Iterative Boundary Traversal of Complete Binary tree
Last Updated :
11 Jul, 2025
Given a complete binary tree, the task is to traverse it such that all the boundary nodes are visited in Anti-Clockwise order starting from the root.
Example:
Input:
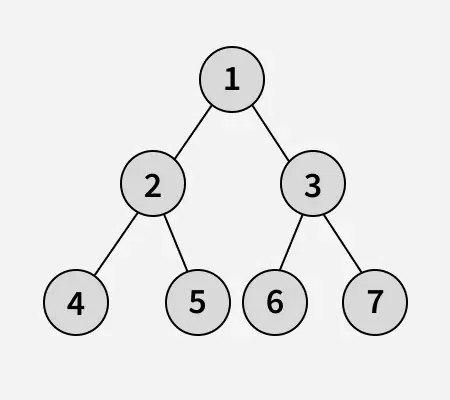
Output: 1 2 4 5 6 7 3
Input:

Output: 18 15 40 50 100 20 30
Approach:
- Traverse left-most nodes of the tree from top to down. (Left boundary)
- Traverse bottom-most level of the tree from left to right. (Leaf nodes)
- Traverse right-most nodes of the tree from bottom to up. (Right boundary)
We can traverse the left boundary quite easily with the help of a while loop that checks when the node doesn't have any left child. Similarly, we can traverse the right boundary quite easily with the help of a while loop that checks when the node doesn't have any right child.
The main challenge here is to traverse the last level of the tree in left to right order. To traverse level-wise there is BFS and order of left to right can be taken care of by pushing left nodes in the queue first. So the only thing left now is to make sure it is the last level. Just check whether the node has any child and only include them.
We will have to take special care of the corner case that same nodes are not traversed again. In the below example 40 is a part of the left boundary as well as leaf nodes. Similarly, 20 is a part of the right boundary as well as leaf nodes. So we will have to traverse only till the second last node of both the boundaries in that case. Also keep in mind we should not traverse the root again.

C++
// C++ program to print boundary traversal
// of a complete binary tree.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = nullptr;
right = nullptr;
}
};
// Function to print the nodes of a complete
// binary tree in boundary traversal order
vector<int> boundaryTraversal(Node *root) {
vector<int> ans;
if (root == nullptr)
return ans;
// If there is only 1 node print it
// and return
if (!(root->left) && !(root->right)) {
ans.push_back(root->data);
return ans;
}
ans.push_back(root->data);
// Traverse left boundary without root
// and last node
Node *l = root->left;
while (l->left) {
ans.push_back(l->data);
l = l->left;
}
// BFS designed to only include
// leaf nodes
queue<Node *> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
Node *curr = q.front();
q.pop();
if (!(curr->left) && !(curr->right)) {
ans.push_back(curr->data);
}
if (curr->left) {
q.push(curr->left);
}
if (curr->right) {
q.push(curr->right);
}
}
// Traverse right boundary without root
// and last node
vector<int> list;
Node *r = root->right;
while (r->right)
{
list.push_back(r->data);
r = r->right;
}
// Concatenate the ans and list
for (int i = list.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
ans.push_back(list[i]);
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
// Create a hard coded tree.
// 18
// / \
// 15 30
// / \ / \
// 40 50 100 20
Node *root = new Node(18);
root->left = new Node(15);
root->right = new Node(30);
root->left->left = new Node(40);
root->left->right = new Node(50);
root->right->left = new Node(100);
root->right->right = new Node(20);
vector<int> ans = boundaryTraversal(root);
int n = ans.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << ans[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}
// Java program to print boundary traversal
// of a complete binary tree.
import java.util.*;
class Node {
int data;
Node left;
Node right;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
class GfG {
// Function to print the nodes of a complete
// binary tree in boundary traversal order
static List<Integer> boundaryTraversal(Node root) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null)
return ans;
// If there is only 1 node print it
// and return
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
ans.add(root.data);
return ans;
}
ans.add(root.data);
// Traverse left boundary without root
// and last node
Node l = root.left;
while (l != null && l.left != null) {
ans.add(l.data);
l = l.left;
}
// BFS designed to only include leaf nodes
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Node curr = q.poll();
if (curr.left == null && curr.right == null) {
ans.add(curr.data);
}
if (curr.left != null) {
q.add(curr.left);
}
if (curr.right != null) {
q.add(curr.right);
}
}
// Traverse right boundary without root
// and last node
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Node r = root.right;
while (r != null && r.right != null) {
list.add(r.data);
r = r.right;
}
// Concatenate the ans and list
for (int i = list.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
ans.add(list.get(i));
}
return ans;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a hard coded tree.
// 18
// / \
// 15 30
// / \ / \
// 40 50 100 20
Node root = new Node(18);
root.left = new Node(15);
root.right = new Node(30);
root.left.left = new Node(40);
root.left.right = new Node(50);
root.right.left = new Node(100);
root.right.right = new Node(20);
List<Integer> ans = boundaryTraversal(root);
for (int value : ans) {
System.out.print(value + " ");
}
}
}
# Python program to print boundary traversal
# of a complete binary tree.
class Node:
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Function to print the nodes of a complete
# binary tree in boundary traversal order
def boundary_traversal(root):
ans = []
if root is None:
return ans
# If there is only 1 node print it
# and return
if root.left is None and root.right is None:
ans.append(root.data)
return ans
ans.append(root.data)
# Traverse left boundary without root
# and last node
l = root.left
while l and l.left:
ans.append(l.data)
l = l.left
# BFS designed to only include leaf nodes
from collections import deque
q = deque([root])
while q:
curr = q.popleft()
if curr.left is None and curr.right is None:
ans.append(curr.data)
if curr.left:
q.append(curr.left)
if curr.right:
q.append(curr.right)
# Traverse right boundary without root
# and last node
list = []
r = root.right
while r and r.right:
list.append(r.data)
r = r.right
# Concatenate the ans and list
ans.extend(reversed(list))
return ans
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Create a hard coded tree.
# 18
# / \
# 15 30
# / \ / \
# 40 50 100 20
root = Node(18)
root.left = Node(15)
root.right = Node(30)
root.left.left = Node(40)
root.left.right = Node(50)
root.right.left = Node(100)
root.right.right = Node(20)
ans = boundary_traversal(root)
for value in ans:
print(value, end=" ")
// C# program to print boundary traversal
// of a complete binary tree.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Node {
public int data;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
class GfG {
// Function to print the nodes of a complete
// binary tree in boundary traversal order
static List<int> boundaryTraversal(Node root) {
List<int> ans = new List<int>();
if (root == null)
return ans;
// If there is only 1 node print it
// and return
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
ans.Add(root.data);
return ans;
}
ans.Add(root.data);
// Traverse left boundary without root
// and last node
Node l = root.left;
while (l != null && l.left != null) {
ans.Add(l.data);
l = l.left;
}
// BFS designed to only include leaf nodes
Queue<Node> q = new Queue<Node>();
q.Enqueue(root);
while (q.Count > 0) {
Node curr = q.Dequeue();
if (curr.left == null && curr.right == null) {
ans.Add(curr.data);
}
if (curr.left != null) {
q.Enqueue(curr.left);
}
if (curr.right != null) {
q.Enqueue(curr.right);
}
}
// Traverse right boundary without root
// and last node
List<int> list = new List<int>();
Node r = root.right;
while (r != null && r.right != null) {
list.Add(r.data);
r = r.right;
}
// Concatenate the ans and list
for (int i = list.Count - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
ans.Add(list[i]);
}
return ans;
}
static void Main(string[] args) {
// Create a hard coded tree.
// 18
// / \
// 15 30
// / \ / \
// 40 50 100 20
Node root = new Node(18);
root.left = new Node(15);
root.right = new Node(30);
root.left.left = new Node(40);
root.left.right = new Node(50);
root.right.left = new Node(100);
root.right.right = new Node(20);
List<int> ans = boundaryTraversal(root);
foreach(var value in ans) {
Console.Write(value + " ");
}
}
}
// JavaScript program to print boundary traversal
// of a complete binary tree.
class Node {
constructor(x) {
this.data = x;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
// Function to print the nodes of a complete
// binary tree in boundary traversal order
function boundaryTraversal(root) {
let ans = [];
if (root === null)
return ans;
// If there is only 1 node print it
// and return
if (root.left === null && root.right === null) {
ans.push(root.data);
return ans;
}
ans.push(root.data);
// Traverse left boundary without root
// and last node
let l = root.left;
while (l && l.left) {
ans.push(l.data);
l = l.left;
}
// BFS designed to only include leaf nodes
let queue = [];
queue.push(root);
while (queue.length > 0) {
let curr = queue.shift();
if (curr.left === null && curr.right === null) {
ans.push(curr.data);
}
if (curr.left) {
queue.push(curr.left);
}
if (curr.right) {
queue.push(curr.right);
}
}
// Traverse right boundary without root
// and last node
let list = [];
let r = root.right;
while (r && r.right) {
list.push(r.data);
r = r.right;
}
// Concatenate the ans and list
for (let i = list.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
ans.push(list[i]);
}
return ans;
}
// Create a hard coded tree.
// 18
// / \
// 15 30
// / \ / \
// 40 50 100 20
let root = new Node(18);
root.left = new Node(15);
root.right = new Node(30);
root.left.left = new Node(40);
root.left.right = new Node(50);
root.right.left = new Node(100);
root.right.right = new Node(20);
let ans = boundaryTraversal(root);
for (let value of ans) {
console.log(value + " ");
}
Output18 15 40 50 100 20 30
Time Complexity: O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the tree.
Auxiliary Space: O(n)
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem