Git Log is one of the most powerful commands in Git. It allows developers to view the entire commit history of a repository - helping them track changes, review project progress, and identify when and by whom changes were made.
Understanding Git Logs is essential for effective version control and collaboration in any project.
Git log displays a list of all commits made in a repository in reverse chronological order (latest commit first).
It shows detailed information about each commit, including:
- Commit hash (ID) – a unique identifier for each commit.
- Author name and email – who made the commit.
- Date and time – when the commit was made.
- Commit message – a short description of the change.
Basic Syntax
git log
Running this command shows a detailed list of all commits in your repository.
Example output:
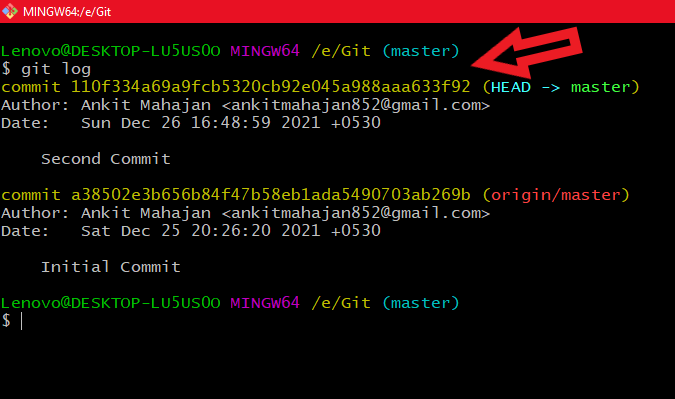 git log
git logEach entry represents one commit.
Useful Git Log Options
Git Log has many options to customize how you view the commit history.
Here are some of the most commonly used ones:
1. View a Compact One-Line Log
Shows each commit in a single line (commit hash and message only).
git log --oneline
2. Show Graph of Branches
Displays a visual branch structure along with commits.
git log --oneline --graph
Helps to understand how different branches have diverged and merged.
3. Show Commits by a Specific Author
View only commits made by a particular developer.
git log --author="Alice"
Useful for reviewing contributions by a specific team member.
4. Filter Commits by Date
View commits within a certain date range.
git log --after="2025-09-01" --before="2025-10-01"
Helps track progress during specific development periods.
5. Search Commits by Message Keyword
Find commits with specific keywords in their message.
git log --grep="bug fix"
Useful for locating when a specific feature or fix was introduced.
6. View Files Changed in Each Commit
Show the list of modified files in each commit.
git log --stat
Displays file-level changes and total insertions/deletions.
7. See the Actual Code Changes
To view the full diff (code changes) in each commit:
git log -p
This is very detailed — great for code review and debugging.
Combining Multiple Options
You can also combine options to customize your log view:
git log --oneline --graph --decorate --all
Displays a compact, colorful, and structured commit history - ideal for understanding the overall repository structure.
Colorizing Git Logs
You can add colors to your Git logs to make them more readable and visually organized.
1. Basic Colored Log
git log --oneline --graph --decorate --color
--color → Forces Git to show output with colors.- Combined with
--graph and --decorate, it highlights branches, tags, and commits in different colors.
2. Always Color Git Logs
To make Git always display colors, set the configuration globally:
git config --global color.ui auto
auto - Git will use colors when output is to a terminal.always - Forces colors even when output is piped (less common).never - Disables color.
3. Example Output (Colored)
- Branch names - green
- Tags - yellow
- Commit hashes - red/magenta
- Commit messages - default or white
This makes it much easier to scan commits visually, especially in large projects.
4. Combine With Other Options
You can combine color with your favorite log command:
git log --oneline --graph --decorate --color --all
- Shows all branches
- Displays a graph of commits
- Highlights branches, tags, and commit hashes with color
Log Search : Finding Specific Commits
Git provides several ways to search through commit history, making it easier to locate specific changes, messages, authors, or dates.
1. Search by Commit Message
Use the --grep option to find commits containing specific keywords in their messages:
git log --grep="fix bug"
- Finds all commits with “fix bug” in their commit message.
- Useful for tracking specific features, fixes, or changes.
2. Search by Author
To see all commits made by a particular developer:
git log --author="Alice"
3. Search by Date
Filter commits by a date range using --after and --before:
git log --after="2025-09-01" --before="2025-10-01"
- Shows commits made between the specified dates.
- Useful for tracking work done in a sprint or project phase.
