Common Git Problems and Their Fixes
Last Updated :
10 Oct, 2025
Git is a free and open-source version control system widely used for tracking changes in code. While working with Git or GitHub, users sometimes make mistakes that can lead to lost or incorrect information. To address this, Git provides various tricks and methods to undo, modify, or roll back changes efficiently.
Some of these problems along with their fixes are listed below:
1. Edit a commit message
Sometimes while writing the commit message, we make a typing error. The following commands can be used to fix the issue. Note that the below command creates a new commit so avoid using --amend for modifying commits which have been already pushed to a central repository.
git commit --amend // start the editor to edit message
git commit --amend -m"New message" // edit the commit message directly
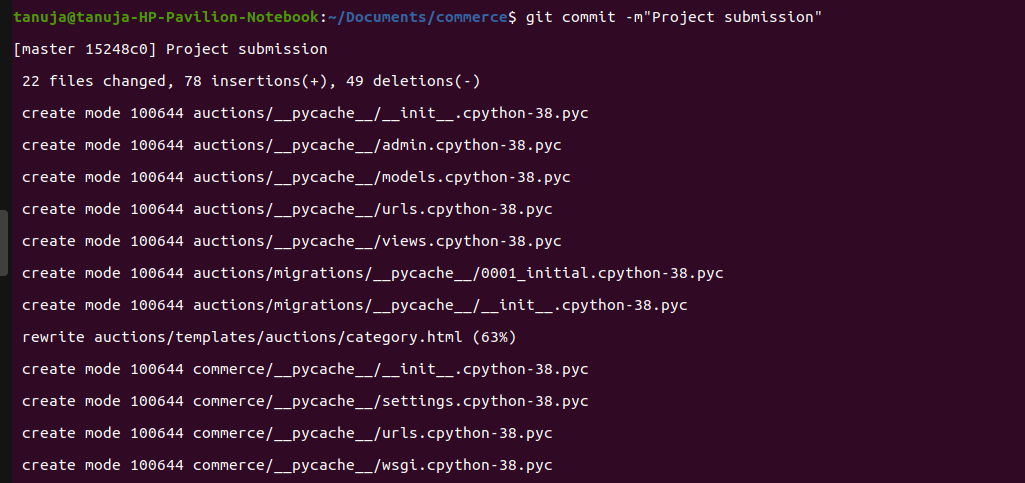 Normal commit
Normal commit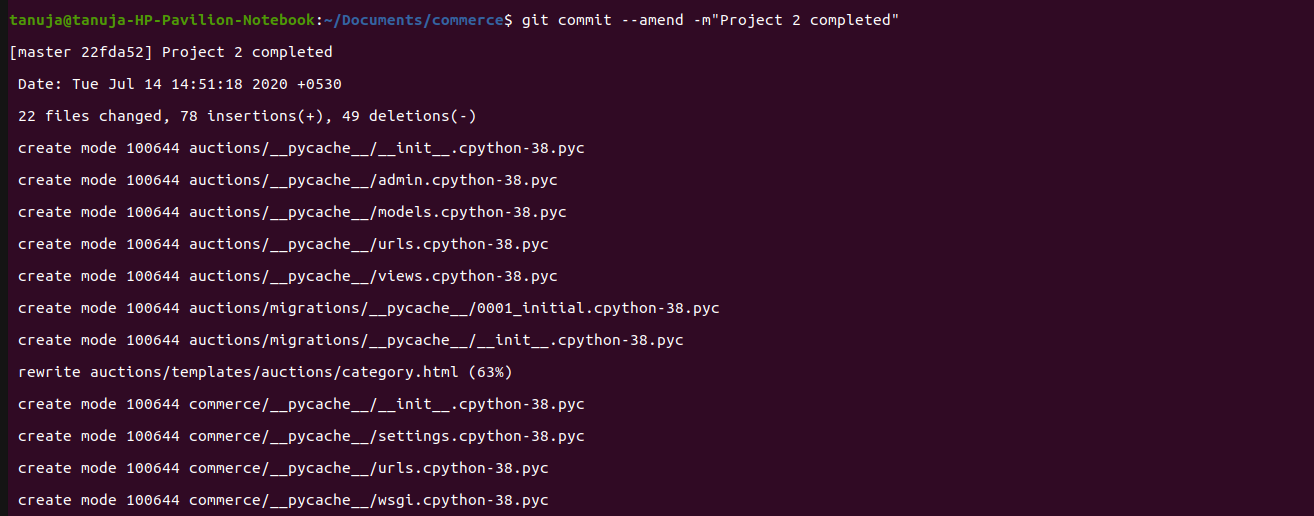 amend commit
amend commitIf you forget to add a file while git add, then just add it and amend the previous commit.
