Program to check similarity of given two triangles
Last Updated :
09 Jan, 2023
Given four array of 3 numbers each which represents sides and angles of two triangles. The task is to check if two triangles are similar or not. If it is similar, print the theorem by which it is.
Examples:
Input : side1 = [2, 3, 3] angle1 = [80, 60, 40]
side2 = [4, 6, 6] angle2 = [40, 60, 80]
Output: Triangles are similar by SSS AA SAS
Input : side1 = [2, 3, 4] angle1 = [85, 45, 50]
side2 = [4, 6, 6] angle2 = [40, 60, 80]
Output: Triangles are not similar
Similar triangles are two or more triangles that have all corresponding angles that are equal and all corresponding sides that are proportionate. It does not matter what direction the triangles are facing. Their size does not matter as long as each side is proportionate. The similarity of triangles can be proved by the following theorems:
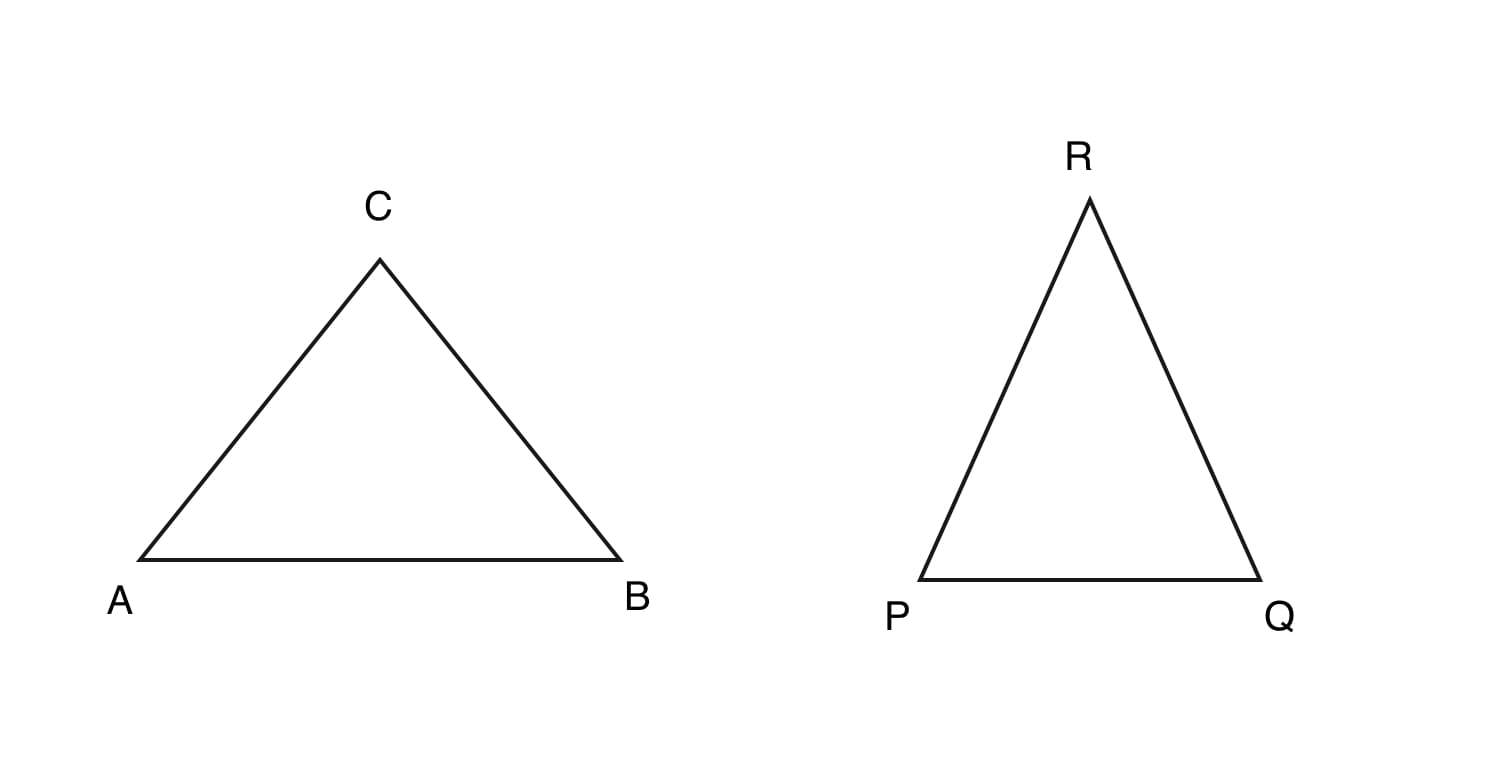
- Side-Side-Side (SSS) similarity criteria :
If all the sides of a triangle are proportional to the corresponding sides of another triangle then the triangles are said to be similar by the property of Side-Side-Side (SSS).
In a triangle ABC and PQR if, AB/PQ = BC/QR = CA/RP triangles are similar.
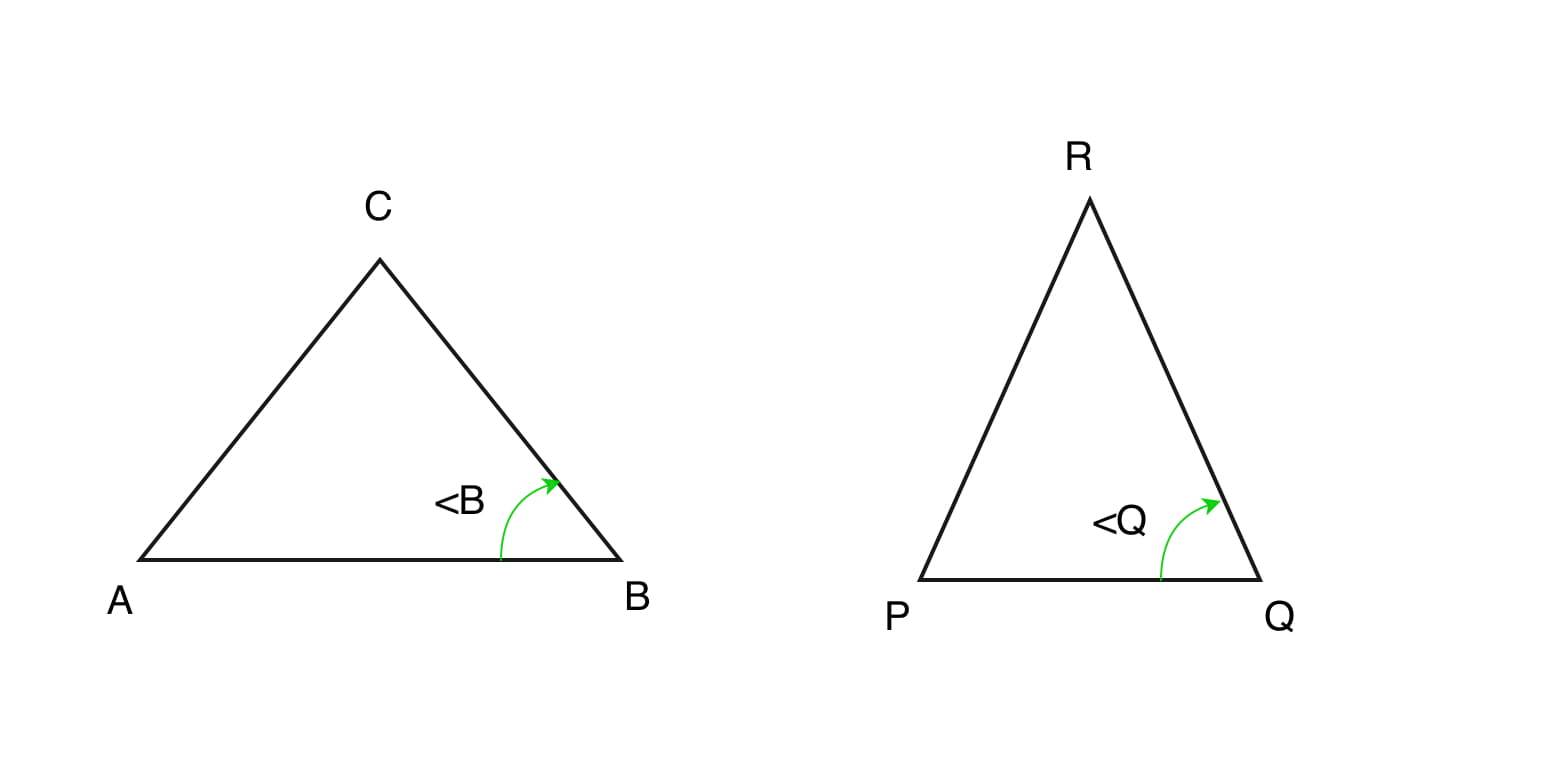
- Side-Angle-Side (SAS) similarity criteria :
If two sides of the two triangles are proportional and the angle between them is same in both triangle then the triangles are said to be similar by the property of Side-Angle-Side (SAS).
In a triangle ABC and PQR if, AB/PQ = BC/QR and \measuredangle ABC = \measuredangle PQR triangles are similar.
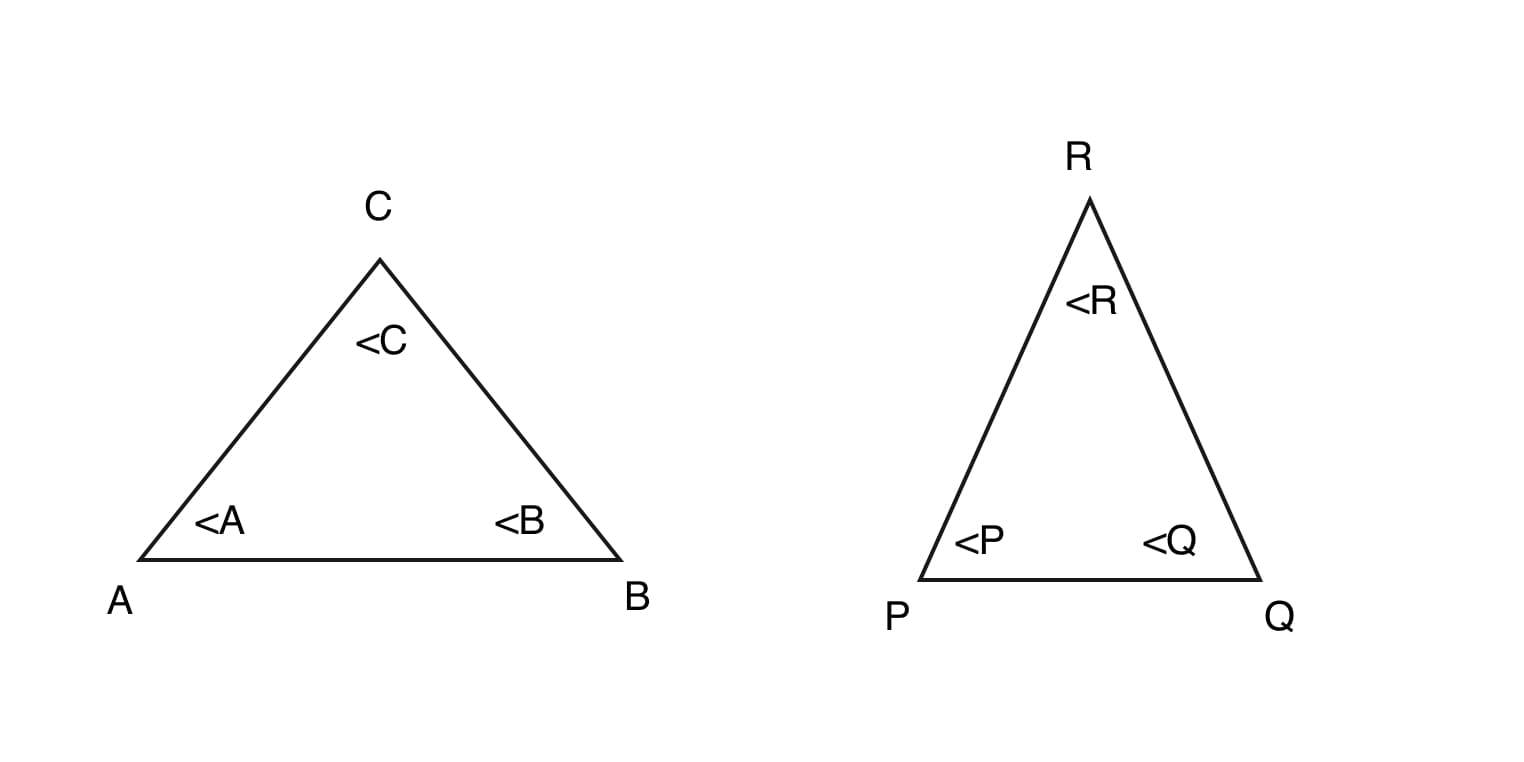
- Angle-Angle (AA) similarity criteria :
If all the angles of a triangle are equal to the corresponding angles of another triangle then the triangles are said to be similar by the property of Angle-Angle (AA).
In a triangle ABC and PQR if \measuredangle ABC = \measuredangle PQR and \measuredangle BCA = \measuredangle QRP or, \measuredangle CAB = \measuredangle RPQ and \measuredangle ABC = \measuredangle PQR or, \measuredangle BCA = \measuredangle QRP and \measuredangle CAB = \measuredangle RPQ then triangles are similar.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// C++ program to check similarity between two triangles.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function for AA similarity
int simi_aa(float a1[], float a2[])
{
sort(a1, a1 + 3);
sort(a2, a2 + 3);
// Check for AA
if ((a1[0] == a2[0] && a1[1] == a2[1])
|| (a1[0] == a2[0] && a1[2] == a2[2])
|| (a1[1] == a2[1] && a1[2] == a2[2]))
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
// Function for SAS similarity
int simi_sas(float s1[], float s2[], float a1[], float a2[])
{
sort(a1, a1 + 3);
sort(a2, a2 + 3);
sort(s1, s1 + 3);
sort(s2, s2 + 3);
// Check for SAS
// angle b / w two smallest
// sides is largest.
if (s1[0] / s2[0] == s1[1] / s2[1]) {
// since we take angle
// b / w the sides.
if (a1[2] == a2[2])
return 1;
}
if (s1[1] / s2[1] == s1[2] / s2[2]) {
if (a1[0] == a2[0])
return 1;
}
if (s1[2] / s2[2] == s1[0] / s2[0]) {
if (a1[1] == a2[1])
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// Function for SSS similarity
int simi_sss(float s1[], float s2[])
{
sort(s1, s1 + 3);
sort(s2, s2 + 3);
// Check for SSS
if (s1[0] / s2[0] == s1[1] / s2[1]
&& s1[1] / s2[1] == s1[2] / s2[2]
&& s1[2] / s2[2] == s1[0] / s2[0])
return 1;
return 0;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
float s1[] = { 2, 3, 3 };
float s2[] = { 4, 6, 6 };
float a1[] = { 80, 60, 40 };
float a2[] = { 40, 60, 80 };
// function call for AA similarity
int aa = simi_aa(a1, a2);
// function call for SSS similarity
int sss = simi_sss(s1, s2);
// function call for SAS similarity
int sas = simi_sas(s1, s2, a1, a2);
// Check if triangles are similar or not
if (aa == 1 || sss == 1 || sas == 1) {
cout << "Triangles are "
<< "similar by ";
if (aa == 1)
cout << "AA ";
if (sss == 1)
cout << "SSS ";
if (sas == 1)
cout << "SAS ";
}
else
cout << "Triangles are "
<< "not similar";
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu
// This code is modified by Susobhan Akhuli
// Java program to check
// similarity between
// two triangles.
