Hibernate - One-to-One Mapping
Last Updated :
31 Oct, 2025
In Hibernate, one-to-one mapping defines a relationship where one entity instance is associated with exactly one instance of another entity. It represents a real-world relationship such as:
- A person has one passport.
- A student has one college ID.
- A vehicle has one engine.
Types of One-to-One Mapping
- Unidirectional: Only one entity maintains the reference of the other.
- Bidirectional: Both entities hold references to each other, allowing navigation from either side.
1. One-to-one unidirectional
In unidirectional mapping, one entity (e.g., Student) maintains a reference to the other (StudentGfgDetail), but not vice versa.
 ER Diagram
ER DiagramStep 1: Database Setup
We will use MySQL for this example.
Java
DROP SCHEMA IF EXISTS hb_one_to_one_mapping;
CREATE SCHEMA hb_one_to_one_mapping;
USE hb_one_to_one_mapping;
CREATE TABLE student_gfg_detail (
id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
college VARCHAR(128),
no_of_problems_solved INT DEFAULT 0,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
CREATE TABLE student (
id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
first_name VARCHAR(45),
last_name VARCHAR(45),
email VARCHAR(45),
student_gfg_detail_id INT UNIQUE,
PRIMARY KEY (id),
FOREIGN KEY (student_gfg_detail_id) REFERENCES student_gfg_detail(id)
);
Step 2: Hibernate Configuration
Create hibernate.cfg.xml in src/main/resources:
XML
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hb_one_to_one_mapping?useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true</property>
<property name="connection.username">your_username</property>
<property name="connection.password">your_password</property>
<property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<property name="current_session_context_class">thread</property>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
Step 3: Maven Dependencies
Java
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>5.6.5.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.28</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Step 4: Entity Classes
Student.java
Java
package com.geeksforgeeks.entity;
import javax.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Table(name = "student")
public class Student {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private int id;
@Column(name = "first_name")
private String firstName;
@Column(name = "last_name")
private String lastName;
private String email;
@OneToOne(cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
@JoinColumn(name = "student_gfg_detail_id")
private StudentGfgDetail studentGfgDetail;
public Student() {}
public Student(String firstName, String lastName, String email) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.email = email;
}
public StudentGfgDetail getStudentGfgDetail() { return studentGfgDetail; }
public void setStudentGfgDetail(StudentGfgDetail studentGfgDetail) { this.studentGfgDetail = studentGfgDetail; }
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id=" + id +
", firstName='" + firstName + '\'' +
", lastName='" + lastName + '\'' +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
", studentGfgDetail=" + studentGfgDetail +
'}';
}
}
StudentGfgDetail.java
Java
package com.geeksforgeeks.entity;
import javax.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Table(name = "student_gfg_detail")
public class StudentGfgDetail {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private int id;
private String college;
@Column(name = "no_of_problems_solved")
private int noOfProblemsSolved;
public StudentGfgDetail() {}
public StudentGfgDetail(String college, int noOfProblemsSolved) {
this.college = college;
this.noOfProblemsSolved = noOfProblemsSolved;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "StudentGfgDetail{" +
"id=" + id +
", college='" + college + '\'' +
", noOfProblemsSolved=" + noOfProblemsSolved +
'}';
}
}
Step 5: CRUD Operations
1. Adding Entry (Unidirectional)
Java
package com.geeksforgeeks.application;
import com.geeksforgeeks.entity.Student;
import com.geeksforgeeks.entity.StudentGfgDetail;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
public class AddingEntryDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SessionFactory factory = new Configuration()
.configure("hibernate.cfg.xml")
.addAnnotatedClass(Student.class)
.addAnnotatedClass(StudentGfgDetail.class)
.buildSessionFactory();
try (factory; Session session = factory.getCurrentSession()) {
Student student = new Student("Vyom", "Yadav", "[email protected]");
StudentGfgDetail detail = new StudentGfgDetail("GFG College", 20);
student.setStudentGfgDetail(detail);
session.beginTransaction();
session.save(student); // CascadeType.ALL saves both
session.getTransaction().commit();
System.out.println("Entry added successfully!");
}
}
}
Run the application and verify whether these values have been successfully inserted into the database.
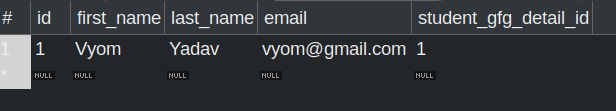 Student Table
Student Table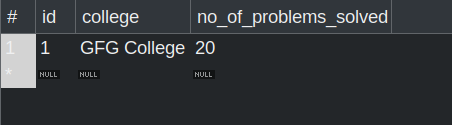 student_gfg_detail Table
student_gfg_detail Table2. Update Entry
Java
Student student = session.get(Student.class, 1);
student.setEmail("[email protected]");
student.getStudentGfgDetail().setNoOfProblemsSolved(40);
session.getTransaction().commit();
Run the application and verify whether these values have been successfully updated into the database.
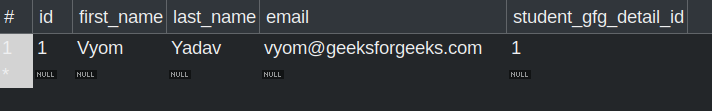 Updated Student table
Updated Student table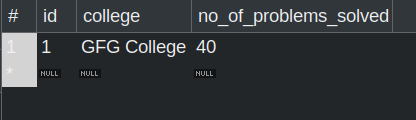 Updated student_gfg_detail Table
Updated student_gfg_detail Table3. Read Entry
Java
Student student = session.get(Student.class, 1);
System.out.println(student);
System.out.println(student.getStudentGfgDetail());
4. Delete Entry
Java
Student student = session.get(Student.class, 1);
session.delete(student); // CascadeType.ALL deletes both
session.getTransaction().commit();
Bidirectional One-to-One Mapping
Unidirectional mapping allows access only one way (Student → StudentGfgDetail). If we want both entities to reference each other, use bidirectional mapping.
Step 1: Entity Modification
Add a student field in StudentGfgDetail and map it back using mappedBy.
StudentGfgDetail.java
Java
package com.geeksforgeeks.entity;
import javax.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Table(name = "student_gfg_detail")
public class StudentGfgDetail {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "id")
private int id;
@Column(name = "college")
private String college;
@Column(name = "no_of_problems_solved")
private int noOfProblemsSolved;
@OneToOne(mappedBy = "studentGfgDetail", cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
private Student student;
public StudentGfgDetail() {}
public StudentGfgDetail(String college, int noOfProblemsSolved) {
this.college = college;
this.noOfProblemsSolved = noOfProblemsSolved;
}
public int getId() { return id; }
public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; }
public String getCollege() { return college; }
public void setCollege(String college) { this.college = college; }
public int getNoOfProblemsSolved() { return noOfProblemsSolved; }
public void setNoOfProblemsSolved(int noOfProblemsSolved) { this.noOfProblemsSolved = noOfProblemsSolved; }
public Student getStudent() { return student; }
public void setStudent(Student student) { this.student = student; }
@Override
public String toString() {
return "StudentGfgDetail{" +
"id=" + id +
", college='" + college + '\'' +
", noOfProblemsSolved=" + noOfProblemsSolved +
", student=" + student +
'}';
}
}
Step 2: Add Entry (Bidirectional)
Java
package com.geeksforgeeks.application;
import com.geeksforgeeks.entity.Student;
import com.geeksforgeeks.entity.StudentGfgDetail;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
public class AddEntryBidirectionalDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SessionFactory factory = new Configuration()
.configure("hibernate.cfg.xml")
.addAnnotatedClass(Student.class)
.addAnnotatedClass(StudentGfgDetail.class)
.buildSessionFactory();
try (factory; Session session = factory.getCurrentSession()) {
Student student = new Student("JJ", "Olatunji", "[email protected]");
StudentGfgDetail detail = new StudentGfgDetail("GFG College", 0);
student.setStudentGfgDetail(detail);
detail.setStudent(student);
session.beginTransaction();
session.save(student); // CascadeType.ALL saves both
session.getTransaction().commit();
System.out.println("Bidirectional entry added successfully!");
}
}
}
Step 3: Read Entry (Bidirectional)
Java
StudentGfgDetail detail = session.get(StudentGfgDetail.class, 5);
System.out.println(detail);
System.out.println(detail.getStudent());
Why Use Bidirectional Mapping?
- Allows navigation in both directions (Student ↔ StudentGfgDetail).
- Prevents dangling foreign keys if a related record is deleted.
- Makes entity relationship management cleaner and more flexible.
Explore
Java Enterprise Edition
Multithreading
Concurrency
JDBC (Java Database Connectivity)
Java Frameworks
JUnit