Git Merge is a command used to combine the changes from two branches into one. It integrates work from different branches into a single unified history without losing progress. For example, you can merge a feature branch into the main branch to include all recent updates.
- Preserves the complete commit history of both branches.
- Performs automatic merges unless conflicts require manual resolution.
- Uses fast-forward merge when no diverging commits exist.
- Creates a merge commit to combine branch histories when necessary.
- Does not delete branches after merging.
- Commonly used to integrate feature branches into the main branch.
Working of Git Merge
Using the diagrams below, we will see how git merge works what the repository looks like before the merge and how Git creates a new merge commit to combine histories.
Before Merge
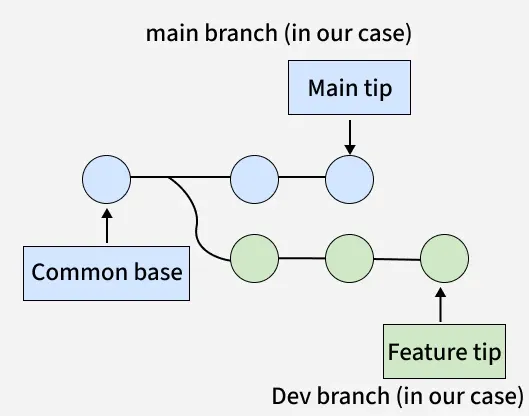
This image shows the state of the repository before the merge takes place.
Key Elements
- Common Base: The commit from which both the
main and feature (dev) branches originated. - Main Branch (in blue): This is your production or main branch where stable code lives.
- Feature/Dev Branch (in green): This branch is where new development work has occurred.
- Main Tip: The latest commit on the
main branch. - Feature Tip: The latest commit on the
feature branch.
Interpretation
- Development has happened in parallel on both the main and
feature branches. - These branches diverged from a common ancestor (the Common Base).
- You are now preparing to merge the feature branch back into the main branch.
After Merge
 Git - Merge
Git - MergeThis image shows what happens after executing a git merge.
During the merge, Git compares the latest commit of the main branch (Main Tip), the feature branch (Feature Tip), and their shared ancestor (Common Base). If there are no conflicts, Git automatically creates a new merge commit combining both histories.
Types of Merging in Git
Git supports several types of merging. The two most common types are:
1. Fast-forward merging
- This occurs when the target branch (e.g., main) is directly ahead of the feature branch (e.g., dev).
- Instead of creating a merge commit, Git simply moves the current branch’s tip to the target branch’s tip.
- Fast-forward merging is only possible when branches haven't diverged
 Git - Merge
Git - Merge2. Three-way merging
- This type occurs when the base branch has changed since the branch was first created.
- Git generates a new merge commit by comparing changes in both branches with the base branch.
 Git - Merge
Git - MergeNote : Git also supports other types of merging like recursive and octopus merging. With the help of a single merge commit "octopus merging" can merge multiple branches at once. "Recursive merging" is similar to three-way merging but it can handle more complex merge operations than the three-way merging.
Steps to Perform Git Merge
To ensure smooth merging, follow these steps:
Step 1: Create a New Branch
Create a new branch from the remote repository you want to merge.
git branch <new-branch-name>
Step 2: Pull the Latest Changes
Before merging, ensure that you pull the latest changes from both branches (e.g., main and the feature branch).
git checkout <target-branch>
git pull origin <target-branch>
git checkout <feature-branch>
git pull origin <feature-branch>
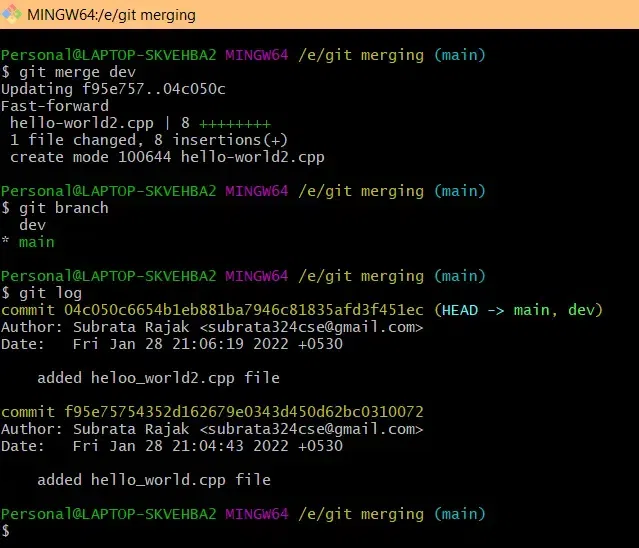
Step 3: Merge the Branch
If any conflicts arise, Git will notify you. Resolve them manually before proceeding.
