Java Multi-Dimensional Arrays
Last Updated :
13 Nov, 2025
Multidimensional arrays store data in the form of rows and columns where each row can itself be an array. They are useful when data needs to be structured in table-like or matrix-like formats.
Example: Creating and Using a Multidimensional Array
Java
public class Geeks {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Declaring a 2D array
int[][] arr;
// Initializing row and column sizes
arr = new int[1][3];
// Assigning values
arr[0][0] = 3;
arr[0][1] = 5;
arr[0][2] = 7;
// Displaying values
System.out.println("arr[0][0] = " + arr[0][0]);
System.out.println("arr[0][1] = " + arr[0][1]);
System.out.println("arr[0][2] = " + arr[0][2]);
}
}
Outputarr[0][0] = 3
arr[0][1] = 5
arr[0][2] = 7
Syntax:
data_type[dim1][dim2]...[dimN] array_name = new data_type[size1][size2]...[sizeN];
Parameters:
- data_type: Type of elements to be stored in the array
- dimension: Number of dimensions such as 1D, 2D, 3D
- array_name: Identifier for the array
- size1, sizeN: Size of each dimension
Examples:
// Two dimensional array:
int[][] arr2d = new int[3][5];
// Three dimensional array:
int[][][] arr3d = new int[3][5][7];
Size Calculation
Total elements = product of all dimension sizes
Example: int[][][] x = new int[3][5][7] can store 3*5*7 = 105 elements.
Two-Dimensional Array (2D-Array)
A 2D array represents data in rows and columns. It can be understood as an array of 1D arrays.
Syntax
data_type[][] array_name = new data_type[x][y];
array_name[row_index][col_index] = value;
A 2-D array can be seen as a table with 'x' rows and 'y' columns where the row number ranges from 0 to (x-1) and column number ranges from 0 to (y-1). A 2-D array 'x' with 3 rows and 3 columns is shown below:
 2D Array Representation
2D Array RepresentationExample 1: We can add the values directly to the array while declaring the array.
Java
import java.io.*;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
// Array Intialised and Assigned
int[][] arr = { { 1, 2 }, { 3, 4 } };
// Printing the Array
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++)
System.out.print(arr[i][j]+" ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Example 2: Updating the values while executing works both ways can be accepted by user or by some variable.
Java
public class Geeks
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Row and Columns in Array
int n = 2;
int m = 2;
// Array declared and initialized
int[][] arr = new int[n][m];
int it = 1;
// Assigning the values to array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
arr[i][j] = it;
it++;
}
}
// Printing the Array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Accessing Elements of Two-Dimensional Arrays
In Two dimensional array the the row is present by the i and the column is present by the j and we can get the element using arr[i][j] using the nested loop. arr is the name of the variable which reference to the two dimensional array.
Note: In an array of size N, indices range from 0 to N-1. Thus, row index 2 corresponds to the actual row number 3.
Example: Accessing the elements of 2D array using indexes.
Java
import java.io.*;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
int[][] arr = { { 1, 2 },
{ 3, 4 } };
System.out.println("a[1][1] : " + arr[1][1]);
}
}
Follow the Steps mentioned below to create a Two Dimensional Array with User input:
- First import the Scanner class from the util package at top of the program.
- Then create a Scanner class object. Then give a prompt to user to enter the size of row and column.
- Then create a nested loop to take input from user to add element in the multi-dimensional array.
- Then print the multi-dimensional array and close the scanner object.
Example: Java program to demonstrate how to create Two Dimensional Array with User input.
Java
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Geeks
{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// Taking Number of Rows and Columns from User
System.out.print("Enter number of rows: ");
int row = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter number of columns: ");
int col = sc.nextInt();
int[][] arr= new int[row][col];
System.out.println("Enter elements of array: ");
// Taking input from user for each element of array using nested for loop
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
arr[i][j]= sc.nextInt();
}
}
System.out.println("Elements of array are: ");
// Printing Elements of Arrays
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][j]+ " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
sc.close();
}
}
Output:
 Output
OutputThree - Dimensional Array (3D-Array)
3D-Array is a complex form of a multidimensional array. A 3D-array can be seen as an array of 2D array for easier understanding.
