Deletion in K Dimensional Tree
Last Updated :
15 May, 2023
We strongly recommend to refer below posts as a prerequisite of this.
K Dimensional Tree | Set 1 (Search and Insert)
K Dimensional Tree | Set 2 (Find Minimum)
In this post delete is discussed. The operation is to delete a given point from K D Tree.
Like Binary Search Tree Delete, we recursively traverse down and search for the point to be deleted. Below are steps are followed for every node visited.
1) If current node contains the point to be deleted
- If node to be deleted is a leaf node, simply delete it (Same as BST Delete)
- If node to be deleted has right child as not NULL (Different from BST)
- Find minimum of current node's dimension in right subtree.
- Replace the node with above found minimum and recursively delete minimum in right subtree.
- Else If node to be deleted has left child as not NULL (Different from BST)
- Find minimum of current node's dimension in left subtree.
- Replace the node with above found minimum and recursively delete minimum in left subtree.
- Make new left subtree as right child of current node.
2) If current doesn't contain the point to be deleted
- If node to be deleted is smaller than current node on current dimension, recur for left subtree.
- Else recur for right subtree.
Why 1.b and 1.c are different from BST?
In BST delete, if a node's left child is empty and right is not empty, we replace the node with right child. In K D Tree, doing this would violate the KD tree property as dimension of right child of node is different from node's dimension. For example, if node divides point by x axis values. then its children divide by y axis, so we can't simply replace node with right child. Same is true for the case when right child is not empty and left child is empty.
Why 1.c doesn't find max in left subtree and recur for max like 1.b?
Doing this violates the property that all equal values are in right subtree. For example, if we delete (!0, 10) in below subtree and replace if with
Wrong Way (Equal key in left subtree after deletion)
(5, 6) (4, 10)
/ Delete(5, 6) /
(4, 10) ------------> (4, 20)
\
(4, 20)
Right way (Equal key in right subtree after deletion)
(5, 6) (4, 10)
/ Delete(5, 6) \
(4, 10) ------------> (4, 20)
\
(4, 20)
Example of Delete:
Delete (30, 40): Since right child is not NULL and dimension of node is x, we find the node with minimum x value in right child. The node is (35, 45), we replace (30, 40) with (35, 45) and delete (30, 40).

Delete (70, 70): Dimension of node is y. Since right child is NULL, we find the node with minimum y value in left child. The node is (50, 30), we replace (70, 70) with (50, 30) and recursively delete (50, 30) in left subtree. Finally we make the modified left subtree as right subtree of (50, 30).
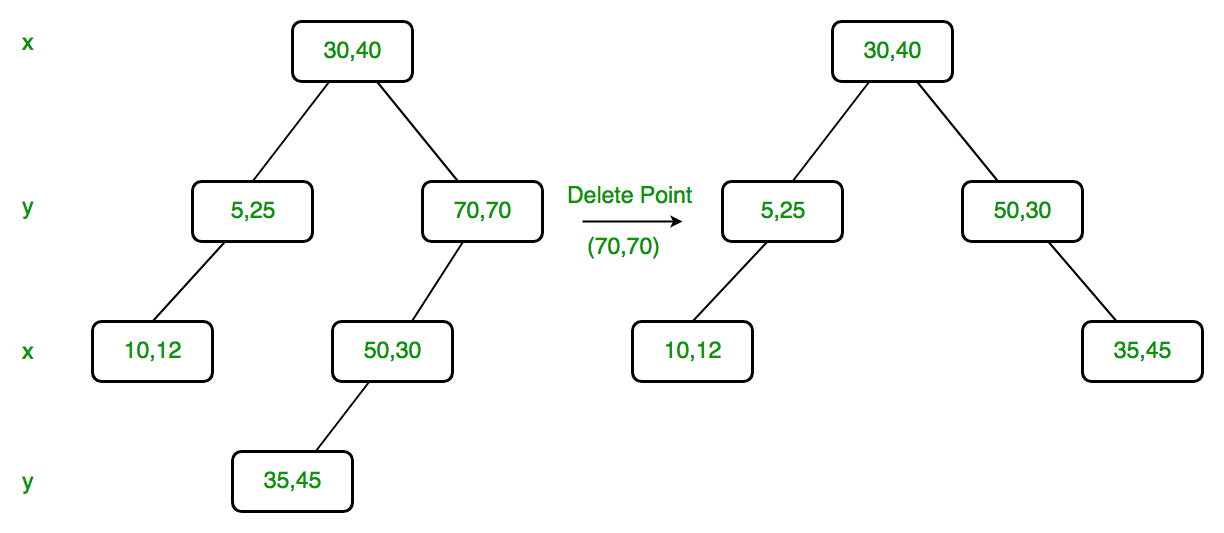
Below is C++ implementation of K D Tree delete.