git add forgotten_file_name
git commit --amend
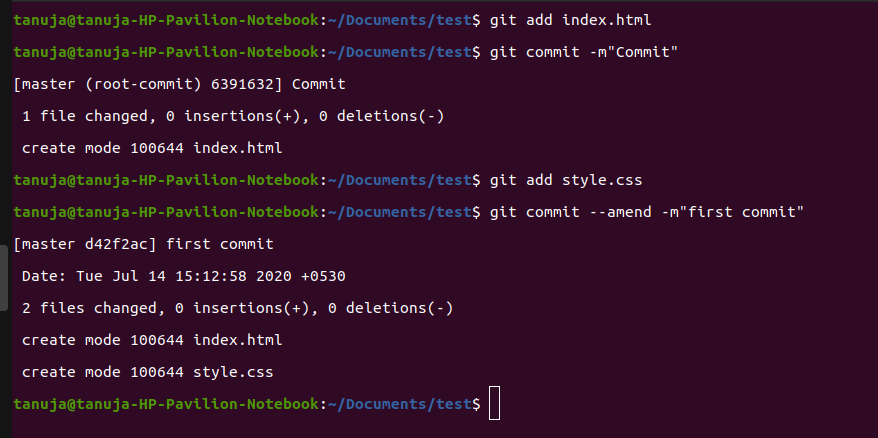
Clean local commits before pushing
--amend is very useful to edit a commit message but it will not work if the commit you want to do is not the last one. In that case, rebase is used.
git rebase --interactive
// if you didn't specify any tracking information for this branch,
// add upstream and remote branch information:
git rebase --interactive origin branch

This will give the following menu:
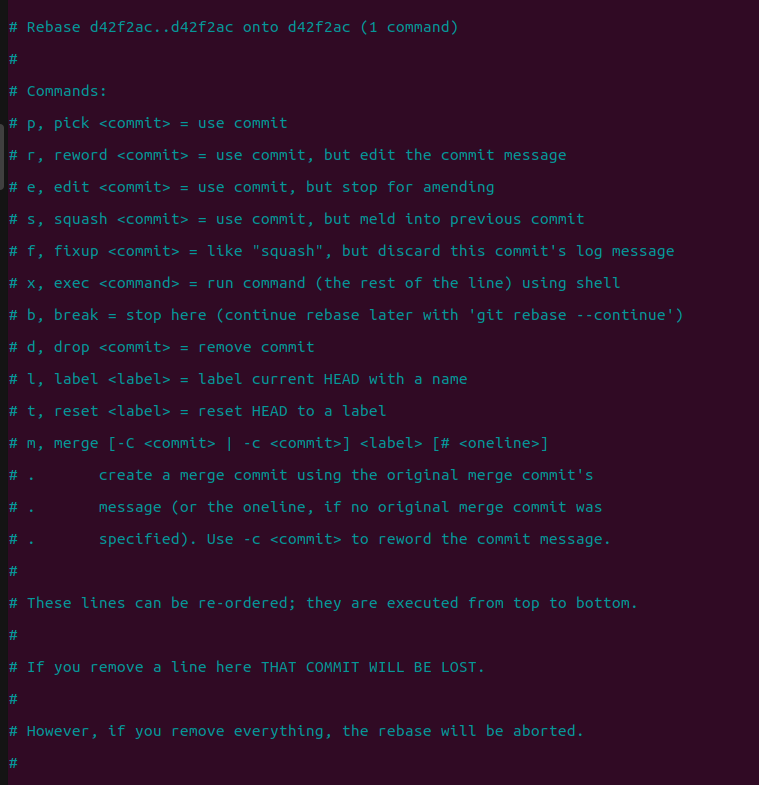
You will see a list of options that you can use to be taken to a view where you can edit the message. However, as can be seen from the above listing, interactive rebases offer a lot more than simple commit message editing: you can completely remove commits by deleting them from the list, as well as edit, reorder, and squash them. Squashing allows you to merge several commits into one before pushing them to the remote.