import java.util.*;
class GFG1 {
// Function for
// AA similarity
static int simi_aa(float a1[], float a2[])
{
Arrays.sort(a1);
Arrays.sort(a2);
// Check for AA
if ((a1[0] == a2[0] && a1[1] == a2[1])
|| (a1[0] == a2[0] && a1[2] == a2[2])
|| (a1[1] == a2[1] && a1[2] == a2[2]))
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
// Function for
// SAS similarity
static int simi_sas(float s1[], float s2[], float a1[],
float a2[])
{
Arrays.sort(a1);
Arrays.sort(a2);
Arrays.sort(s1);
Arrays.sort(s2);
// Check for SAS
// angle b / w two smallest
// sides is largest.
if (s1[0] / s2[0] == s1[1] / s2[1]) {
// since we take angle
// b / w the sides.
if (a1[2] == a2[2])
return 1;
}
if (s1[1] / s2[1] == s1[2] / s2[2]) {
if (a1[0] == a2[0])
return 1;
}
if (s1[2] / s2[2] == s1[0] / s2[0]) {
if (a1[1] == a2[1])
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// Function for
// SSS similarity
static int simi_sss(float s1[], float s2[])
{
Arrays.sort(s1);
Arrays.sort(s2);
// Check for SSS
if (s1[0] / s2[0] == s1[1] / s2[1]
&& s1[1] / s2[1] == s1[2] / s2[2]
&& s1[2] / s2[2] == s1[0] / s2[0])
return 1;
return 0;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
float s1[] = { 2, 3, 3 };
float s2[] = { 4, 6, 6 };
float a1[] = { 80, 60, 40 };
float a2[] = { 40, 60, 80 };
// function call for
// AA similarity
int aa = simi_aa(a1, a2);
// function call for
// SSS similarity
int sss = simi_sss(s1, s2);
// function call for
// SAS similarity
int sas = simi_sas(s1, s2, a1, a2);
// Check if triangles
// are similar or not
if (aa == 1 || sss == 1 || sas == 1) {
System.out.print("Triangles are "
+ "similar by ");
if (aa == 1)
System.out.print("AA ");
if (sss == 1)
System.out.print("SSS ");
if (sas == 1)
System.out.print("SAS ");
}
else
System.out.println("Triangles are "
+ "not similar");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu
// This code is modified by Susobhan Akhuli
# Python program to check
# similarity between two triangles.
# Function for AA similarity
def simi_aa(a1, a2):
a1 = [float(i) for i in a1]
a2 = [float(i) for i in a2]
a1.sort()
a2.sort()
# Check for AA
if ((a1[0] == a2[0] and a1[1] == a2[1]) or (a1[0] == a2[0] and a1[2] == a2[2]) or (a1[1] == a2[1] and a1[2] == a2[2])):
return 1
return 0
# Function for SAS similarity
def simi_sas(s1, s2, a1, a2):
s1 = [float(i) for i in s1]
s2 = [float(i) for i in s2]
a1 = [float(i) for i in a1]
a2 = [float(i) for i in a2]
s1.sort()
s2.sort()
a1.sort()
a2.sort()
# Check for SAS
# angle b / w two smallest sides is largest.
if s1[0] / s2[0] == s1[1] / s2[1]:
# since we take angle b / w the sides.
if a1[2] == a2[2]:
return 1
if s1[1] / s2[1] == s1[2] / s2[2]:
if a1[0] == a2[0]:
return 1
if s1[2] / s2[2] == s1[0] / s2[0]:
if a1[1] == a2[1]:
return 1
return 0
# Function for SSS similarity
def simi_sss(s1, s2):
s1 = [float(i) for i in s1]
s2 = [float(i) for i in s2]
s1.sort()
s2.sort()
# Check for SSS
if(s1[0] / s2[0] == s1[1] / s2[1]
and s1[1] / s2[1] == s1[2] / s2[2]
and s1[2] / s2[2] == s1[0] / s2[0]):
return 1
return 0
# Driver Code
s1 = [2, 3, 3]
s2 = [4, 6, 6]
a1 = [80, 60, 40]
a2 = [40, 60, 80]
# function call for AA similarity
aa = simi_aa(a1, a2)
# function call for SSS similarity
sss = simi_sss(s1, s2)
# function call for SAS similarity
sas = simi_sas(s1, s2, a1, a2)
# Check if triangles are similar or not
if aa or sss or sas:
print "Triangles are similar by",
if aa:
print "AA",
if sss:
print "SSS",
if sas:
print "SAS"
else:
print "Triangles are not similar"
# This code is modified by Susobhan Akhuli
// C# program to check
// similarity between
// two triangles.
using System;
class GFG1 {
// Function for
// AA similarity
static int simi_aa(float[] a1, float[] a2)
{
Array.Sort(a1);
Array.Sort(a2);
// Check for AA
if ((a1[0] == a2[0] && a1[1] == a2[1])
|| (a1[0] == a2[0] && a1[2] == a2[2])
|| (a1[1] == a2[1] && a1[2] == a2[2]))
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
// Function for
// SAS similarity
static int simi_sas(float[] s1, float[] s2, float[] a1,
float[] a2)
{
Array.Sort(a1);
Array.Sort(a2);
Array.Sort(s1);
Array.Sort(s2);
// Check for SAS
// angle b / w two smallest
// sides is largest.
if (s1[0] / s2[0] == s1[1] / s2[1]) {
// since we take angle
// b / w the sides.
if (a1[2] == a2[2])
return 1;
}
if (s1[1] / s2[1] == s1[2] / s2[2]) {
if (a1[0] == a2[0])
return 1;
}
if (s1[2] / s2[2] == s1[0] / s2[0]) {
if (a1[1] == a2[1])
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// Function for
// SSS similarity
static int simi_sss(float[] s1, float[] s2)
{
Array.Sort(s1);
Array.Sort(s2);
// Check for SSS
if (s1[0] / s2[0] == s1[1] / s2[1]
&& s1[1] / s2[1] == s1[2] / s2[2]
&& s1[2] / s2[2] == s1[0] / s2[0])
return 1;
return 0;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
float[] s1 = { 2, 3, 3 };
float[] s2 = { 4, 6, 6 };
float[] a1 = { 80, 60, 40 };
float[] a2 = { 40, 60, 80 };
// function call for
// AA similarity
int aa = simi_aa(a1, a2);
// function call for
// SSS similarity
int sss = simi_sss(s1, s2);
// function call for
// SAS similarity
int sas = simi_sas(s1, s2, a1, a2);
// Check if triangles
// are similar or not
if (aa == 1 || sss == 1 || sas == 1) {
Console.Write("Triangles are "
+ "similar by ");
if (aa == 1)
Console.Write("AA ");
if (sss == 1)
Console.Write("SSS ");
if (sas == 1)
Console.Write("SAS ");
}
else
Console.WriteLine("Triangles are "
+ "not similar");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Ryuga
// This code is modified by Susobhan Akhuli
<?php
// PHP program to check similarity between
// two triangles.
// Function for AA similarity
function simi_aa($a1, $a2)
{
sort($a1);
sort($a2);
// Check for AA
if (($a1[0] == $a2[0] && $a1[1] == $a2[1])
|| ($a1[0] == $a2[0] && $a1[2] == $a2[2])
|| ($a1[1] == $a2[1] && $a1[2] == $a2[2]))
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
// Function for SAS similarity
function simi_sas($s1, $s2, $a1, $a2)
{
sort($a1);
sort($a2);
sort($s1);
sort($s2);
// Check for SAS
// angle b / w two smallest
// sides is largest.
if( $s1[0] / $s2[0] == $s1[1] / $s2[1])
{
// since we take angle b / w the sides.
if ($a1[2] == $a2[2])
return 1;
}
if ($s1[1] / $s2[1] == $s1[2] / $s2[2])
{
if ($a1[0] == $a2[0])
return 1;
}
if ($s1[2] / $s2[2] == $s1[0] / $s2[0])
{
if($a1[1] == $a2[1])
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// Function for SSS similarity
function simi_sss($s1, $s2)
{
sort($s1);
sort($s2);
// Check for SSS
if($s1[0] / $s2[0] == $s1[1] / $s2[1] &&
$s1[1] / $s2[1] == $s1[2] / $s2[2] &&
$s1[2] / $s2[2] == $s1[0] / $s2[0])
return 1;
return 0;
}
// Driver Code
$s1 = array(2, 3, 3);
$s2 = array(4, 6, 6);
$a1 = array(80, 60, 40);
$a2 = array(40, 60, 80);
// function call for
// AA similarity
$aa = simi_aa($a1, $a2);
// function call for
// SSS similarity
$sss = simi_sss($s1, $s2) ;
// function call for
// SAS similarity
$sas = simi_sas($s1, $s2,
$a1, $a2) ;
// Check if triangles
// are similar or not
if($aa == 1 || $sss == 1 || $sas == 1)
{
echo "Triangles are similar by ";
if($aa == 1) echo "AA ";
if($sss == 1) echo "SSS ";
if($sas == 1) echo "SAS ";
}
else
echo "Triangles are not similar";
// This code is contributed by ajit.
// This code is modified by Susobhan Akhuli
?>
<script>
// Javascript program to check
// similarity between
// two triangles.
// Function for
// AA similarity
function simi_aa(a1, a2)
{
a1.sort(function(a, b){return a - b});
a2.sort(function(a, b){return a - b});
// Check for AA
if ((a1[0] == a2[0] && a1[1] == a2[1])
|| (a1[0] == a2[0] && a1[2] == a2[2])
|| (a1[1] == a2[1] && a1[2] == a2[2]))
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
// Function for
// SAS similarity
function simi_sas(s1, s2, a1, a2)
{
a1.sort(function(a, b){return a - b});
a2.sort(function(a, b){return a - b});
s1.sort(function(a, b){return a - b});
s2.sort(function(a, b){return a - b});
// Check for SAS
// angle b / w two smallest
// sides is largest.
if(s1[0] / s2[0] == s1[1] / s2[1])
{
// since we take angle
// b / w the sides.
if (a1[2] == a2[2])
return 1;
}
if (s1[1] / s2[1] == s1[2] / s2[2])
{
if (a1[0] == a2[0])
return 1;
}
if (s1[2] / s2[2] == s1[0] / s2[0])
{
if(a1[1] == a2[1])
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// Function for
// SSS similarity
function simi_sss(s1, s2)
{
s1.sort(function(a, b){return a - b});
s2.sort(function(a, b){return a - b});
// Check for SSS
if(s1[0] / s2[0] == s1[1] / s2[1] &&
s1[1] / s2[1] == s1[2] / s2[2] &&
s1[2] / s2[2] == s1[0] / s2[0])
return 1;
return 0;
}
let s1 = [2, 3, 3];
let s2 = [4, 6, 6];
let a1 = [80, 60, 40];
let a2 = [40, 60, 80];
// function call for
// AA similarity
let aa = simi_aa(a1, a2);
// function call for
// SSS similarity
let sss = simi_sss(s1, s2) ;
// function call for
// SAS similarity
let sas = simi_sas(s1, s2, a1, a2) ;
// Check if triangles
// are similar or not
if(aa == 1 || sss == 1 || sas == 1)
{
document.write("Triangles are " + "similar by ");
if(aa == 1) document.write("AA ");
if(sss == 1) document.write("SSS ");
if(sas == 1) document.write("SAS ");
}
else
document.write("Triangles are not similar");
// This code is contributed by rameshtravel07.
// This code is modified by Susobhan Akhuli
</script>
OutputTriangles are similar by AA SSS SAS
Time Complexity: O(1) As the arrays have only 3 elements, so the total time taken can be treated as constant.
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem