The JDBC ResultSet is an Object that represents the result of a SQL Query executed on a database. It has a cursor that points to the current row in the ResultSet and we are able to navigate in the ResultSet by using the next(), previous(), first() and last() methods. We can retrieve data using different methods, such as getString(), getInt() and getDouble(), among others.
JDBC ResultSet Usage Example
Java
try {
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM your_table");
while (rs.next()) {
// Process the result set
}
rs.close();
stmt.close();
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace(); // Handle the exception
}
Common Operations with ResultSet
- Fetching data from database: We can fetch data from the database based on the requirements by using conditional statements.
- Navigating the ResultSet: We can able navigating the ResultSet by using methods like next(), previous(), first() and last().
- Getting column values: We can fetch column values with specific conditions or without conditions.
- Closing the result: Once database operations are completed we need close the connections related to database here we close the ResultSet connection. By using close method.
Types of ResultSet
There are three different characteristics by which ResultSet types are differentiated
Determines whether you can move back and forth in the ResultSet
- TYPE_FORWARD_ONLY: Can only move forward through the rows
- TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE: Can move forward and backward but changes are not reflect ResultSet
- TYPE_SCROLL_SENSITIVE: Can move forward and backward but changes are affect the ResultSet
2. Concurrency
Determines whether you can update the ResultSet
- CONCUR_READ_ONLY: Can only read data
- CONCUR_UPDATABLE: Allows updates to the ResultSet
3. Holdability
Determines what happens to the ResultSet when a Transaction is committed.
- HOLD_CURSORS_OVER_COMMIT: The ResultSet remains open after a commit
- CLOSE_CURSORS_AT_COMMIT: The ResultSet closes after a commit
Categories of Methods in ResultSet
We have different types of Methods are available based on their functionality below we listed them for you reference.
1. Navigating a ResultSet
Basically these methods are allow is to navigating through the ResultSet and we can navigate in different ways, Below We provide those methods to navigate in the ResultSet.
- next(): Used for move next row in the ResultSet.
- previous(): Used for move to previous row in the ResultSet
- first(): Used for move to first row in the ResultSet
- last(): Used for move to last row in the ResultSet
- absolute(int row): Used to move to specific row
- relative(int rows): Used for Moves forward or backward by the specified number of rows
- beforeFirst(): Used for Positions the cursor before the first row
- afterLast(): Used for Positions the cursor after the last row
2. Retrieving Data from a ResultSet
These methods retrieve data from the current row in the ResultSet. And also You can retrieve data by column index or column name.
- getInt(int columnIndex): Used for Retrieves an integer from the specified column
- getString(int columnIndex): Used for Retrieves a string from the specified column
- getDouble(int columnIndex): Used for Retrieves a double from the specified column
- getBoolean(int columnIndex): Used for Retrieves true or false from the specified column
- getDate(int columnIndex): Used for Retrieves a java.sql.Date
- getObject(int columnIndex): Used for Retrieves any type of object
- getArray(int columnIndex): Used for Retrieves a SQL array
3. Updating Data in a ResultSet
These methods allow you to update data in the Result.
- updateInt(int columnIndex, int x): Used for Updates an integer value in the specified column
- updateString(int columnIndex, String x): used for Updates a string value
- updateBoolean(int columnIndex, boolean x): used for Updates a boolean value
- updateRow(): used for Updates a row
- deleteRow(): used for delete a row
Example: Employees Table
We create a employees table in work database. Below we provide table structure
 Employees Table
Employees TableProgram Implementing the JDBC Result Set
In this example we perform CRUD operations by using ResultSet. After running this program as java application It show four options to you. Need to select 1 to 4 based on your requirement below I provide the example with related images.
Java
package geeksforgeeks;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class JDBCOperations {
// Establish database connection
private static Connection getConnection()
throws Exception {
String jdbcUrl = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/data";
String jdbcUser = "root";
String jdbcPassword = "password";
return DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl, jdbcUser, jdbcPassword);
}
// Insert record into the database
private static void insertRecord(Connection connection,
String name, double salary)
throws Exception {
String query = "INSERT INTO employees (name, salary) VALUES (?, ?)";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement
= connection.prepareStatement(query);
preparedStatement.setString(1, name);
preparedStatement.setDouble(2, salary);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("Record inserted successfully.");
}
// Update record in the database
private static void updateRecord(Connection connection,
int id, String name,double salary)
throws Exception {
String query
= "UPDATE employees SET name = ?, salary = ? WHERE id = ?";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement
= connection.prepareStatement(query);
preparedStatement.setString(1, name);
preparedStatement.setDouble(2, salary);
preparedStatement.setInt(3, id);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("Record updated successfully.");
}
// Retrieve records from the database
private static void
retrieveRecords(Connection connection) throws Exception {
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM employees");
System.out.println("Records in the database:");
while (resultSet.next()) {
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String name = resultSet.getString("name");
double salary = resultSet.getDouble("salary");
System.out.println("ID: " + id + ", Name: " + name +
", Salary: " + salary);
}
}
// Delete record from the database
private static void deleteRecord(Connection connection,
int id)
throws Exception {
String query = "DELETE FROM employees WHERE id = ?";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement
= connection.prepareStatement(query);
preparedStatement.setInt(1, id);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("Record deleted successfully.");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
try {
Connection connection = getConnection();
System.out.println("Select an operation:");
System.out.println("1. Insert");
System.out.println("2. Update");
System.out.println("3. Retrieve");
System.out.println("4. Delete");
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
switch (choice) {
case 1:
System.out.println("Enter name:");
String nameToInsert = scanner.next();
System.out.println("Enter salary:");
double salaryToInsert = scanner.nextDouble();
insertRecord(connection, nameToInsert,
salaryToInsert);
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("Enter ID to update:");
int idToUpdate = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter new name:");
String nameToUpdate = scanner.next();
System.out.println("Enter new salary:");
double salaryToUpdate
= scanner.nextDouble();
updateRecord(connection, idToUpdate,
nameToUpdate, salaryToUpdate);
break;
case 3:
retrieveRecords(connection);
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("Enter ID to delete:");
int idToDelete = scanner.nextInt();
deleteRecord(connection, idToDelete);
break;
default:
System.out.println("Invalid choice.");
break;
}
// Close the connection at the end
connection.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
scanner.close();
}
}
}
Explanation of the above Program:
- Database Connection: Establishes connection using DriverManager with database URL, username and password.
- Insert Record: Uses PreparedStatement with placeholders to insert new employee data safely (avoiding SQL injection).
- Update Record: Updates existing employee details by matching employee ID.
- Fetch All Records: Executes SELECT query, stores results in ResultSet and iterates through rows to display data.
- Delete Record: Removes employee record based on employee ID.
- Main Function: Provides a console-based menu (via switch) to select and perform CRUD operations.
Output:
Showing available database operations
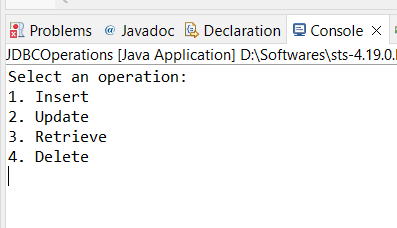
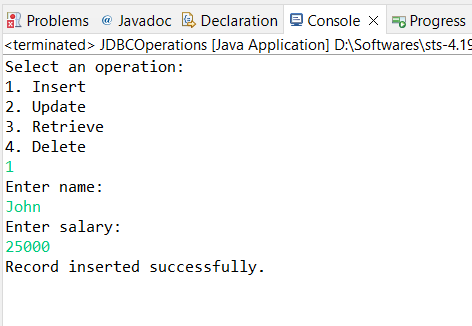
Now enter option 1, That means you can ready to insert data into database.
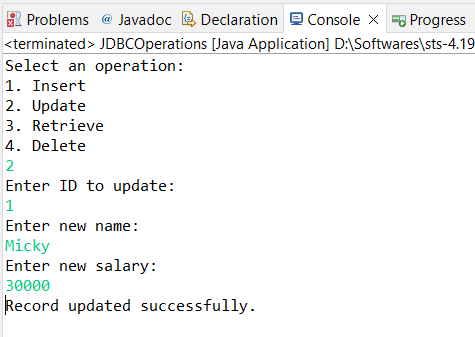
Now enter option 2, That means you can ready to update employee data by employee ID
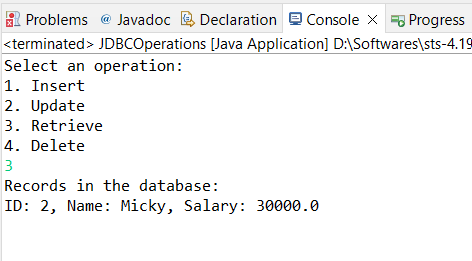
Now enter option 3, That means you can fetch all data from table.
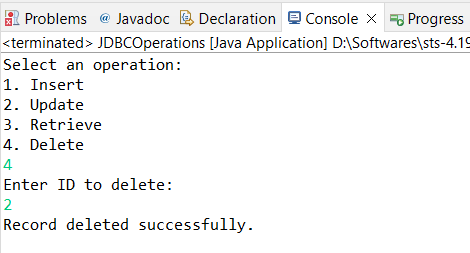
Now enter option 4, That means you can delete an employee details by using employee ID.
Explore
Java Basics
OOP & Interfaces
Collections
Exception Handling
Java Advanced
Practice Java