How to Fix - Reading A File: Permission Denied on Linux
Last Updated :
23 Jul, 2025
In this article, we will see how to fix when a permission error occurs while reading any file in Linux. We'll see how to fix that and also why that error occurs, and its common causes so that in future you will be able to solve those kinds of errors yourself. We'll learn various methods to solve this error allowing you to choose the approach that best suits your preferences.
Error: Reading A File: Permission Denied
 Error
ErrorWhat is Reading A File: Permission Denied on Linux?
"Reading a file: Permission denied" on Linux is an error message that indicates the user or process attempting to read a file does not have the necessary permissions to do so. In Linux and Unix-based systems, file permissions are controlled through the file's permission settings, which include read, write, and execute permissions for the file owner, group, and others.
Here are some common scenarios where you might encounter the "Permission denied" error while trying to read a file:
- Insufficient Permissions: If the file you are trying to read does not have read permissions set for your user or group, you will encounter a "Permission denied" error. You can check the file's permissions using the
ls -l command in the terminal. - Ownership: If the file is owned by another user or group, and you do not belong to that user or group, you may not have permission to read the file. Only the file owner or users with appropriate permissions can access the file.
- File Location: If the file is located in a directory where you do not have read permissions, you will not be able to access the file even if the file itself has the correct permissions set.
How to Fix - Reading A File: Permission Denied on Linux?
Below are the solutions to resolve the “Reading A File: Permission Denied” problem in the Linux Operating System.
Solution 1: Changing File Permission
Step 1: To fix "Reading A File: Permission Denied" on Linux, you can change the file's permissions using the chmod command. First, check the current permissions with ls -l, where the output shows permissions for the owner, group, and others in the format rwxrwxrwx. Use chmod to modify permissions, such as chmod +r filename to add read permission for the file. If you don't have permission to change permissions, use sudo before the chmod command.
Syntax:
ls -l or ls -l filename
Example: This will list the current permissions granted to the file.
ls -l
Output:
 Check File Permissions
Check File PermissionsStep 2: Now change the file permission so that the user can read the file. For that, we have to chmod command specifying whom you want to give permission to owner/user (u), group (g), others (o), or all (a) followed by the '+' symbol which means to give permission and then that followed by the 'r' which means 'read' and after that filename.
Syntax:
chmod [recipient]+r filename
Example: This will grant read permission to the user, others, and the group.
chmod og+r demo.txt #read permission to other and group
or
chmod u+r demo.txt #read permission to user
Output:
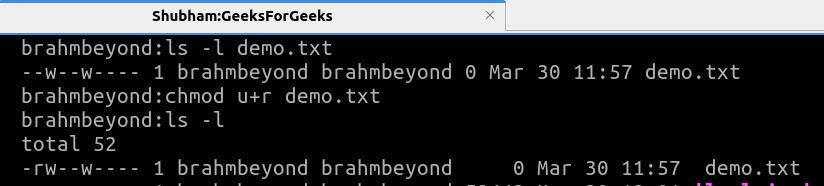 File Permission Changed
File Permission ChangedSolution 2: Using sudo Command
You can use the sudo command to run commands as a superuser, allowing you to access files and perform actions that require elevated privileges. For example, if you encounter "Permission Denied" while reading a file, you can use sudo cat filename to read the file with superuser permissions. This grants you the necessary access to bypass permission restrictions and read the file content.
Syntax:
sudo cat <filename>
Example: Using sudo with cat command to read demo.txt file
sudo cat demo.txt
Output:
 Reading files being superuser
Reading files being superuserSolution 3: Change file Ownership
You can change the ownership of the file using the chown command. For instance, if the file is owned by another user and you have permission to change ownership, you can use sudo chown your_username filename to change ownership to your user account. This allows you to read the file without encountering "Permission Denied."
Syntax:
sudo chown <your_username> <filename>
Example: This command will change the ownership of the file and grant read permissions to the brahmbeyond user.
sudo chown brahmbeyond test.txt
Output:
 Transferred the ownership from root to user
Transferred the ownership from root to userTo verify and read the file after granting permission, execute the below command in the terminal to read the contents of the file.
Command:
cat test.txt
Output:
 Reading File Contents
Reading File Contents
Conclusion
In conclusion, when encountering "Reading A File: Permission Denied" on Linux, understanding file permissions, ownership, and file locations is crucial. Solutions such as changing file permissions with chmod, using sudo for elevated privileges, and changing file ownership with chown provide ways to resolve this error effectively, ensuring access to the file content without permission issues.
Similar Reads
How to Fix SSH Failed Permission Denied SSH, or Secure Shell, is a widely used protocol for securely accessing and managing remote devices over unsecured networks. By using cryptographic network protocols, SSH ensures the confidentiality and integrity of data exchanged between devices, providing a secure channel for communication. Develop
7 min read
How to Set File Permissions in Linux Linux file permissions form the foundation of the system’s security model. They define who can read, write, or execute files and directories, ensuring only authorized users or processes can access sensitive data. You can modify these permissions using the chmod command.chmod +rwx filename – Adds rea
9 min read
How to Fix: PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission Denied in Python When your Python code encounters a situation where it lacks the necessary permissions to access a file or directory, it raises PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied in Python. This article will explore how to address the Errno 13 Error in Python effectively.What is PermissionError: [Errno 13
5 min read
How to Fix - rm: Cannot Remove Directory/: Permission Denied In Linux, file removal, particularly directories, is a common task performed using the rm command. However, encountering a "Permission Denied" error can hinder this process, often due to insufficient permissions or system restrictions. Since, encountering the error "rm: Cannot Remove Directory/: Per
3 min read
Advance File Permissions in Linux The Linux file permissions are not limited to "rwx" bits, there are 3 special permissions apart from these "rwx" permissions which are SUID,SGID,The Sticky Bit. This article is about the 3 special file permissions and how to set and remove those permission bits. Set-user-ID (SUID) In Linux by defaul
4 min read
How To Resolve Permission Denied Error On Ubuntu/Debian? Linux is a community of open-source Unix-like operating systems that are based on the Linux Kernel. Linux distributions are constructed in such a secure way that a user cannot make changes unless he/she has administration access. Users who are first time exploring Linux encounter the problem of Perm
3 min read