2. Undo the local commits
Sometimes we realize that there is some error /mistake but by that time a few of the changes are committed locally.
git reset HEAD-2 // undo last 2 commits and keep changes
git reset --hard HEAD-2 // undo last two Commits,discard changes

Remove a file from GIT without removing it from the file system
If you are not careful, you may add some unnecessary files during git add.
If you try to use git rm, it will remove the file from both the staging area as well as the file system.
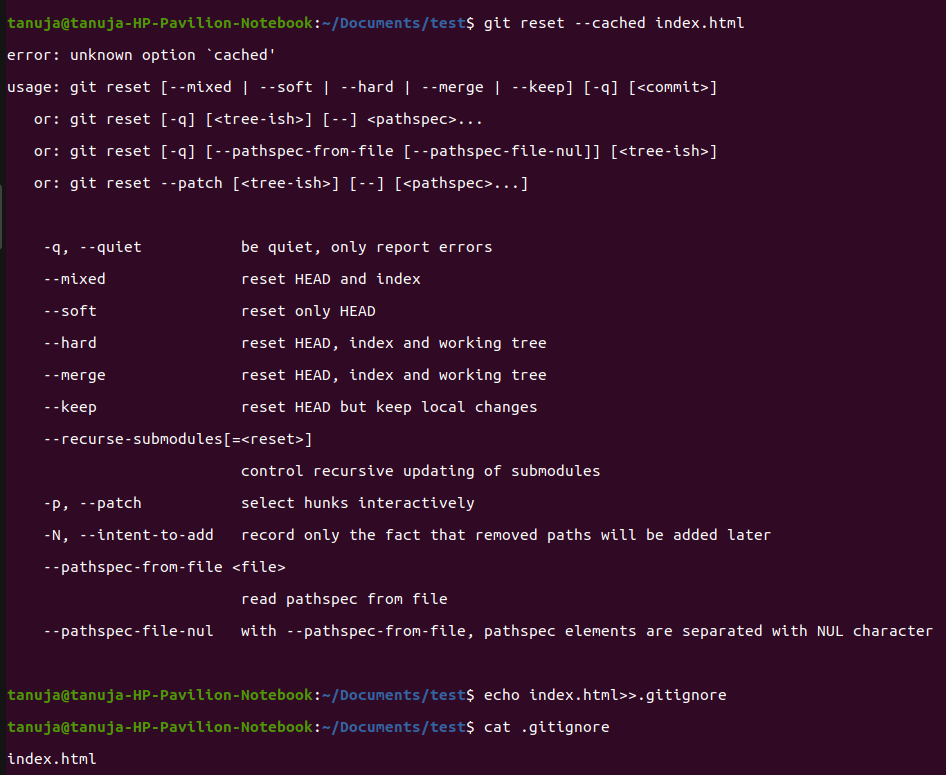
git reset filename // or git remove --cached filename
echo filename >> .gitignore // add it to .gitignore to avoid re-adding it
This command removes the staged version only and adds the file to your .gitignore to avoid making the same mistake again.