git checkout <target-branch>
git merge <feature-branch>
Step 4: Test the Merged Code
Make sure the merged code functions correctly by testing it either automatically or manually.
# Run tests or manually test your application
Step 5: Commit the Merged Code
Once satisfied with the merged code, commit the changes:
git commit -m "Merge branch 'dev' into main"
Step 6: Push the Merged Branch
Push the changes to the remote repository to share the new merged branch:
git push origin main
Git Merge Vs Rebase
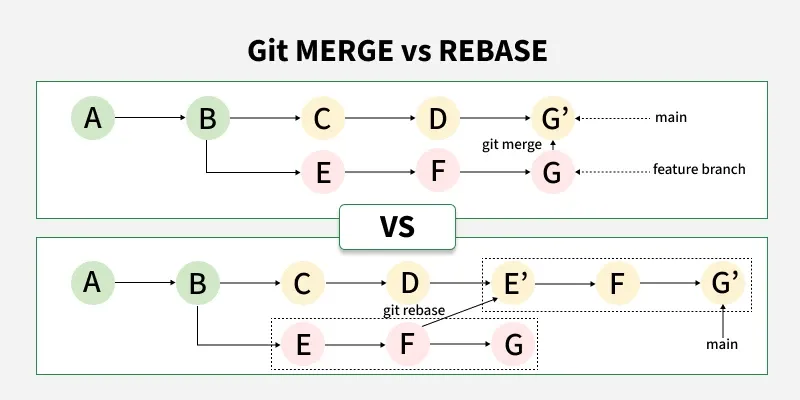 Git Merge vs Git Rebase
Git Merge vs Git Rebase| Git Merge | Git Rebase |
|---|
| Combines changes from one branch into another with a merge commit. | Applies commits from one branch onto another by rewriting history. |
| Preserves the complete commit history. | Creates a linear history by removing merge commits. |
| Useful for integrating feature branches. | Ideal for a clean, simplified project history. |
| Does not alter existing commits. | Rewrites commit hashes and order. |
What is the main purpose of git merge?
-
Delete branches permanently
-
-
Combine changes from two branches into one
-
Create a backup of remote repository
Explanation:
git merge is used to integrate work from one branch into another without losing commit history.
In which scenario does Git perform a fast-forward merge?
-
When there are merge conflicts
-
When branches have diverged
-
When the target branch has no new commits since branching
-
When merging multiple branches at once
Explanation:
Fast-forward merges happen only when the branch to be merged is ahead in a straight line, so Git just moves the pointer.
What does Git create during a three-way merge?
Explanation:
Three-way merge compares two tips with a common ancestor and generates a merge commit.
Which command is used to merge a feature branch into the main branch?
-
-
-
git checkout main → git merge feature
-
git push origin feature main
Explanation:
You must switch to the target branch first using git checkout main, then merge using git merge feature.
Which of the following statements is true regarding Merge vs Rebase?
-
Merge rewrites commit history
-
Rebase preserves all merge commits
-
Merge keeps history intact without rewriting commits
-
Rebase cannot be used on feature branches
Explanation:
Merge preserves complete commit history, whereas rebase rewrites history to create a linear structure.
Quiz Completed Successfully
Your Score : 2/5
Accuracy : 0%
Login to View Explanation
1/5
1/5
< Previous
Next >
Explore
Git Introduction
Git Installation and Setup
All Git Commands
Most Used Git Commands
Git Branch
Git Merge
Git Tools and Integration
Git Remote Repositories
Collaborating with Git
Advanced Git Commands