In Java, variables are containers used to store data in memory. Variables define how data is stored, accessed, and manipulated.
A variable in Java has three components,
- Data Type: Defines the kind of data stored (e.g., int, String, float).
- Variable Name: A unique identifier following Java naming rules.
- Value: The actual data assigned to the variable.
Java
class Geeks {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Declaring and initializing variables
// Integer variable
int age = 25;
// String variable
String name = "GeeksforGeeks";
// Double variable
double salary = 50000.50;
// Displaying the values of variables
System.out.println("Age: " + age);
System.out.println("Name: " + name);
System.out.println("Salary: " + salary);
}
}
OutputAge: 25
Name: GeeksforGeeks
Salary: 50000.5
How to Declare Java Variables?
The image below demonstrates how we can declare a variable in Java:
 Variable Declaration
Variable DeclarationFrom the image, it can be easily perceived that while declaring a variable, we need to take care of two things that are data type of the variable and name.
How to Initialize Java Variables?
It can be perceived with the help of 3 components explained above:
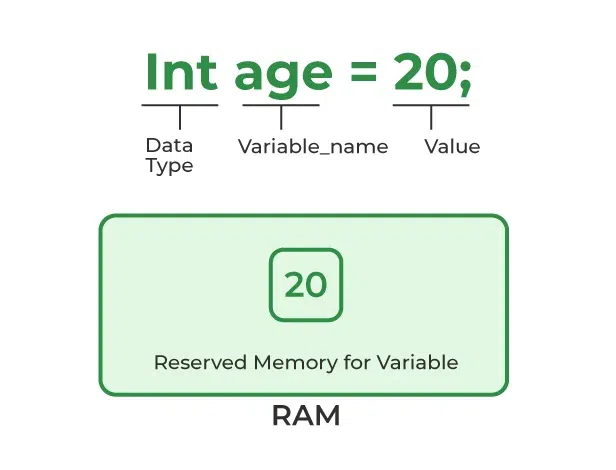 Variable Initialization
Variable InitializationExample: Here, we are initializing variables of different types like float, int and char.
Java
class Geeks{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Declaring and initializing variables
// Initializing float variable
float si = 5.5f;
// Initializing integer variables
int t = 10;
int s = 20;
// Initializing character variable
char var = 'h';
// Displaying the values of the variables
System.out.println("Simple Interest: " + si);
System.out.println("Speed: " + s);
System.out.println("Time: " + t);
System.out.println("Character: " + var);
}
}
OutputSimple Interest: 5.5
Speed: 20
Time: 10
Character: h
Rules to Name Java Variables
- Start with a Letter, $, or _ – Variable names must begin with a letter (a–z, A–Z), dollar sign $, or underscore _.
- No Keywords: Reserved Java keywords (e.g., int, class, if) cannot be used as variable names.
- Case Sensitive: age and Age are treated as different variables.
- Use Letters, Digits, $, or _ : After the first character, you can use letters, digits (0–9), $, or _.
- Meaningful Names: Choose descriptive names that reflect the purpose of the variable (e.g., studentName instead of s).
- No Spaces: Variable names cannot contain spaces.
- Follow Naming Conventions: Typically, use camelCase for variable names in Java (e.g., totalMarks).
Related articles:
Explore
Java Basics
OOP & Interfaces
Collections
Exception Handling
Java Advanced
Practice Java