How to Back Commit in Git?
Last Updated :
23 Jul, 2025
In this article, we are covering how to undo commits in Git. Sometimes, you might make mistakes or realize you need to revert changes you made in a previous commit. Luckily, Git offers a few ways to undo commits.
Approach 1: Using 'git revert'
'git revert' is the generally preferred approach as it creates a new commit that essentially cancels out the changes introduced by the commit you want to undo. The original commit remains in the history, but the new revert commit applies the opposite changes, effectively reversing the effects of the original commit.
Step 1: Identify the commit to revert
You'll need the commit hash of the specific commit you want to revert. You can find this using the `git log` command.
git log
This command will display the history of your commits, including their unique hash IDs.
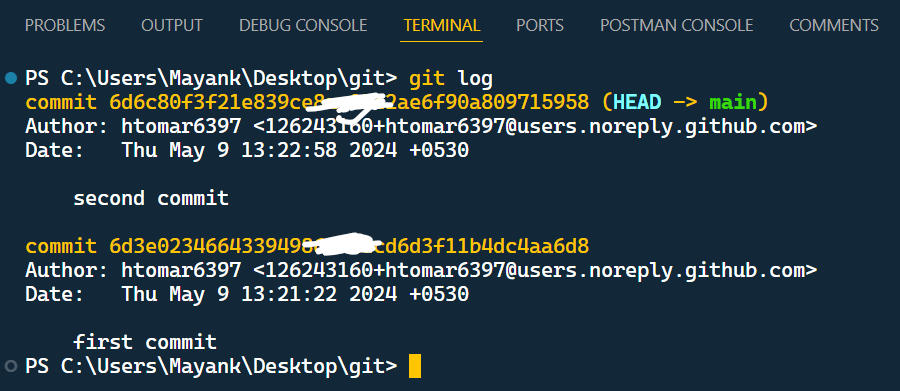 Identify the commit to revert
Identify the commit to revertStep 2: Execute the 'git revert' command
Once you have the commit hash, use the following command to initiate the revert process.
git revert <commit-hash>
Replace '<commit-hash>' with the actual hash ID of the commit you want to revert.
For example, to revert the most recent commit, you can use:
git revert HEAD
 Execute the `git revert` command
Execute the `git revert` command Step 3: Review and commit the changes
Git will create a new commit that reverses the changes introduced by the specified commit. You'll be given a chance to review the changes introduced by the revert commit before committing it.
Step 4: Push the revert commit (if necessary)
If you've already shared your commits with a remote repository (e.g., GitHub), you'll need to push the newly created revert commit as well:
git push origin <your-branch-name>
Replace '<your-branch-name>' with the name of the branch you're working on.
Approach 2: Using 'git reset'
'git reset' offers a more forceful approach to undoing commits. It directly rewrites Git history by moving the HEAD pointer back to a previous commit. This can be useful if you want to completely remove the unwanted commit from the history. However, use 'git reset' cautiously, especially if you've already shared your commits with others, as it can cause issues for collaborators who have pulled the original commit.
Step 1: Identify the commit to reset to
Similar to 'git revert', you'll need the commit hash of the commit you want to reset to. Use 'git log' to find the desired commit hash.
Step 2: Execute the 'git reset' command
Use the following command to move the HEAD pointer back to the desired commit.
git reset --hard <commit-hash>
Replace '<commit-hash>' with the actual hash ID of the commit you want to reset to.
 Execute the 'git reset' command
Execute the 'git reset' commandWarning: Uncommitted changes will be lost!
Before running 'git reset --hard', be aware that any uncommitted changes you have in your working directory will be discarded.
Step 3: Force push (if necessary, use with caution)
If you've already pushed the commit you want to remove and need to update the remote repository, you'll have to use a force push.
git push --force origin <your-branch-name>
Warning: Force pushing rewrites remote history on the server, potentially causing problems for collaborators who have already pulled the original commit. Use it as a last resort, and communicate the changes clearly to your team.
Choosing the Right Approach
In most cases, `git revert` is the recommended approach as it creates a clearer audit trail and avoids potentially disruptive rewrites of history. Use `git reset` cautiously, especially when collaborating with others.
Additional Considerations
- If you have uncommitted changes before using `git reset --hard`, you can use `git stash` to save them temporarily and reapply them later.
- `git revert` offers more flexibility as you can inspect the changes introduced by the revert commit before committing it.
Explore
Git Tutorial
6 min read
Git Introduction
Git Installation and Setup
All Git Commands
Most Used Git Commands
Git Branch
Git Merge
Git Tools and Integration
Git Remote Repositories
Collaborating with Git