4. Search by File Changes
To see commits that affected a particular file:
git log -- <file-path>
5. Search by Commit Hash
If you know part of the commit hash, you can search for it directly:
git log a1b2c3
Displays the full commit with that hash or any partial match.
6. Combining Search Options
You can combine multiple search filters for precise results:
git log --author="Alice" --grep="login" --after="2025-09-01"
7. git shortlog
Basically it displays the log output format in the following syntax:
Committer1(number of commits)
- Commit Message 1
- Commit Message 2
- Commit Message n
where n represents the last commit message number committed by the author
Committer2(number of commits)
- Commit Message 1
- Commit Message 2
- Commit Message n
where n represents the last commit message number committed by the author
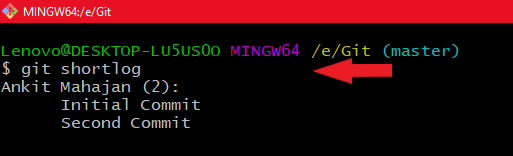 Using git shortlog
Using git shortlogHere, only my commits are shown since I’m the sole contributor. In larger projects, you’ll see multiple developers with their commit counts and messages. The git shortlog command also includes various options to customize its output.
Parameter | Details |
|---|
| -s or --summary | It displays the number of commits and the committer's name |
| -e or --email | It displays the committer's name, number of commits, commit messages along with the mail id |
| -n or --numbered | It sorts the output by the number of commits instead of alphabetically by committer's name |
8. git grep
So how git grep works is if you want to fetch where a particular string exists in a file or whether a particular string is associated with a particular commit id. In such cases git grep is a very useful command. Just you have to pass a particular string in the command when checking for the existence of a string in a file and when checking for a particular string in a commit id mention the string in double quotes.
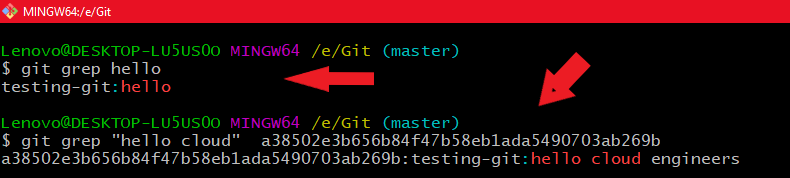 Using git grep
Using git grepFor a range of lines within a file: The command would be the same git log just some new parameters we have to pass in it for checking for a range of lines within a file. The command is:
git log -L starting_line_number,ending_line_number:file_name here -L denotes the line range for a file.
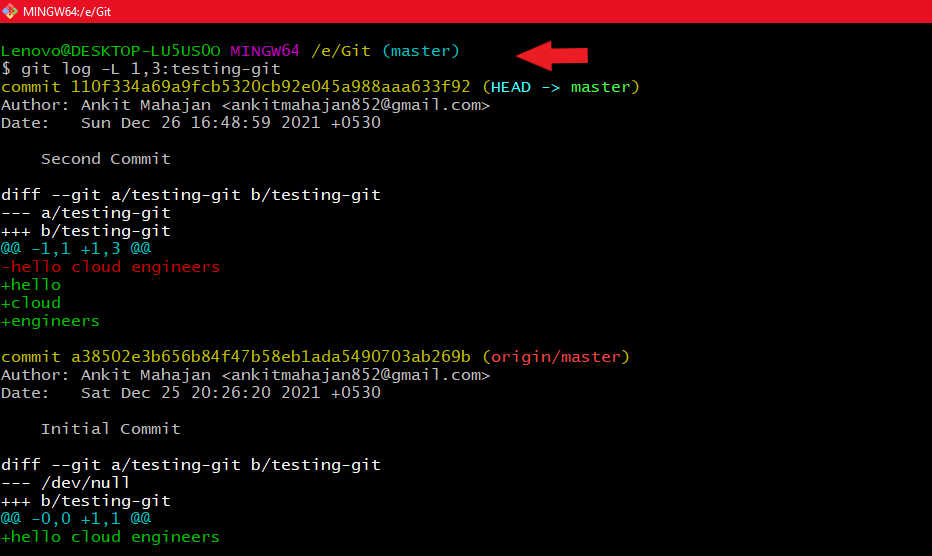 Using git log -L starting_line_number,ending_line_number:file_name
Using git log -L starting_line_number,ending_line_number:file_name9. Filter logs:
In this concept, we will see various parameters used in the command to filter logs.
- For some days: git log --after 'mention the days ago'
- for e.g: git log --after '4 days ago'
- For specific dates: git log --after year_number-month_number-date_number
- For Author name: git log --author="Author_name"
We can also use the since clause instead of after in this command.
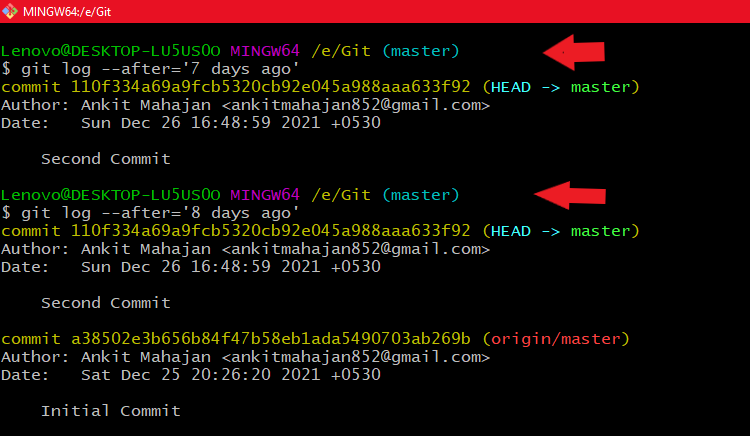 Using git log --after 'number_of_days days ago'
Using git log --after 'number_of_days days ago'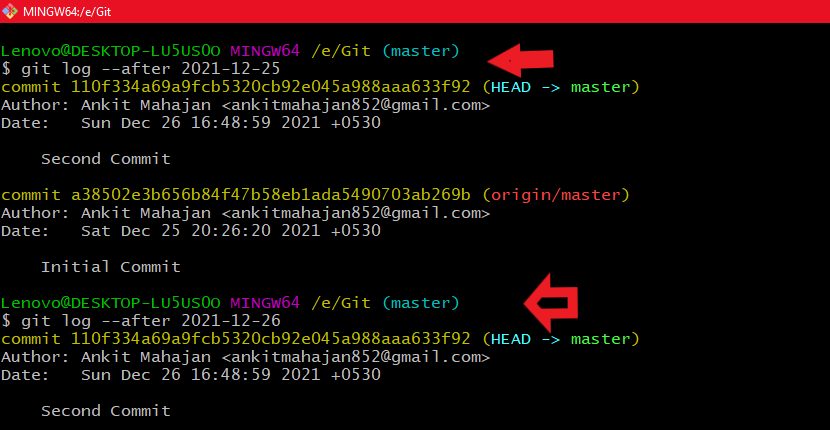 Using git log --after year_number-month_number-Date_number
Using git log --after year_number-month_number-Date_number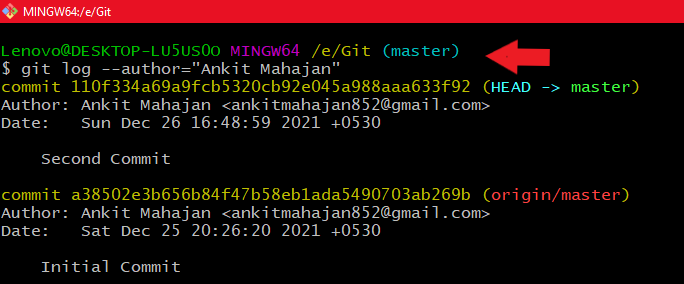 Using git log --author="author-name"
Using git log --author="author-name"10. Changes inline
If our use-case is to see the logs with changes inline we use a parameter -p or --patch to see the logs with changes inline.
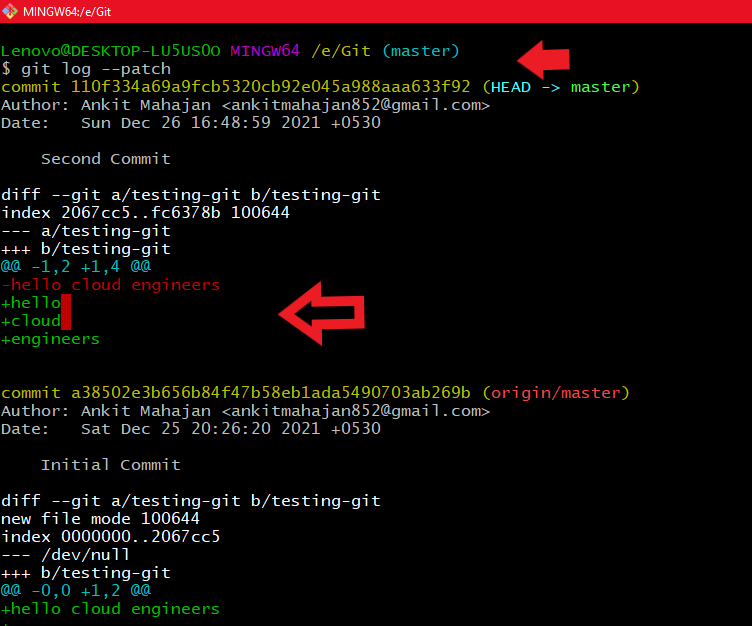 Using git log --patch
Using git log --patch11. Committed files
If you want to see the files in logs that are being committed by commits. we use the command
git log --stat
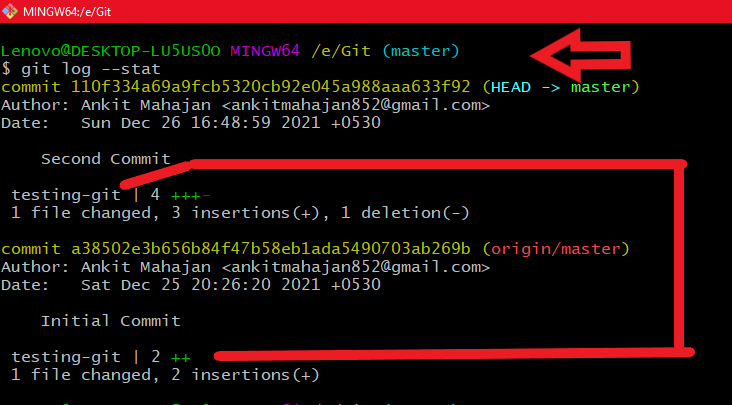 Using git log --stat
Using git log --statContents of a Commit:
Now if you want to view the contents of a commit you can use a simple command
git show commit-id
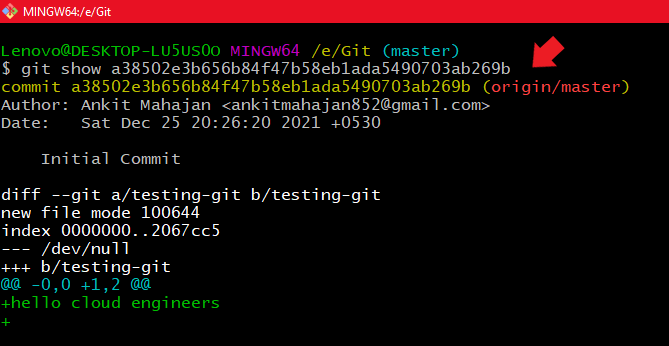 Using git show commit-id
Using git show commit-idCommitter name and time since commit
Now if you want to see the committer name and time since he committed in oneline. We use the following command
git log --oneline --decorate --source --pretty=format:'"%Cblue %h %Cgreen %ar %Cblue %an %C(yellow) %d %Creset %s"' --all --graph
 The output of the above command
The output of the above command
What does the git log command primarily display?
-
-
Complete history of commits in reverse chronological order
-
List of merged branches only
-
Explanation:
git log shows the entire commit history with latest commits first, including hash, author, date, and message.
Which command shows each commit in a compact one-line format?
Explanation:
git log --oneline displays commits in single-line format, useful for quick browsing.
To visually display commit history along with branch structure, which command is used?
-
git log --graph --oneline
-
-
-
Explanation:
--graph draws the branch structure, and --oneline compresses output for better readability.
Which command lists commit history with files changed, insertions, and deletions?
Explanation:
git log --stat shows commit details with file-level statistics like additions and deletions.
What is the purpose of git shortlog?
-
Shows file differences inside commits
-
Lists commits grouped by author with commit count
-
-
Filters logs based on date only
Explanation:
git shortlog organizes commits per contributor, showing number of commits and commit messages.
Quiz Completed Successfully
Your Score : 2/5
Accuracy : 0%
Login to View Explanation
1/5
1/5
< Previous
Next >
Explore
Git Introduction
Git Installation and Setup
All Git Commands
Most Used Git Commands
Git Branch
Git Merge
Git Tools and Integration
Git Remote Repositories
Collaborating with Git
Advanced Git Commands