C++
// A C++ program to demonstrate delete in K D tree
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int k = 2;
// A structure to represent node of kd tree
struct Node
{
int point[k]; // To store k dimensional point
Node *left, *right;
};
// A method to create a node of K D tree
struct Node* newNode(int arr[])
{
struct Node* temp = new Node;
for (int i=0; i<k; i++)
temp->point[i] = arr[i];
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Inserts a new node and returns root of modified tree
// The parameter depth is used to decide axis of comparison
Node *insertRec(Node *root, int point[], unsigned depth)
{
// Tree is empty?
if (root == NULL)
return newNode(point);
// Calculate current dimension (cd) of comparison
unsigned cd = depth % k;
// Compare the new point with root on current dimension 'cd'
// and decide the left or right subtree
if (point[cd] < (root->point[cd]))
root->left = insertRec(root->left, point, depth + 1);
else
root->right = insertRec(root->right, point, depth + 1);
return root;
}
// Function to insert a new point with given point in
// KD Tree and return new root. It mainly uses above recursive
// function "insertRec()"
Node* insert(Node *root, int point[])
{
return insertRec(root, point, 0);
}
// A utility function to find minimum of three integers
Node *minNode(Node *x, Node *y, Node *z, int d)
{
Node *res = x;
if (y != NULL && y->point[d] < res->point[d])
res = y;
if (z != NULL && z->point[d] < res->point[d])
res = z;
return res;
}
// Recursively finds minimum of d'th dimension in KD tree
// The parameter depth is used to determine current axis.
Node *findMinRec(Node* root, int d, unsigned depth)
{
// Base cases
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
// Current dimension is computed using current depth and total
// dimensions (k)
unsigned cd = depth % k;
// Compare point with root with respect to cd (Current dimension)
if (cd == d)
{
if (root->left == NULL)
return root;
return findMinRec(root->left, d, depth+1);
}
// If current dimension is different then minimum can be anywhere
// in this subtree
return minNode(root,
findMinRec(root->left, d, depth+1),
findMinRec(root->right, d, depth+1), d);
}
// A wrapper over findMinRec(). Returns minimum of d'th dimension
Node *findMin(Node* root, int d)
{
// Pass current level or depth as 0
return findMinRec(root, d, 0);
}
// A utility method to determine if two Points are same
// in K Dimensional space
bool arePointsSame(int point1[], int point2[])
{
// Compare individual pointinate values
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i)
if (point1[i] != point2[i])
return false;
return true;
}
// Copies point p2 to p1
void copyPoint(int p1[], int p2[])
{
for (int i=0; i<k; i++)
p1[i] = p2[i];
}
// Function to delete a given point 'point[]' from tree with root
// as 'root'. depth is current depth and passed as 0 initially.
// Returns root of the modified tree.
Node *deleteNodeRec(Node *root, int point[], int depth)
{
// Given point is not present
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
// Find dimension of current node
int cd = depth % k;
// If the point to be deleted is present at root
if (arePointsSame(root->point, point))
{
// 2.b) If right child is not NULL
if (root->right != NULL)
{
// Find minimum of root's dimension in right subtree
Node *min = findMin(root->right, cd);
// Copy the minimum to root
copyPoint(root->point, min->point);
// Recursively delete the minimum
root->right = deleteNodeRec(root->right, min->point, depth+1);
}
else if (root->left != NULL) // same as above
{
Node *min = findMin(root->left, cd);
copyPoint(root->point, min->point);
root->right = deleteNodeRec(root->left, min->point, depth+1);
}
else // If node to be deleted is leaf node
{
delete root;
return NULL;
}
return root;
}
// 2) If current node doesn't contain point, search downward
if (point[cd] < root->point[cd])
root->left = deleteNodeRec(root->left, point, depth+1);
else
root->right = deleteNodeRec(root->right, point, depth+1);
return root;
}
// Function to delete a given point from K D Tree with 'root'
Node* deleteNode(Node *root, int point[])
{
// Pass depth as 0
return deleteNodeRec(root, point, 0);
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
struct Node *root = NULL;
int points[][k] = {{30, 40}, {5, 25}, {70, 70},
{10, 12}, {50, 30}, {35, 45}};
int n = sizeof(points)/sizeof(points[0]);
for (int i=0; i<n; i++)
root = insert(root, points[i]);
// Delete (30, 40);
root = deleteNode(root, points[0]);
cout << "Root after deletion of (30, 40)\n";
cout << root->point[0] << ", " << root->point[1] << endl;
return 0;
}
// A Java program to demonstrate delete in K D tree
import java.util.*;
public class Gfg {
static int k = 2;
// A structure to represent node of kd tree
static class Node {
int[] point = new int[k]; // To store k dimensional point
Node left, right;
}
// A method to create a node of K D tree
static Node newNode(int[] arr) {
Node temp = new Node();
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
temp.point[i] = arr[i];
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// Inserts a new node and returns root of modified tree
// The parameter depth is used to decide axis of comparison
static Node insertRec(Node root, int[] point, int depth) {
// Tree is empty?
if (root == null)
return newNode(point);
// Calculate current dimension (cd) of comparison
int cd = depth % k;
// Compare the new point with root on current dimension 'cd'
// and decide the left or right subtree
if (point[cd] < root.point[cd])
root.left = insertRec(root.left, point, depth + 1);
else
root.right = insertRec(root.right, point, depth + 1);
return root;
}
// Function to insert a new point with given point in
// KD Tree and return new root. It mainly uses above recursive
// function "insertRec()"
static Node insert(Node root, int[] point) {
return insertRec(root, point, 0);
}
// A utility function to find minimum of three integers
static Node minNode(Node x, Node y, Node z, int d) {
Node res = x;
if (y != null && y.point[d] < res.point[d])
res = y;
if (z != null && z.point[d] < res.point[d])
res = z;
return res;
}
// Recursively finds minimum of d'th dimension in KD tree
// The parameter depth is used to determine current axis.
static Node findMinRec(Node root, int d, int depth) {
// Base cases
if (root == null)
return null;
// Current dimension is computed using current depth and total
// dimensions (k)
int cd = depth % k;
// Compare point with root with respect to cd (Current dimension)
if (cd == d) {
if (root.left == null)
return root;
return findMinRec(root.left, d, depth + 1);
}
// If current dimension is different then minimum can be anywhere
// in this subtree
return minNode(root, findMinRec(root.left, d, depth + 1), findMinRec(root.right, d, depth + 1), d);
}
// A wrapper over findMinRec(). Returns minimum of d'th dimension
static Node findMin(Node root, int d) {
// Pass current level or depth as 0
return findMinRec(root, d, 0);
}
// A utility method to determine if two Points are same
// in K Dimensional space
static boolean arePointsSame(int[] point1, int[] point2) {
// Compare individual pointinate values
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i)
if (point1[i] != point2[i])
return false;
return true;
}
// Copies point p2 to p1
static void copyPoint(int[] p1, int[] p2) {
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
p1[i] = p2[i];
}
// Function to delete a given point 'point[]' from tree with root
// as 'root'. depth is current depth and passed as 0 initially.
