JDBC (Java Database Connectivity)
Last Updated :
12 Jul, 2025
JDBC is an API that helps applications to communicate with databases, it allows Java programs to connect to a database, run queries, retrieve, and manipulate data. Because of JDBC, Java applications can easily work with different relational databases like MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, and more.
JDBC Architecture
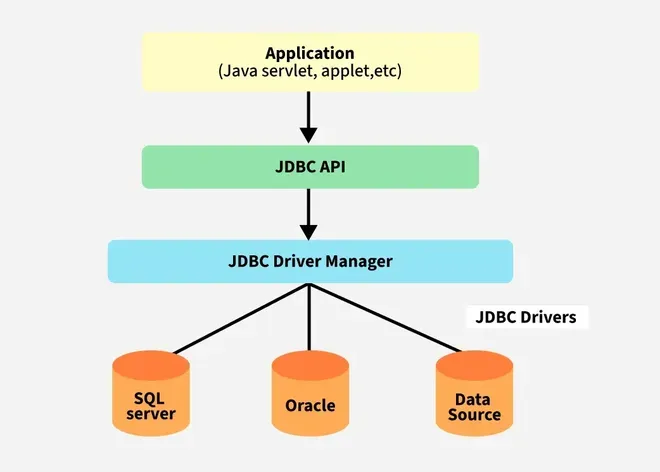
Explanation:
- Application: It can be a Java application or servlet that communicates with a data source.
- The JDBC API: It allows Java programs to execute SQL queries and get results from the database. Some key components of JDBC API include
- Interfaces like Driver, ResultSet, RowSet, PreparedStatement, and Connection that helps managing different database tasks.
- Classes like DriverManager, Types, Blob, and Clob that helps managing database connections.
- DriverManager: It plays an important role in the JDBC architecture. It uses some database-specific drivers to effectively connect enterprise applications to databases.
- JDBC drivers: These drivers handle interactions between the application and the database.
The JDBC architecture consists of two-tier and three-tier processing models to access a database. They are as described below:
1. Two-Tier Architecture
A Java Application communicates directly with the database using a JDBC driver. It sends queries to the database and then the result is sent back to the application. For example, in a client/server setup, the user's system acts as a client that communicates with a remote database server.
Structure:
Client Application (Java) -> JDBC Driver -> Database
2. Three-Tier Architecture
In this, user queries are sent to a middle-tier services, which interacts with the database. The database results are processed by the middle tier and then sent back to the user.
Structure:
Client Application -> Application Server -> JDBC Driver -> Database
JDBC Components
There are generally 4 main components of JDBC through which it can interact with a database. They are as mentioned below:
1. JDBC API
It provides various methods and interfaces for easy communication with the database. It includes two key packages
- java.sql: This package, is the part of Java Standard Edition (Java SE) , which contains the core interfaces and classes for accessing and processing data in relational databases. It also provides essential functionalities like establishing connections, executing queries, and handling result sets
- javax.sql: This package is the part of Java Enterprise Edition (Java EE) , which extends the capabilities of
java.sql by offering additional features like connection pooling, statement pooling, and data source management.
It also provides a standard to connect a database to a client application.
2. JDBC Driver Manager
Driver manager is responsible for loading the correct database-specific driver to establish a connection with the database. It manages the available drivers and ensures the right one is used to process user requests and interact with the database.
3. JDBC Test Suite
It is used to test the operation(such as insertion, deletion, updating) being performed by JDBC Drivers.
4. JDBC Drivers
JDBC drivers are client-side adapters (installed on the client machine, not on the server) that convert requests from Java programs to a protocol that the DBMS can understand. There are 4 types of JDBC drivers:
- Type-1 driver or JDBC-ODBC bridge driver
- Type-2 driver or Native-API driver (partially java driver)
- Type-3 driver or Network Protocol driver (fully java driver)
- Type-4 driver or Thin driver (fully java driver) - It is a widely used driver. The older drivers like (JDBC-ODBC) bridge driver have been deprecated and no longer supported in modern versions of Java.
JDBC Classes and Interfaces
Class/Interfaces | Description |
|---|
| DriverManager | Manages JDBC drivers and establishes database connections. |
| Connection | Represents a session with a specific database. |
| Statement | Used to execute static SQL queries. |
| PreparedStatement | Precompiled SQL statement, used for dynamic queries with parameters. |
| CallableStatement | Used to execute stored procedures in the database. |
| ResultSet | Represents the result set of a query, allowing navigation through the rows. |
| SQLException | Handles SQL-related exceptions during database operations. |
Steps to Connect to MySQL Database Using JDBC
Step 1: Load the JDBC Driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
Step 2: Establish a Connection
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/your_database",
"your_username",
"your_password"
);
Step 3: Create a Statement
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
Step 4: Execute a Query
String query = "INSERT INTO students (id, name) VALUES (101, 'John Doe')";
int rowsAffected = statement.executeUpdate(query);
System.out.println("Rows affected: " + rowsAffected);
Step 5: Close the Connection
statement.close();
connection.close();
Create a Simple JDBC Application
The below Java program demonstrates how to establish a MYSQL database connection using JDBC and execute a query.
Java
// Java program to implement a simple JDBC application
import java.sql.*;
public class Geeks {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Database URL, username, and password
// Replace with your database name
String url
= "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/your_database";
// Replace with your MySQL username
String username = "your_username";
// Replace with your MySQL password
String password = "your_password";
// Updated query syntax for modern databases
String query
= "INSERT INTO students (id, name) VALUES (109, 'bhatt')";
// Establish JDBC Connection
try {
// Load Type-4 Driver
// MySQL Type-4 driver class
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
// Establish connection
Connection c = DriverManager.getConnection(
url, username, password);
// Create a statement
Statement st = c.createStatement();
// Execute the query
int count = st.executeUpdate(query);
System.out.println(
"Number of rows affected by this query: "
+ count);
// Close the connection
st.close();
c.close();
System.out.println("Connection closed.");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.err.println("JDBC Driver not found: "
+ e.getMessage());
}
catch (SQLException e) {
System.err.println("SQL Error: "
+ e.getMessage());
}
}
}
Output:

Note: When the program runs successfully, a new record is added to the students table as shown below:

Key Features of JDBC:
- Platform Independence: JDBC can perform database operation on any platform
- Standard API: It provides different ways to interact with different databases.
- Support for Multiple Databases: JDBC provide support to work with different databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, etc.
Similar Reads
Java Database Connectivity with MySQL In Java, we can connect our Java application with the MySQL database through the Java code. JDBC ( Java Database Connectivity) is one of the standard APIs for database connectivity, using it we can easily run our query, statement, and also fetch data from the database. Prerequisite to understand Jav
3 min read
Establishing JDBC Connection in Java Before Establishing a JDBC Connection in Java (the front end, i.e., your Java Program, and the back end, i.e., the database), we should learn what precisely a JDBC is and why it came into existence. Now, let us discuss what exactly JDBC stands for and why it is essential, and how to establish a data
7 min read
Establishing JDBC Connection in Java Before Establishing a JDBC Connection in Java (the front end, i.e., your Java Program, and the back end, i.e., the database), we should learn what precisely a JDBC is and why it came into existence. Now, let us discuss what exactly JDBC stands for and why it is essential, and how to establish a data
7 min read
Servlet - Database Access Servlets are mainly used in Dynamic web applications which provides dynamic responses to client requests. In most cases, Dynamic web applications access a database to provide the client requested data. We can use Java standard database connection - JDBC in Servlets to perform database operations. To
8 min read
Difference between JDBC and Hibernate in Java Java is one of the most powerful and popular server-side languages in the current scenario. One of the main features of a server-side language is the ability to communicate with the databases. In this article, let's understand the difference between two ways of connecting to the database (i.e.) JDBC
2 min read
Java Servlet and JDBC Example | Insert data in MySQL Prerequisites: Servlet, JDBC Connectivity To start with interfacing Java Servlet Program with JDBC Connection: Proper JDBC Environment should set-up along with database creation. To do so, download the mysql-connector.jar file from the internet, As it is downloaded, move the jar file to the apache-t
4 min read