
if (pu == pv) return;
parent[pu] = pv;
}
};
// function to check if two nodes are in the same component using DSU
bool dsu(vector<vector<int>>& adj, int src, int dest) {
int V = adj.size();
DSU dsuObj(V);
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
for (int next : adj[i]) {
dsuObj.unite(i, next);
}
}
return dsuObj.findParent(src) == dsuObj.findParent(dest);
}
// Function to check path between u and v
bool checkPath(vector<vector<int>>& adj, int u, int v) {
return dsu(adj, u, v);
}
//Driver Code Starts
int main() {
vector<vector<int>> adj = {{2, 3},{2},{0, 1},{0},{5},{4}};
int u = 2, v = 3;
bool pathExists = checkPath(adj, u, v);
cout << (pathExists ? "true" : "false") << endl;
return 0;
}
//Driver Code Ends
//Driver Code Starts
import java.util.ArrayList;
class GFG {
//Driver Code Ends
// DSU class
static class DSU {
int[] parent;
DSU(int n) {
// Each node is its own parent initially
parent = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
}
// Find with path compression
int findParent(int u) {
if (parent[u] == u) return u;
parent[u] = findParent(parent[u]);
return parent[u];
}
// Union the sets of u and v
void unite(int u, int v) {
int pu = findParent(u);
int pv = findParent(v);
if (pu == pv) return;
parent[pu] = pv;
}
}
// function to check if two nodes are in the same component using DSU
static boolean dsu(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj, int src, int dest) {
int V = adj.size();
DSU dsuObj = new DSU(V);
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
for (int next : adj.get(i)) {
dsuObj.unite(i, next);
}
}
return dsuObj.findParent(src) == dsuObj.findParent(dest);
}
// Function to check path between u and v
static boolean checkPath(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj, int u, int v) {
return dsu(adj, u, v);
}
//Driver Code Starts
// Function to add undirected edge
static void addEdge(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj, int u, int v) {
adj.get(u).add(v);
adj.get(v).add(u);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int V = 6;
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
addEdge(adj, 0, 2);
addEdge(adj, 0, 3);
addEdge(adj, 1, 2);
addEdge(adj, 4, 5);
int u = 2, v = 3;
System.out.println(checkPath(adj, u, v) ? "true" : "false");
}
}
//Driver Code Ends
# DSU class
class DSU:
def __init__(self, n):
# Each node is its own parent initially
self.parent = list(range(n))
# Find with path compression
def findParent(self, u):
if self.parent[u] == u:
return u
self.parent[u] = self.findParent(self.parent[u])
return self.parent[u]
# Union the sets of u and v
def unite(self, u, v):
pu = self.findParent(u)
pv = self.findParent(v)
if pu == pv:
return
self.parent[pu] = pv
# function to check if two nodes are in the same component using DSU
def dsu(adj, src, dest):
V = len(adj)
dsuObj = DSU(V)
for i in range(V):
for next_node in adj[i]:
dsuObj.unite(i, next_node)
return dsuObj.findParent(src) == dsuObj.findParent(dest)
# Function to check path between u and v
def checkPath(adj, u, v):
return dsu(adj, u, v)
#Driver Code Starts
if __name__ == "__main__":
adj = [[2, 3],[2],[0, 1],[0],[5],[4]]
u, v = 2, 3
pathExists = checkPath(adj, u, v)
print("true" if pathExists else "false")
#Driver Code Ends
//Driver Code Starts
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
//Driver Code Ends
// DSU class
class DSU
{
int[] parent;
public DSU(int n)
{
// Each node is its own parent initially
parent = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
parent[i] = i;
}
// Find with path compression
public int findParent(int u)
{
if (parent[u] == u) return u;
parent[u] = findParent(parent[u]);
return parent[u];
}
// Union the sets of u and v
public void unite(int u, int v)
{
int pu = findParent(u);
int pv = findParent(v);
if (pu == pv) return;
parent[pu] = pv;
}
}
// function to check if two nodes are in the same component using DSU
static bool dsu(List<List<int>> adj, int src, int dest)
{
int V = adj.Count;
DSU dsuObj = new DSU(V);
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
foreach (int next in adj[i])
dsuObj.unite(i, next);
}
return dsuObj.findParent(src) == dsuObj.findParent(dest);
}
// Function to check path between u and v
static bool checkPath(List<List<int>> adj, int u, int v)
{
return dsu(adj, u, v);
}
//Driver Code Starts
// Function to add undirected edge
static void addEdge(List<List<int>> adj, int u, int v)
{
adj[u].Add(v);
adj[v].Add(u);
}
static void Main()
{
int V = 6;
List<List<int>> adj = new List<List<int>>();
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
adj.Add(new List<int>());
addEdge(adj, 0, 2);
addEdge(adj, 0, 3);
addEdge(adj, 1, 2);
addEdge(adj, 4, 5);
int u = 2, v = 3;
Console.WriteLine(checkPath(adj, u, v) ? "true" : "false");
}
}
//Driver Code Ends
// DSU class
class DSU {
constructor(n) {
// Each node is its own parent initially
this.parent = Array.from({ length: n }, (_, i) => i);
}
// Find with path compression
findParent(u) {
if (this.parent[u] === u) return u;
this.parent[u] = this.findParent(this.parent[u]);
return this.parent[u];
}
// Union the sets of u and v
unite(u, v) {
const pu = this.findParent(u);
const pv = this.findParent(v);
if (pu === pv) return;
this.parent[pu] = pv;
}
}
// function to check if two nodes are in the same component using DSU
function dsu(adj, src, dest) {
const V = adj.length;
const dsuObj = new DSU(V);
for (let i = 0; i < V; i++) {
for (let next of adj[i]) {
dsuObj.unite(i, next);
}
}
return dsuObj.findParent(src) === dsuObj.findParent(dest);
}
// Function to check path between u and v
function checkPath(adj, u, v) {
return dsu(adj, u, v);
}
//Driver Code Starts
// Driver Code
const adj = [[2, 3],[2],[0, 1],[0],[5],[4]];
const u = 2, v = 3;
const pathExists = checkPath(adj, u, v);
console.log(pathExists ? "true" : "false");
//Driver Code Ends
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem