Errors V/s Exceptions In Java
Last Updated :
01 Mar, 2024
In Java, errors and exceptions are both types of throwable objects, but they represent different types of problems that can occur during the execution of a program.
Errors are usually caused by serious problems that are outside the control of the program, such as running out of memory or a system crash. Errors are represented by the Error class and its subclasses. Some common examples of errors in Java include:
- OutOfMemoryError: Thrown when the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) runs out of memory.
- StackOverflowError: Thrown when the call stack overflows due to too many method invocations.
- NoClassDefFoundError: Thrown when a required class cannot be found.
Since errors are generally caused by problems that cannot be recovered from, it's usually not appropriate for a program to catch errors. Instead, the best course of action is usually to log the error and exit the program.
Exceptions, on the other hand, are used to handle errors that can be recovered from within the program. Exceptions are represented by the Exception class and its subclasses. Some common examples of exceptions in Java include:
- NullPointerException: Thrown when a null reference is accessed.
- IllegalArgumentException: Thrown when an illegal argument is passed to a method.
- IOException: Thrown when an I/O operation fails.
Since exceptions can be caught and handled within a program, it's common to include code to catch and handle exceptions in Java programs. By handling exceptions, you can provide more informative error messages to users and prevent the program from crashing.
In summary, errors and exceptions represent different types of problems that can occur during program execution. Errors are usually caused by serious problems that cannot be recovered from, while exceptions are used to handle recoverable errors within a program.
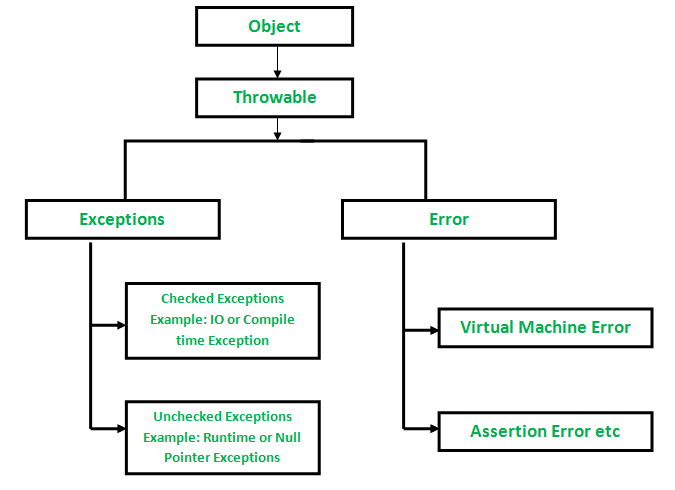
In java, both Errors and Exceptions are the subclasses of java.lang.Throwable class. Error refers to an illegal operation performed by the user which results in the abnormal working of the program. Programming errors often remain undetected until the program is compiled or executed. Some of the errors inhibit the program from getting compiled or executed. Thus errors should be removed before compiling and executing. It is of three types:
- Compile-time
- Run-time
- Logical
Whereas exceptions in java refer to an unwanted or unexpected event, which occurs during the execution of a program i.e at run time, that disrupts the normal flow of the program’s instructions.
Now let us discuss various types of errors in order to get a better understanding over arrays. As discussed in the header an error indicates serious problems that a reasonable application should not try to catch. Errors are conditions that cannot get recovered by any handling techniques. It surely causes termination of the program abnormally. Errors belong to unchecked type and mostly occur at runtime. Some of the examples of errors are Out of memory errors or System crash errors.
Example 1 Run-time Error
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Error
// Stack overflow error via infinite recursion
// Class 1
class StackOverflow {
// method of this class
public static void test(int i)
{
// No correct as base condition leads to
// non-stop recursion.
if (i == 0)
return;
else {
test(i++);
}
}
}
// Class 2
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Testing for error by passing
// custom integer as an argument
StackOverflow.test(5);
}
}
Output:
Example 2
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Run-time Errors
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Declaring and initializing numbers
int a = 2, b = 8, c = 6;
if (a > b && a > c)
System.out.println(a
+ " is the largest Number");
else if (b > a && b > c)
System.out.println(b
+ " is the smallest Number");
// The correct message should have been
// System.out.println
// (b+" is the largest Number"); to make logic
else
System.out.println(c
+ " is the largest Number");
}
}
Output8 is the smallest Number
Now let us dwell onto Exceptions which indicates conditions that a reasonable application might want to catch. Exceptions are the conditions that occur at runtime and may cause the termination of the program. But they are recoverable using try, catch and throw keywords. Exceptions are divided into two categories:
Checked exceptions like IOException known to the compiler at compile time while unchecked exceptions like ArrayIndexOutOfBoundException known to the compiler at runtime. It is mostly caused by the program written by the programmer.
Example Exception
Java
// Java program illustrating exception thrown
// by Arithmetic Exception class
// Main class
class GFG {
// main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = 5, b = 0;
// Try-catch block to check and handle exceptions
try {
// Attempting to divide by zero
int c = a / b;
}
catch (ArithmeticException e) {
// Displaying line number where exception occurred
// using printStackTrace() method
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Output:

Finally now wrapping-off the article by plotting the differences out between them in a tabular format as provided below as follows:
| Errors | Exceptions |
|---|
| Recovering from Error is not possible. | We can recover from exceptions by either using try-catch block or throwing exceptions back to the caller. |
| All errors in java are unchecked type. | Exceptions include both checked as well as unchecked type. |
| Errors are mostly caused by the environment in which program is running. | Program itself is responsible for causing exceptions. |
Errors can occur at compile time.
| Unchecked exceptions occur at runtime whereas checked exceptions occur at compile time |
| They are defined in java.lang.Error package. | They are defined in java.lang.Exception package |
| Examples : java.lang.StackOverflowError, java.lang.OutOfMemoryError | Examples : Checked Exceptions : SQLException, IOException Unchecked Exceptions : ArrayIndexOutOfBoundException, NullPointerException, ArithmeticException. |
Similar Reads
Java Tutorial Java is a high-level, object-oriented programming language used to build web apps, mobile applications, and enterprise software systems. It is known for its Write Once, Run Anywhere capability, which means code written in Java can run on any device that supports the Java Virtual Machine (JVM).Java s
10 min read
Java OOP(Object Oriented Programming) Concepts Java Object-Oriented Programming (OOPs) is a fundamental concept in Java that every developer must understand. It allows developers to structure code using classes and objects, making it more modular, reusable, and scalable.The core idea of OOPs is to bind data and the functions that operate on it,
13 min read
Java Interview Questions and Answers Java is one of the most popular programming languages in the world, known for its versatility, portability, and wide range of applications. Java is the most used language in top companies such as Uber, Airbnb, Google, Netflix, Instagram, Spotify, Amazon, and many more because of its features and per
15+ min read
SQL Commands | DDL, DQL, DML, DCL and TCL Commands SQL commands are crucial for managing databases effectively. These commands are divided into categories such as Data Definition Language (DDL), Data Manipulation Language (DML), Data Control Language (DCL), Data Query Language (DQL), and Transaction Control Language (TCL). In this article, we will e
7 min read
Arrays in Java Arrays in Java are one of the most fundamental data structures that allow us to store multiple values of the same type in a single variable. They are useful for storing and managing collections of data. Arrays in Java are objects, which makes them work differently from arrays in C/C++ in terms of me
15+ min read
TCP/IP Model The TCP/IP model is a framework that is used to model the communication in a network. It is mainly a collection of network protocols and organization of these protocols in different layers for modeling the network.It has four layers, Application, Transport, Network/Internet and Network Access.While
7 min read
Collections in Java Any group of individual objects that are represented as a single unit is known as a Java Collection of Objects. In Java, a separate framework named the "Collection Framework" has been defined in JDK 1.2 which holds all the Java Collection Classes and Interface in it. In Java, the Collection interfac
15+ min read
Inheritance in Java Java Inheritance is a fundamental concept in OOP(Object-Oriented Programming). It is the mechanism in Java by which one class is allowed to inherit the features(fields and methods) of another class. In Java, Inheritance means creating new classes based on existing ones. A class that inherits from an
13 min read
Basics of Computer Networking A computer network is a collection of interconnected devices that share resources and information. These devices can include computers, servers, printers, and other hardware. Networks allow for the efficient exchange of data, enabling various applications such as email, file sharing, and internet br
14 min read
Java Exception Handling Exception handling in Java allows developers to manage runtime errors effectively by using mechanisms like try-catch block, finally block, throwing Exceptions, Custom Exception handling, etc. An Exception is an unwanted or unexpected event that occurs during the execution of a program, i.e., at runt
10 min read