A three-dimensional array can be seen as a table of arrays with 'x' rows and 'y' columns where the row number ranges from 0 to (x-1) and column number ranges from 0 to (y-1). A three - dimensional array with 3 array containing 3 rows and 3 columns is shown below:
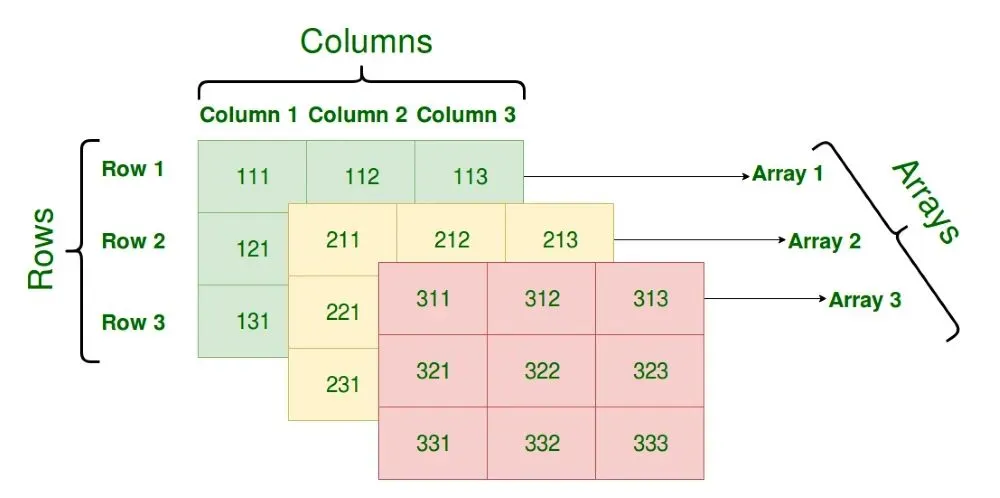 3D Array
3D ArrayExample 1: Java program to show how to create and print 3D array.
Java
import java.io.*;
class Geeks
{
public static void main(String[] args){
// Array Created and Initialized
int[][][] arr = { { { 1, 2 }, { 3, 4 } }, { { 5, 6 }, { 7, 8 } } };
// Defining the x,y,z in Multi-dimensional Array
int n = arr.length;
int m = arr[0].length;
int o = arr[0][0].length;
// Printing the Array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < o; k++) {
System.out.println("arr[" + i + "][" + j + "][" + k + "] = " + arr[i][j][k]);
}
}
}
}
}
Outputarr[0][0][0] = 1
arr[0][0][1] = 2
arr[0][1][0] = 3
arr[0][1][1] = 4
arr[1][0][0] = 5
arr[1][0][1] = 6
arr[1][1][0] = 7
arr[1][1][1] = 8
Example 2: Java program to assigning the values in 3D array using indexes.
Java
import java.io.*;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
int[][][] arr = new int[2][2][2];
// Three Dimensional x,y,z dimension
int n=arr.length;
int m=arr[0].length;
int o=arr[0][0].length;
int it=1;
// Assigning the values to array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
for(int k=0; k < o; k++){
arr[i][j][k] = it;
it++;
}
}
}
// Printing the Array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++){
for(int k=0; k < o; k++)
System.out.print(arr[i][j][k] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Accessing Elements of Three-Dimensional Arrays
Elements in three-dimensional arrays are commonly referred by x[i][j][k] where 'i' is the array number, 'j' is the row number and 'k' is the column number.
Note: In arrays if size of array is N. Its index will be from 0 to N-1. Therefore, for row_index 2, actual row number is 2+1 = 3.
Example: Accessing the elements of 3D array using indexes.
Java
import java.io.*;
class Geeks
{
public static void main(String[] args){
// Creating an Array
int[][][] arr = { { { 1, 2 }, { 3, 4 } },
{ { 5, 6 }, { 7, 8 } } };
// Printing array at index 0 , 0 , 0
System.out.println("arr[0][0][0] = " + arr[0][0][0]);
}
}
Inserting a Multi-Dimensional Array During Runtime
Now we can insert a multidimensional array at runtime here we are going to use the Scanner class and then we take the element of the multidimensional array from the user and then we print the count of the even and odd element which user give as an input.
Example: Taking a input from user of multidimensional array (Runtime) and print the count of even and odd number given by user.
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
class Geeks {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
// Number of rows
int n = s.nextInt();
// Initialize a 2D array
int[][] arr = new int[n][];
int t = 0;
// Input for each row
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int m = s.nextInt();
// Assuming all rows have the same column count
t = m;
arr[i] = new int[m];
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
arr[i][j] = s.nextInt();
}
}
int odd = 0, even = 0;
System.out.println("Rows " + n + " with " + t
+ " Columns");
System.out.println("Elements of Array:");
// Print the entire array and count even/odd numbers
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + " ");
// Count even and odd numbers
if (arr[i][j] % 2 == 0) {
even++;
}
else {
odd++;
}
}
System.out.println();
}
// Print the aggregated results
System.out.println("Even: " + even
+ ", Odd: " + odd);
s.close();
}
}
 Output
OutputApplication of Multi-Dimensional Array
- Used to organize data in tabular form such as storing student records like roll number and marks
- Representing images in matrix form
- Dynamic programming problems where states are stored in 2D or 3D structures
- Matrix multiplication
- Adjacency matrix representation of graphs
- Grid traversal problems
Explore
Java Basics
OOP & Interfaces
Collections
Exception Handling
Java Advanced
Practice Java