// Returns root of the modified tree.
static Node deleteNodeRec(Node root, int[] point, int depth) {
// Given point is not present
if (root == null)
return null;
// Find dimension of current node
int cd = depth % k;
// If the point to be deleted is present at root
if (arePointsSame(root.point, point)) {
// 2.b) If right child is not NULL
if (root.right != null) {
// Find minimum of root's dimension in right subtree
Node min = findMin(root.right, cd);
// Copy the minimum to root
copyPoint(root.point, min.point);
// Recursively delete the minimum
root.right = deleteNodeRec(root.right, min.point, depth + 1);
}
else if (root.left != null) // same as above
{
Node min = findMin(root.left, cd);
copyPoint(root.point, min.point);
root.right = deleteNodeRec(root.left, min.point, depth + 1);
}
else // If node to be deleted is leaf node
{
root = null;
}
return root;
}
// 2) If current node doesn't contain point, search downward
if (point[cd] < root.point[cd])
root.left = deleteNodeRec(root.left, point, depth + 1);
else
root.right = deleteNodeRec(root.right, point, depth + 1);
return root;
}
// Function to delete a given point from K D Tree with 'root'
static Node deleteNode(Node root, int[] point) {
// Pass depth as 0
return deleteNodeRec(root, point, 0);
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node root = null;
int[][] points = {{30, 40}, {5, 25}, {70, 70}, {10, 12}, {50, 30}, {35, 45}};
int n = points.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
root = insert(root, points[i]);
}
// Delete (30, 40);
root = deleteNode(root, points[0]);
System.out.println("Root after deletion of (30, 40)");
System.out.println(root.point[0] + ", " + root.point[1]);
}
}
from typing import List
# Set the number of dimensions for each point
k = 2
# Define a class for each node in the K-Dimensional Tree
class Node:
def __init__(self, point: List[int]):
# The point in the tree is stored in this node
self.point = point
# The left child node
self.left = None
# The right child node
self.right = None
# Function to insert a new point into the tree
def insert(root, point: List[int]):
# If the tree is empty, return a new node with the point
if not root:
return Node(point)
# Start from the root node
current_node = root
# Find the correct leaf node to insert the new point
while current_node:
# If the new point is smaller than the current node's point in the current dimension, go to the left child node
next_node = current_node.left if point[k-1] < current_node.point[k-1] else current_node.right
# If the next node doesn't exist, we have found the correct leaf node to insert the new point
if not next_node:
break
# If the next node exists, continue searching in the tree
current_node = next_node
# Insert the new point as a left or right child node of the correct leaf node
if point[k-1] < current_node.point[k-1]:
current_node.left = Node(point)
else:
current_node.right = Node(point)
return root
# Function to copy the values of one point to another
def copyPoint(p1, p2):
for i in range(k):
p1[i] = p2[i]
# Function to find the node with the minimum value in a subtree
def minValueNode(node):
current_node = node
# Go to the leftmost leaf node in the subtree
while current_node.left:
current_node = current_node.left
return current_node
# Recursive function to delete a node from the tree
def deleteNodeRec(root, point, depth):
# If the tree is empty or the node is not found, return None
if not root:
return None
# Calculate the current dimension based on the depth
current_depth = depth % k
# If the point to be deleted is smaller than the current node's point in the current dimension, go to the left subtree
if point[current_depth] < root.point[current_depth]:
root.left = deleteNodeRec(root.left, point, depth + 1)
# If the point to be deleted is larger than the current node's point in the current dimension, go to the right subtree
elif point[current_depth] > root.point[current_depth]:
root.right = deleteNodeRec(root.right, point, depth + 1)
# If the point to be deleted is equal to the current node's point, delete the node
else:
# If the node has no left child, return its right child
if not root.left:
return root.right
elif not root.right:
return root.left
else:
temp = minValueNode(root.right)
copyPoint(root.point, temp.point)
root.right = deleteNodeRec(root.right, temp.point, depth + 1)
return root
def deleteNode(root, point):
return deleteNodeRec(root, point, 0)
# Driver program to test above functions
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = None
points = [[30, 40], [5, 25], [70, 70], [10, 12], [50, 30], [35, 45]]
n = len(points)
for i in range(n):
root = insert(root, points[i])
# Delete (30, 40)
root = deleteNode(root, points[0])
print("Root after deletion of (30, 40)")
print(root.point[0], root.point[1])
# This code is contributed by Vikram_Shirsat
// A C# program to demonstrate delete in K D tree
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace kdtree {
class Node {
public int[] point;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int[] point)
{
this.point = point;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
class Program {
static int k = 2;
// Inserts a new node and returns root of modified tree
// The parameter depth is used to decide axis of
// comparison
static Node insertRec(Node root, int[] point, int depth)
{
// Tree is empty?
