Java Program to Print the Elements of an Array
An array is a data structure that stores a collection of like-typed variables in contiguous memory allocation. Once created, the size of an array in Java cannot be changed. It’s important to note that arrays in Java function differently than they do in C/C++
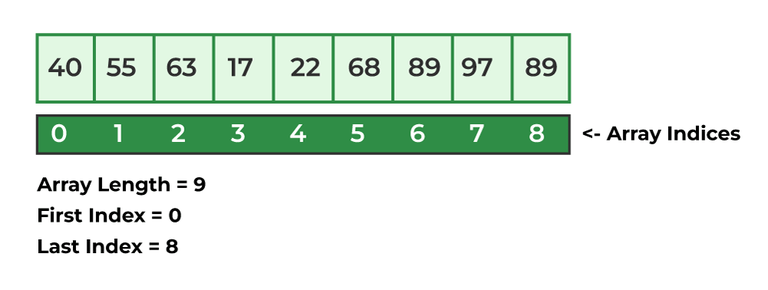
As you see, the array of size 9 holds elements including 40, 55, 63, 17, 22, 68, 89, 97, and 89. and each element has its corresponding index value. we can use this index value i.e. array_name[Index_Value] to access the element.
Properties of Java Array
Here are some important points about Java Arrays:
- In Java, all arrays are dynamically allocated.
- Since arrays are objects in Java, user can find their length using the object property length. This is different from C/C++ where length is calculated using function sizeof()
- A Java array variable can also be declared like other variables with [] after the data type.
- The variables in the array are ordered and each has an index beginning from 0.
- Java array can be also be used as a static field, a local variable, or a method parameter.
- The size of an array must be specified by an int value and not long or short.
- The direct superclass of an array type is Object.
- Every array type implements the interfaces Cloneable and java.io.Serializable.
How to Print an Array in Java?
There are two methods to Print an Array in Java as mentioned below:
- Using for loop
- Using standard library arrays
- Using while loop
- Using forEach() method
1. Printing elements of an array Using for loop
The algorithm used in this approach is as follows:
Step 1: Declare and initialize an array.
Step 2: Loop through the array by incrementing the value of the iterative variable/s.
Step 3: Print out each element of the array.
Below is the Java example illustrating the printing elements of an array
// Java Program to Print the Elements of an Array
// Using for loop
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initialize array of random numbers and size
// Suppose array named 'arr' contains 9 elements
int[] arr = { -7, -5, 5, 10, 0, 3, 20, 25, 12 };
System.out.print("Elements of given array are: ");
// Looping through array by incrementing value of i
//'i' is an index of array 'arr'
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
// Print array element present at index i
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
}
Output
Elements of given array are: -7 -5 5 10 0 3 20 25 12
The complexity of the above method:
Time Complexity: O(n) Here other no major execution is taking place except just the cell memory taken by variables that even get destroyed as the scope is over. Whenever there is iteration just by using one loop time taken is of the order of n always. If nested then the order of number of loops that are nested
Space Complexity: O(1) because the algorithm uses only a constant amount of extra space for variables (
arr,i, andSystem.out), regardless of the size of the input array.
2. Printing Elements of an Array Using Standard Library Arrays
The algorithm used in the approach:
Step 1: Declare and initialize an array
Step 2: Use Arrays.toString() function inside the print statement to print array
Below is the implementation of the above method:
// Java Program to Print the Elements of an Array
// Importing specific array class
// so as to use inbuilt functions
import java.util.Arrays;
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initialize array
// Array 'arr' contains 9 elements
int[] arr = { -7, -5, 5, 10, 0, 3, 20, 25, 12 };
System.out.print("Elements of given array are: ");
// Pass the array 'arr' in Arrays.toString()
// function to print array
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
Output
Elements of given array are: [-7, -5, 5, 10, 0, 3, 20, 25, 12]
The complexity of the above method
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(n)
3. Printing elements of an array Using while loop
The algorithm used in the approach
Step 1: Declare and initialize an array.
Step 2: Use the while loop to iterate over the array elements.
Step 3: Print out each element of the array.
Below is the implementation of the above discussed approach:
// Java Program to Print the Elements of an Array
// Using while loop
public class GFG {
// main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Initialize array of random numbers and size
int[] arr = { -17, 15, 5, 10, 0, 3, 18, 25, 12 };
System.out.print("Elements of the given array are: ");
// while loop to iterate through array
int i = 0;
while (i < arr.length) {
// Print array elements
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
i++;
}
}
}
Output
Elements of the given array are: -17 15 5 10 0 3 18 25 12
The complexity of the above code:
Time Complexity: O(n )
Space Complexity: O(1) or Constant
4. Printing elements of an array Using forEach() method
The algorithm used in the approach:
Step 1: Declare and initialize an array.
Step 2: Use Arrays.stream() to convert the array to a stream.
Step 3: Then print array elements using forEach() method
Below is the example of printing elements of an array using forEach() method:
// Java Program to Print the Elements of an Array
// Using forEach() method
import java.util.Arrays;
public class GFG {
// main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Initialize array of random numbers and size
int[] arr = { -17, 15, 5, 10, 0, 3, 18, 25, 12 };
System.out.println("Elements of the given array are: ");
// Using Arrays.stream() to convert the array to a stream
Arrays.stream(arr)
// printing the elements
.forEach(elem -> System.out.println(elem));
}
}
Output
Elements of the given array are: -17 15 5 10 0 3 18 25 12
The complexity of the above approach:
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(1) or Constant
How to Print Java Multidimensional Array?
Printing a Multidimensional Array is more like a one-dimensional Array.
Below is the implementation of the above method:
// Java Program for printing
// Java multidimensional array
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[][] array
= { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 }, { 7, 8, 9 } };
System.out.println(
"Values of Multi-Dimensional Array:");
System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(array));
}
}
Output
Values of Multi-Dimensional Array: [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]