3. Reverting pushed commits
Sometimes faulty commits do make it into the central repository even after amend and rebase. Therefore you can use the below commands
git revert c761f5c // reverts the commit with the specified id
git revert HEAD^ // reverts the second to last commit
git revert develop~4..develop~2 // reverts a whole range of commits
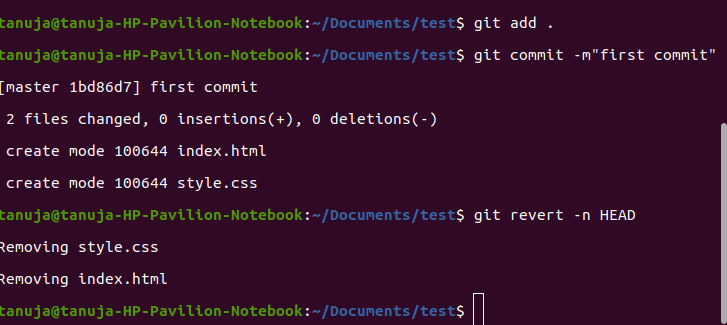
However, If you don’t want to create additional revert commits but only apply the necessary changes to your working tree, you can use the --no-commit/-n option.
git revert -n HEAD
4. Avoid repeated merge conflicts
Fixing Merge conflicts repeatedly is really bothersome.
Suppose your team is working on various feature branches at the same time. Now you want to merge all of them together. There are several merge conflicts, which you resolve. But it turns out that one of the branches isn’t quite there yet, so you decide to un-merge it again. After few days when the branch is finally ready,you merge it again, but thanks to the recorded resolutions, you won’t have to resolve the same merge conflicts again.

// Add it to your global config to enable it for all projects
git config --global rerere.enabled true
5. Find a commit that broke something after a merge
Sometimes there is a need to find a commit that changed the project wrongly. This bad commit is difficult to find and hence consumes a lot of time. Git has introduced a method to find this commit which broke something after the merge:
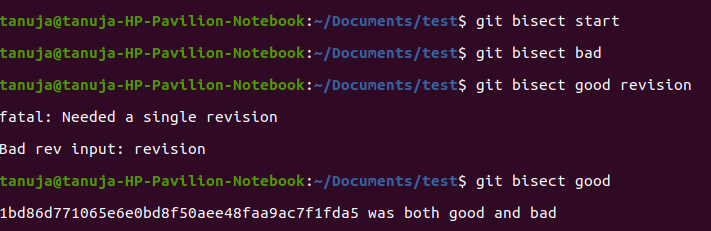
git bisect start // starts the bisecting session
git bisect bad // marks the current revision as bad
git bisect good revision // marks the last known good revision
Now, git will automatically checkout a revision halfway between the known “good” and “bad” versions.
git bisect good // OR git bisect bad
Which command is used to modify the most recent commit message?
Explanation:
git commit --amend lets you edit the latest commit message or add forgotten files. It replaces the previous commit with a new one.
Which command will undo the last two commits but keep the file changes in the working directory?
Explanation:
git reset HEAD~2 rolls back two commits while keeping changes unstaged.
--hard would delete changes.
What is the correct way to remove a file from Git without deleting it from the local file system?
-
-
-
git reset filename or git rm --cached filename
-
Explanation:
git rm --cached unstages/removes file from Git tracking but keeps it locally.
Often followed by adding it in .gitignore.
Which Git feature helps avoid resolving the same merge conflicts repeatedly?
Explanation:
rerere (Reuse Recorded Resolution) remembers conflict resolutions and applies them automatically in future similar conflicts.
A developer wants to find the commit that introduced a bug. Which Git tool should they use?
Explanation:
git bisect performs a binary search between good and bad commits to detect which commit caused the issue.
Quiz Completed Successfully
Your Score : 2/5
Accuracy : 0%
Login to View Explanation
1/5
1/5
< Previous
Next >
Explore
Git Introduction
Git Installation and Setup
All Git Commands
Most Used Git Commands
Git Branch
Git Merge
Git Tools and Integration
Git Remote Repositories
Collaborating with Git
Advanced Git Commands