Important Points About Circle
Last Updated :
25 Mar, 2025
The collection of all the points in a plane, which are at a fixed distance from a fixed point in the plane, is called a circle. Here, the fixed point is called the center “O”. Some of the important terminologies used in the circle are as follows:
 circle
circleThese are following important points about circle in geometry :
1. Equation of circle having center at (0, 0) and radius r :
x2 + y2= r2
2. Equation of circle having center at (h, k) and radius a :
(x - h)2+ (y - k)2= a2
3. The standard equation of a circle is x^2 + y^2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0, where the radius is \sqrt{g^2 + f^2 - c} and the center is (−g,−f) The condition for the existence of a real circle is g^2 + f^2 - c \geq 0.
4. If g2 + f2 - c = 0 then equation represents a point circle having center only (-g, -f).
5. Diametrical form of a circle
 Diametrical of a circle
Diametrical of a circle Figure - (X-x)(X-a)+(Y-y)(Y-b) = 0
S1 = x12+ y12+ 2gx1 + 2fy1 + c
S2 = x22 + y22 + 2gx2 + 2fy2 + c
6. Equation of Circle Passing through point of intersection of circles S1 = 0 and S2 = 0 is S1 + kS2 = 0 where k is not equal to -1.
7. Equation of circle passing through a point of intersection of circle s = 0 and line u = 0 is s+ ku = 0
8. If the circles S1 = 0 and S2 = 0 intersect then S1 - S2 = 0 is their common chord.
 common chord of circles
common chord of circles9. If two circles S1 = 0 and S2 = 0 have internal contact the S1 - S2 =0 is their internal common tangent.
 internal common tangent of circle
internal common tangent of circle10. If Two Circles S1 = 0 and S2 = 0 do not intersect then S1 - S2 = 0 is their radial axis.
 radial axis of circle
radial axis of circle11. If Two Circles S1 = 0 and S2 = 0 have external contact the S1 - S2 = 0 is their external common tangent.
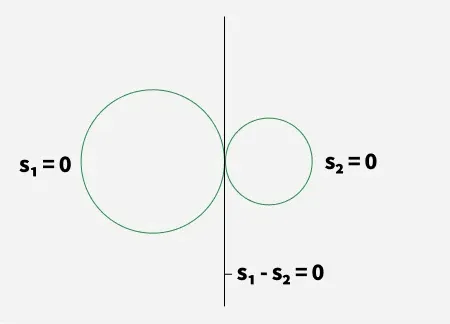 external common tangent of circle
external common tangent of circleSome important terms of a circle and their meanings
| Terms | Description |
|---|
| Circumference | The boundary of the circle is known as the circumference. |
|---|
| Radius | The line from the center "O" of the circle to the circumference of the circle is called the radius, and it is denoted by "R" or "r". |
|---|
| Diameter | The line that passes through the center of the circle and touches two points on the circumference is called the diameter and is denoted by "D" or "d". |
|---|
| Arc | An arc is a part of the circumference where the largest arc is called the major arc and the smaller one is called the minor arc. |
|---|
| Sector | A sector is a slice of a circle bounded by two radii and the included arc of the circle. |
|---|
| Chord | The straight line that joins any two points on the circumference of a circle is called the chord. |
|---|
| Tangent | A line that touches the circumference of a circle at a point is called the tangent. |
|---|
| Secant | A line that cuts the circle at two distinct points is known as the secant. |
|---|
Circle Formulas
- Area of a circle: A = \pi r^2(square units)
- Circumference of a circle: C = 2\pi r(units) Alternatively, the circumference can also be expressed as: C = π d (units) Where d is the diameter of the circle.
- Relationship between diameter and radius: d = 2r Where r represents the radius of the circle, and d represents the diameter.
These formulas are essential for calculating the area, circumference, and other properties related to a circle.
What is the sector of a circle?
A sector is a region enclosed by two radii and the arc between them. It is often referred to as the "slice" of the circle.
What is the segment of a circle?
A segment is the region between a chord (a straight line joining two points on the circle) and the arc that connects these two points.
Explore
Linear Algebra
Sequence & Series
Calculus
Probability & Statistics
Practice Questions