HDF5 file stands for Hierarchical Data Format 5. It is an open-source file which comes in handy to store large amount of data. As the name suggests, it stores data in a hierarchical structure within a single file. So if we want to quickly access a particular part of the file rather than the whole file, we can easily do that using HDF5. This functionality is not seen in normal text files hence HDF5 is becoming seemingly popular in fact of being a new concept. To use HDF5, numpy needs to be imported. One important feature is that it can attach metaset to every data in the file thus provides powerful searching and accessing. Let's get started with installing HDF5 to the computer.
To install HDF5, type this in your terminal:
pip install h5py
We will use a special tool called HDF5 Viewer to view these files graphically and to work on them. To install HDF5 Viewer, type this code :
pip install h5pyViewer
As HDF5 works on numpy, we would need numpy installed in our machine too.
python -m pip install numpy
After all the installations are done, let's see how can we write into an HDF5 file.
Note: Working with HDF5 requires basic understanding of numpy and its attributes, so one must be familiar with numpy in order to understand the codes following in this article. To know more about numpy click here.
We will create a file and save a random array of numpy in it:
Python3
# Python program to demonstrate
# HDF5 file
import numpy as np
import h5py
# initializing a random numpy array
arr = np.random.randn(1000)
# creating a file
with h5py.File('test.hdf5', 'w') as f:
dset = f.create_dataset("default", data = arr)
Output:

In the above code, we first import the modules which were installed previously. Then we initialize the variable arr to a random array of numpy ranging till 1000.
Hence, we can say that this array consists of a large number of data. Next, we open the file as "write only" attribute. This means that if there isn't any file with the name test.hdf5 then it will create one otherwise it will delete (overwrite) the content of the existing file. While opening the file, we used with instead of open as it has an upper-hand when compared to open() method. We don't need to close a file if we open it using with Finally, we use the .create_dataset() to set the variable dset to the array which was created earlier.
We will now read the file which we wrote above:
Python3
# open the file as 'f'
with h5py.File('test.hdf5', 'r') as f:
data = f['default']
# get the minimum value
print(min(data))
# get the maximum value
print(max(data))
# get the values ranging from index 0 to 15
print(data[:15])
Output:

Here, we open the file again but this time we open it by "read-only" attribute so that no changes can be made to the file. We set the variable data to the data we stored in the previous file. Let's look at the output:
It may seem that there's nothing new. It is just an array and we are printing out the numbers just as in an array. But, the variable data is not an array. It's actually very different than array. It's a dataset. Rather than storing data in the RAM, it saves it in hard-drive of the computer, thus maintaining a hierarchy of structures just like directories:

When the below line is used
data = f['default']
in the previous code, we did not access the content of the file directly but created a pointer to point at our content. Let's look at an advantage of this:
Python3
import numpy as np
import h5py
arr1 = np.random.randn(10000)
arr2 = np.random.randn(10000)
with h5py.File('test_read.hdf5', 'w') as f:
f.create_dataset('array_1', data = arr1)
f.create_dataset('array_2', data = arr2)
We created two datasets but the whole procedure is same as before. A file named "test_read.hdf5" is created using the "w" attribute and it contains two datasets (array1 and array2) of random numbers. Now suppose we want to read only a selective portion of array2. For example, we want to read that part of array2 corresponding to where values of array1 are greater than 1. If we were using the conventional text files instead of HDF5 files, it would be nearly impossible to achieve this. That's exactly were we see the power of HDF5 files:
Python3
with h5py.File('test_read.hdf5', 'r') as f:
d1 = f['array_1']
d2 = f['array_2']
data = d2[d1[:]>1]
We use the [:] to create a copy of the dataset d1 into the RAM. We did this because a dataset (the data in hard-drive) cannot be compared to the integers.
Output:
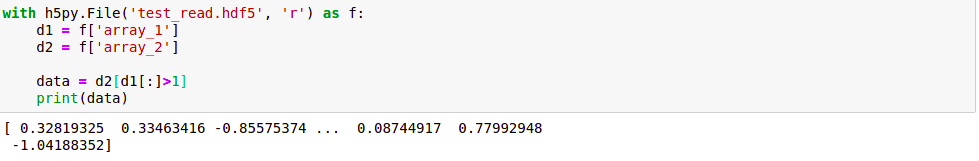
So, we conclude that HDF5 files are our best tools when we are dealing with large files as it allows us selective reading and writing of files which otherwise would have consumed a lot of memory and time.

Similar Reads
Python Tutorial - Learn Python Programming Language Python is one of the most popular programming languages. It’s simple to use, packed with features and supported by a wide range of libraries and frameworks. Its clean syntax makes it beginner-friendly. It'sA high-level language, used in web development, data science, automation, AI and more.Known fo
10 min read
Python Interview Questions and Answers Python is the most used language in top companies such as Intel, IBM, NASA, Pixar, Netflix, Facebook, JP Morgan Chase, Spotify and many more because of its simplicity and powerful libraries. To crack their Online Assessment and Interview Rounds as a Python developer, we need to master important Pyth
15+ min read
Python OOPs Concepts Object Oriented Programming is a fundamental concept in Python, empowering developers to build modular, maintainable, and scalable applications. By understanding the core OOP principles (classes, objects, inheritance, encapsulation, polymorphism, and abstraction), programmers can leverage the full p
11 min read
Python Projects - Beginner to Advanced Python is one of the most popular programming languages due to its simplicity, versatility, and supportive community. Whether you’re a beginner eager to learn the basics or an experienced programmer looking to challenge your skills, there are countless Python projects to help you grow.Here’s a list
10 min read
Python Exercise with Practice Questions and Solutions Python Exercise for Beginner: Practice makes perfect in everything, and this is especially true when learning Python. If you're a beginner, regularly practicing Python exercises will build your confidence and sharpen your skills. To help you improve, try these Python exercises with solutions to test
9 min read
Python Programs Practice with Python program examples is always a good choice to scale up your logical understanding and programming skills and this article will provide you with the best sets of Python code examples.The below Python section contains a wide collection of Python programming examples. These Python co
11 min read
Python Introduction Python was created by Guido van Rossum in 1991 and further developed by the Python Software Foundation. It was designed with focus on code readability and its syntax allows us to express concepts in fewer lines of code.Key Features of PythonPython’s simple and readable syntax makes it beginner-frien
3 min read
Python Data Types Python Data types are the classification or categorization of data items. It represents the kind of value that tells what operations can be performed on a particular data. Since everything is an object in Python programming, Python data types are classes and variables are instances (objects) of thes
9 min read
Input and Output in Python Understanding input and output operations is fundamental to Python programming. With the print() function, we can display output in various formats, while the input() function enables interaction with users by gathering input during program execution. Taking input in PythonPython input() function is
8 min read
Enumerate() in Python enumerate() function adds a counter to each item in a list or other iterable. It turns the iterable into something we can loop through, where each item comes with its number (starting from 0 by default). We can also turn it into a list of (number, item) pairs using list().Let's look at a simple exam
3 min read