if (root == null) {
return new Node(point);
}
// Calculate current dimension (cd) of comparison
int cd = depth % k;
// Compare the new point with root on current
// dimension 'cd' and decide the left or right
// subtree
if (point[cd] < root.point[cd]) {
root.left
= insertRec(root.left, point, depth + 1);
}
else {
root.right
= insertRec(root.right, point, depth + 1);
}
return root;
}
// Function to insert a new point with given point in
// KD Tree and return new root. It mainly uses above
// recursive function "insertRec()"
static Node insert(Node root, int[] point)
{
return insertRec(root, point, 0);
}
// A utility function to find minimum of three integers
static Node minNode(Node x, Node y, Node z, int d)
{
Node res = x;
if (y != null && y.point[d] < res.point[d]) {
res = y;
}
if (z != null && z.point[d] < res.point[d]) {
res = z;
}
return res;
}
// Recursively finds minimum of d'th dimension in KD
// tree
// The parameter depth is used to determine current
// axis.
static Node findMinRec(Node root, int d, int depth)
{
// Base cases
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
// Current dimension is computed using current depth
// and total
// dimensions (k)
int cd = depth % k;
// Compare point with root with respect to cd
// (Current dimension)
if (cd == d) {
if (root.left == null) {
return root;
}
return findMinRec(root.left, d, depth + 1);
}
// If current dimension is different then minimum
// can be anywhere
// in this subtree
return minNode(
root, findMinRec(root.left, d, depth + 1),
findMinRec(root.right, d, depth + 1), d);
}
// A wrapper over findMinRec(). Returns minimum of d'th
// dimension
static Node findMin(Node root, int d)
{
// Pass current level or depth as 0
return findMinRec(root, d, 0);
}
// A utility method to determine if two Points are same
// in K Dimensional space
static bool arePointsSame(int[] point1, int[] point2)
{
// Compare individual pointinate values
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
if (point1[i] != point2[i]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// Copies point p2 to p1
static void copyPoint(int[] p1, int[] p2)
{
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
p1[i] = p2[i];
}
}
// Function to delete a given point 'point[]' from tree
// with root
// as 'root'. depth is current depth and passed as 0
// initially. Returns root of the modified tree.
static Node deleteNodeRec(Node root, int[] point,
int depth)
{
// Given point is not present
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
// Find dimension of current node
int cd = depth % k;
// If the point to be deleted is present at root
if (arePointsSame(root.point, point)) {
// 2.b) If right child is not NULL
if (root.right != null) {
// Find minimum of root's dimension in right
// subtree
Node min = findMin(root.right, cd);
// Copy the minimum to root
copyPoint(root.point, min.point);
// Recursively delete the minimum
root.right = deleteNodeRec(
root.right, min.point, depth + 1);
}
else if (root.left != null) {
Node min = findMin(root.left, cd);
copyPoint(root.point, min.point);
root.right = deleteNodeRec(
root.left, min.point, depth + 1);
}
else // If node to be deleted is leaf node
{
root = null;
return null;
}
return root;
}
// 2) If current node doesn't contain point, search
// downward
if (point[cd] < root.point[cd]) {
root.left = deleteNodeRec(root.left, point,
depth + 1);
}
else {
root.right = deleteNodeRec(root.right, point,
depth + 1);
}
return root;
}
// Function to delete a given point from K D Tree with
// 'root'
static Node deleteNode(Node root, int[] point)
{
// Pass depth as 0
return deleteNodeRec(root, point, 0);
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Driver program to test above functions
Node root = null;
int[][] points = new int[][] {
new int[] { 30, 40 }, new int[] { 5, 25 },
new int[] { 70, 70 }, new int[] { 10, 12 },
new int[] { 50, 30 }, new int[] { 35, 45 }
};
int n = points.Length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
root = insert(root, points[i]);
}
// Delete (30, 40);
root = deleteNode(root, points[0]);
Console.WriteLine(
"Root after deletion of (30, 40)");
Console.WriteLine(root.point[0] + ","
+ root.point[1]);
}
}
}
//This code is contributed by NarasingaNikhil
// A javascript program to demonstrate delete in K D tree
const k = 2;
class Node
{
// A structure to represent node of kd tree
constructor(point) {
this.point = point; // To store k dimensional point
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
// A method to create a node of K D tree
function newNode(point) {
const temp = new Node(point);
temp.left = null;
temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// Inserts a new node and returns root of modified tree
// The parameter depth is used to decide axis of comparison
function insertRec(root, point, depth)
{
// Tree is empty?
if (root === null) return newNode(point);
// Calculate current dimension (cd) of comparison
const cd = depth % k;
// Compare the new point with root on current dimension 'cd'
// and decide the left or right subtree
if (point[cd] < root.point[cd]) {
root.left = insertRec(root.left, point, depth + 1);
} else {
root.right = insertRec(root.right, point, depth + 1);
}
return root;
}
// Function to insert a new point with given point in
// KD Tree and return new root. It mainly uses above recursive
// function "insertRec()"
function insert(root, point) {
return insertRec(root, point, 0);
}
// A utility function to find minimum of three integers
function minNode(x, y, z, d) {
let res = x;
if (y !== null && y.point[d] < res.point[d]) res = y;
if (z !== null && z.point[d] < res.point[d]) res = z;
return res;
}
// Recursively finds minimum of d'th dimension in KD tree
// The parameter depth is used to determine current axis.
function findMinRec(root, d, depth) {
// Base cases
if (root === null) return null;
// Current dimension is computed using current depth and total
// dimensions (k)
const cd = depth % k;
// Compare point with root with respect to cd (Current dimension)
if (cd === d) {
if (root.left === null) return root;
return findMinRec(root.left, d, depth + 1);
}
return minNode(root, findMinRec(root.left, d, depth + 1),
findMinRec(root.right, d, depth + 1), d);
}
// A wrapper over findMinRec(). Returns minimum of d'th dimension
function findMin(root, d)
{
// Pass current level or depth as 0
return findMinRec(root, d, 0);
}
// A utility method to determine if two Points are same
// in K Dimensional space
function arePointsSame(point1, point2)
{
// Compare individual pointinate values
for (let i = 0; i < k; i++) {
if (point1[i] !== point2[i]) return false;
}
return true;
}
// Copies point p2 to p1
function copyPoint(p1, p2) {
for (let i = 0; i < k; i++) {
p1[i] = p2[i];
}
}
// Function to delete a given point 'point[]' from tree with root
// as 'root'. depth is current depth and passed as 0 initially.
// Returns root of the modified tree.
function deleteNodeRec(root, point, depth) {
// Given point is not present
if (root === null) return null;
// Find dimension of current node
const cd = depth % k;
// If the point to be deleted is present at root
if (arePointsSame(root.point, point)) {
// 2.b) If right child is not NULL
if (root.right !== null) {
// Find minimum of root's dimension in right subtree
const min = findMin(root.right, cd);
// Copy the minimum to root
copyPoint(root.point, min.point);
// Recursively delete the minimum
root.right = deleteNodeRec(root.right, min.point, depth + 1);
} else if (root.left !== null) // same as above
{
const min = findMin(root.left, cd);
copyPoint(root.point, min.point);
root.right = deleteNodeRec(root.left, min.point, depth + 1);
} else // If node to be deleted is leaf node
{
delete root;
return null;
}
return root;
}
// 2) If current node doesn't contain point, search downward
if (point[cd] < root.point[cd]) {
root.left = deleteNodeRec(root.left, point, depth + 1);
} else {
root.right = deleteNodeRec(root.right, point, depth + 1);
}
return root;
}
// Function to delete a given point from K D Tree with 'root'
function deleteNode(root, point) {
// Pass depth as 0
return deleteNodeRec(root, point, 0);
}
// Driver program to test above functions
const points = [
[30, 40],
[5, 25],
[70, 70],
[10, 12],
[50, 30],
[35, 45],
];
const n = points.length;
let root = null;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
root = insert(root, points[i]);
}
// Delete (30, 40);
root = deleteNode(root, points[0]);
console.log("Root after deletion of (30, 40)");
console.log(root.point[0] + "," + root.point[1]);
// This code is contributed by NarasingaNikhil
OutputRoot after deletion of (30, 40)
35, 45
The time complexity is O(log N), where N is the number of nodes in the KD-Tree. This is because the KD-Tree has a balanced structure with log N levels, and the insertion, deletion, and search operations traverse the tree in a way that reduces the search space by half at each level.
The space complexity is also O(N) since each node requires space for k integers (where k is the number of dimensions), as well as two pointers to child nodes, each of which requires a pointer-sized space. Additionally, the program uses recursive functions to traverse the tree, which adds to the stack space required, which is also O(N) in the worst case if the tree is unbalanced.
Source:
https://www.cs.umd.edu/class/spring2008/cmsc420/L19.kd-trees.pdf
Similar Reads
DSA Tutorial - Learn Data Structures and Algorithms
DSA (Data Structures and Algorithms) is the study of organizing data efficiently using data structures like arrays, stacks, and trees, paired with step-by-step procedures (or algorithms) to solve problems effectively. Data structures manage how data is stored and accessed, while algorithms focus on
7 min read
Quick Sort
QuickSort is a sorting algorithm based on the Divide and Conquer that picks an element as a pivot and partitions the given array around the picked pivot by placing the pivot in its correct position in the sorted array. It works on the principle of divide and conquer, breaking down the problem into s
12 min read
Merge Sort - Data Structure and Algorithms Tutorials
Merge sort is a popular sorting algorithm known for its efficiency and stability. It follows the divide-and-conquer approach. It works by recursively dividing the input array into two halves, recursively sorting the two halves and finally merging them back together to obtain the sorted array. Merge
14 min read
Breadth First Search or BFS for a Graph
Given a undirected graph represented by an adjacency list adj, where each adj[i] represents the list of vertices connected to vertex i. Perform a Breadth First Search (BFS) traversal starting from vertex 0, visiting vertices from left to right according to the adjacency list, and return a list conta
15+ min read
Bubble Sort Algorithm
Bubble Sort is the simplest sorting algorithm that works by repeatedly swapping the adjacent elements if they are in the wrong order. This algorithm is not suitable for large data sets as its average and worst-case time complexity are quite high.We sort the array using multiple passes. After the fir
8 min read
Data Structures Tutorial
Data structures are the fundamental building blocks of computer programming. They define how data is organized, stored, and manipulated within a program. Understanding data structures is very important for developing efficient and effective algorithms. What is Data Structure?A data structure is a st
2 min read
Binary Search Algorithm - Iterative and Recursive Implementation
Binary Search Algorithm is a searching algorithm used in a sorted array by repeatedly dividing the search interval in half. The idea of binary search is to use the information that the array is sorted and reduce the time complexity to O(log N). Binary Search AlgorithmConditions to apply Binary Searc
15 min read
Insertion Sort Algorithm
Insertion sort is a simple sorting algorithm that works by iteratively inserting each element of an unsorted list into its correct position in a sorted portion of the list. It is like sorting playing cards in your hands. You split the cards into two groups: the sorted cards and the unsorted cards. T
9 min read
Dijkstra's Algorithm to find Shortest Paths from a Source to all
Given a weighted undirected graph represented as an edge list and a source vertex src, find the shortest path distances from the source vertex to all other vertices in the graph. The graph contains V vertices, numbered from 0 to V - 1.Note: The given graph does not contain any negative edge. Example
12 min read
Selection Sort
Selection Sort is a comparison-based sorting algorithm. It sorts an array by repeatedly selecting the smallest (or largest) element from the unsorted portion and swapping it with the first unsorted element. This process continues until the entire array is sorted.First we find the smallest element an
8 min read