Handling Repositories with Git Remote
Last Updated :
18 Nov, 2025
Git remote is a reference to a repository hosted externally on platforms like GitHub, GitLab, or your own server. It acts as a link between your local repository and a remote repository, allowing you to:
- Push your local changes to the remote repository.
- Pull updates from the remote repository to your local one.
This enables multiple developers to work on the same project and stay in sync with each other.
Git Origin
When you run git remote -v in your project, you’ll often see a remote named origin. This is Git’s default name for the remote repository URL you are connected to.
Think of it like a shortcut for the remote location where your code is stored (e.g., on GitHub or GitLab). It works like a key-value pair, where:
- origin is the key (the name),
- and the remote URL is the value (the actual address).
You will see origin used in many Git commands and messages, such as:
git push origin main
This tells Git to push your local main branch to the remote repository named origin.
Managing Git Remote Repositories
Git remote commands help you connect, manage, and interact with remote repositories like GitHub or GitLab. Here are the commonly used commands
1. Add a Remote Repository
To establish a connection between your local repository and a remote repository, use the following command:
git remote add origin <URL>
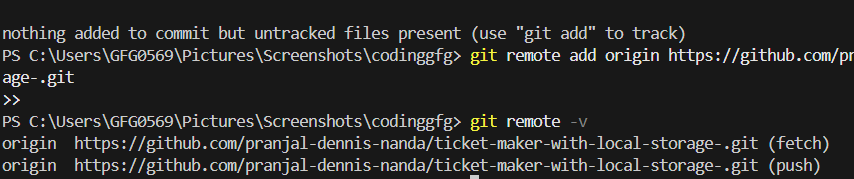 Add a Remote Repository
Add a Remote Repository2. View Remote Repositories
To display a list of linked remote repositories along with their URLs for the local system user attempting to connect to a GitHub server.
git remote -v
 View Remote Repositories
View Remote Repositories3. Rename a Remote
To change the name of an existing remote that you are currently connected to on the server.
git remote rename <oldname> <newname>
4. Remove a Remote
To unlink a remote repository from your local repo use the following command. If the repository name does not exist you can write origin instead of the repository name.
git remote remove <repositoryname>
 Remove a Remote
Remove a Remote5. Show Remote Details
To display information about a specific remote, including branches and fetch/push URLs use the following command.
git remote show <name>
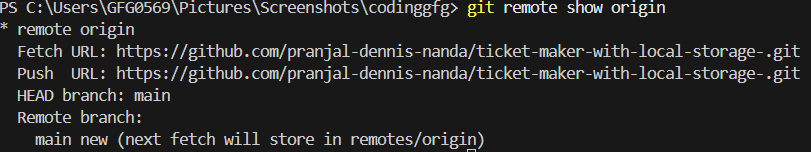 Show Remote Details
Show Remote DetailsWorking with Remote Repositories
1. Clone a Remote Repository
To create a local copy of a remote repository, use:
git clone <remote-repository-URL>
This downloads the entire repository along with its history.
2. Fetch Changes from Remote
To retrieve updates from a remote repository without merging them:
git fetch <remote-name>
3. Pull Changes from Remote
To fetch and merge the latest changes from a remote repository into your local branch:
git pull <remote-name> <branch-name>
4. Push Changes to Remote
After making changes locally, push them to the remote repository:
git push <remote-name> <branch-name>
If pushing for the first time, use
git push --set-upstream origin main
Handling Remote Branches
1. List Remote Branches
To see all branches available on the remote repository:
git branch -r
2. Track a Remote Branch
To create a local branch that tracks a remote branch:
git checkout --track origin/<branch-name>
3. Delete a Remote Branch
To remove a branch from the remote repository:
git push origin --delete <branch-name>
Resolving Common Remote Issues
1. Authentication Issues
If Git keeps asking for a username and password multiple times, consider setting up SSH authentication:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "[email protected]"
Add the public key to your GitHub/GitLab account.
2. Merge Conflicts While Pulling
If conflicts arise while pulling changes, manually resolve them and commit:
git add .
git commit -m "Resolved merge conflicts"
git push origin main
3. Remote Repository Not Found Error
If Git shows "repository not found", update the remote URL:
git remote set-url origin <correct-URL>
4. Permission Denied Error
If access is denied:
- Check if you have permission to access the repo.
- Make sure you are using the correct SSH key or HTTPS credentials.
Important Git Remote Commands
Below are some of the most useful Git remote commands that developers commonly use in real projects:
Remote Setup and Management
| Command | Description |
|---|
| git remote add <name> <url> | Adds a new remote repository (e.g., origin) |
| git remote -v | Shows all remotes and their fetch/push URLs |
| git remote rename <old> <new> | Renames an existing remote |
| git remote remove <name> | Removes a remote from the local repository |
| git remote show <name> | Shows detailed info about a remote (branches, URLs, etc.) |
| git remote set-url <name> <new-url> | Updates the URL of an existing remote |
Working with Remotes
| Command | Description |
|---|
| git clone <url> | Clones a remote repository to your local machine |
| git fetch <remote> | Fetches changes from the remote without merging |
| git pull <remote> <branch> | Fetches and merges changes from a remote branch |
| git push <remote> <branch> | Pushes your local branch to a remote branch |
| git push --set-upstream origin <branch> | Sets upstream for tracking and pushes branch to remote |
Remote Branch Handling
| Command | Description |
|---|
| git branch -r | Lists all remote-tracking branches |
| git checkout --track origin/<branch> | Creates a local branch tracking a remote branch |
| git push origin --delete <branch> | Deletes a branch from the remote repository |
| git remote prune origin | Removes references to deleted branches from the remote |
What does the term origin typically refer to in Git?
-
The name of your local repository
-
A branch that stores backup commits
-
Git’s default name for the remote repository URL
-
A temporary remote connection
Explanation:
In Git, origin is the default name given to the remote repository when you clone or manually add a remote using git remote add. It serves as a shorthand key for the URL where your project is hosted (e.g., GitHub or GitLab).
Which command is used to add a new remote repository to your local Git project?
-
-
-
-
git remote add origin <url>
Explanation:
To link your local repository with a remote one, you use:
git remote add origin <url>
Here, origin is the name of the remote and <url> is the actual location of the remote repository.
What is the difference between git fetch and git pull?
-
git fetch merges changes automatically, while git pull only downloads
-
git fetch downloads remote changes without merging them
-
git pull deletes local commits before merging
-
git pull is only used for remote branch creation
Explanation:
git fetch retrieves updates from the remote repository but does not merge them into your local branch.
git pull = fetch + merge, meaning it downloads and then immediately merges the update into your active branch.
Which command deletes a remote branch from the server?
-
-
-
git push origin --delete <branch>
-
git remote remove <branch>
Explanation:
To delete a branch from a remote repository like GitHub, the correct command is:
git push origin --delete <branch>
This removes the branch from the remote but does not affect your local branches.
If Git shows "repository not found" when pushing, which command can update the remote URL?
-
git remote rename origin <new>
-
git remote add origin <new-url>
-
git set-url origin <new-url>
-
git remote set-url origin <new-url>
Explanation:
If the remote URL changes or is incorrect, you fix it using:
git remote set-url origin <new-url>
This updates the URL without removing or re-adding the remote.
Quiz Completed Successfully
Your Score : 2/5
Accuracy : 0%
Login to View Explanation
1/5
1/5
< Previous
Next >
Explore
Git Introduction
Git Installation and Setup
All Git Commands
Most Used Git Commands
Git Branch
Git Merge
Git Tools and Integration
Git Remote Repositories
Collaborating with Git
Advanced Git Commands