Main Components of Java Netbeans IDE
Last Updated :
09 Mar, 2021
Before somebody starts developing the applications, make sure that JAVA SDK along with NetBeans IDE is installed on our computer.
After downloading you can install the software. Once the software is installed, now let us go through all 5 components after installation. After installation of the software, we can start working on it by following these steps as follows
1. Start
2. All Programs
3. NetBeans
4. NetBeans IDE
Initially, wait for a while till the program(NetBeans IDE) window opens in the fully functional mode. It consists of many features & by using it we are able to prepare all type of programs (Desktop Application & Web Application) and games also. Let us discuss the components one by one which are as follows:
- Title bar
- Menu bar and pull-down menus
- Toolbar
- GUI building
- Palette

Starting Window
Component 1: Title Bar
It displays the title of the application. Netbeans will give names as JavaApplication1, JavaApplication2,………..etc., to your project, random arbitrary is pictorially shown below

Title Bar
Component 2: Menu Bar and Pulldown Menus
The environment if working is the same as that of familiar with menu bars as you have worked with MS – Windows operating system. A menu bar is displayed directly below that title bar and includes a lot of options. Each option on the menu bar has a drop–down list of items (known as Pull-down menus) that help you perform various tasks.

Menu Bar
Component 3: Tool Bar
A toolbar is a bar that displays icons for commonly used tasks. The standard Toolbar of Netbeans IDE displays icons for the most frequently used commands in NetBeans.

Tool Bar
Component 4: GUI Building
Also called Design Area or Design Space. The Design Area is where you will visually construct your GUI. It is the primary workspace within which GUI design takes place in the IDE. The GUI Builder enables you to layout forms by placing components where you want them and by providing visual feedback in the form of guidelines. It has 2 views : source View and Design View. Design View is the default, as shown above. The Source View opens the code editor for you where you can add/edit the code for your application. You can toggle between views at any time by clicking their respective tabs.
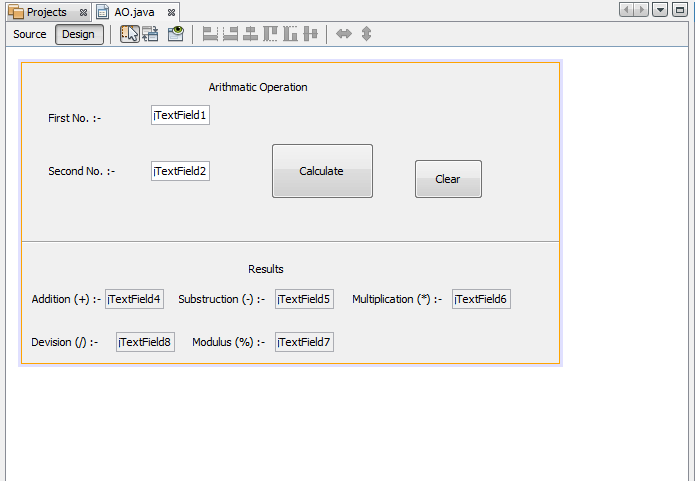
GUI Building Design View
Component 5: The Palette
The palette contains all the components needed to create GUI applications. Before discussing Palette, let us talk about windows/frame and controls.
5(a) Frames
A–Frame is a window that typically has decorations such as a border, a title, and buttons for closing and iconifying itself. A GUI application typically uses at least one frame. Frames are used to display things like labels, Text Fields, Buttons, and other Controls
5(b) Controls
Controls are component objects such as text Fields, labels list boxes, etc., that are drawn on the frame to get data input or to display output. After introducing frames and controls, let us now talk about Palette As you can see in the figure below that a Palette displays a set of component tools that may be used to place controls on a frame.

Control Window
5(c) Inspector window
This window displays a tree hierarchy of all components contained in the currently opened from. Displayed items include visual components and containers, such as buttons, labels, menus, and panels, as well as non-visual components such as timers and data sources.

Inspector window
5(d) Property window
This window displays the editable settings for the currently selected component. The figure on your right shows the property Editor for a JFrame object.

Property Window
5(e) Code Editor window
The code editor window is where you write Java code for your application. By code, we mean language statements, constants, and declarations. The Code Editor window servers as an editor for entering application code. A separate code editor window is created for each top-level frame that you create in your application. Using the code Editor Window, you can quickly view and edit any of the codes in your application. To open the Code window you can Double-click the control for which you choose to write code. Or from the GUI Builder window, click on the source tab. You may also press ‘Ctrl + Alt + Page UP/Page Down’.
Similar Reads
heapDump() Method of MBean in Java
The heapDump() method in Java is a solid and powerful tool for troubleshooting and analyzing the performance of Java Programs. MBeans, or Managed Beans, are the objects of Java that provide various information and control aspects of a Java Application, Such as memory usage, threading, and performanc
5 min read
Eclipse Vs IntelliJ IDEA Vs NetBeans for Java Development
IDE stands for Integrated Development Environment. It is used for developing software and projects faster because it has various tools that you require in your project like a line debugger that will keep a check of each and every line, version control like git for an easy workflow with GitHub, smart
8 min read
How to Create a Project In NetBeans GUI?
All Java Development in the IDE takes place within Projects, we first need to create a new project within which to store sources and other project files. An IDE project is a group of JAVA Source files plus its associated metadata (data about data), including project-specific properties files, and ma
2 min read
How to Install NetBeans Java IDE on Windows?
NetBeans IDE is a Free open-Source, Cross-plate form Integrated Development Environment (IDE) with built-in support for the JAVA Programming Language. It can run any machine which consists of the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). It consists of many features for application development as follows: Drag
2 min read
Setting up Java Competitive Programming Environment
An operating system is required to be installed on your system. here we will be discussing the setup in windows. However, you can choose any operating system. Install JDK (Java Development Kit) JDK, is a program that allows you to write Java code from the comfort of your desktop. It contains a varie
5 min read
Java Developer Learning Path – A Complete Roadmap
Java is one of the most widely used programming languages in the world. Talking about its popularity, more than nine million developers considered the Java Programming language as their mother tongue. So there is no doubt about Java’s popularity worldwide. Java is a general-purpose, object-oriented
6 min read
Java Programming Course : A Complete Guide
Hey tech Geeks! Welcome back! Thinking to begin learning Java from scratch to pro level! No worries, get ready to complete your learning journey as GeeksforGeeks 'Master Java Programming Course' is here to be your learning partner. Java as being the most object-oriented & network- centric langua
7 min read
10 Best Java IDE's to Consider
When we talk about popular programming languages, it is important to remember Java! In fact, it is currently the most popular programming language in the world with approximately 70 Lakh Developers using it daily. And one of the reasons for this is the versatile nature of Java. Be it desktop apps, m
8 min read
Apache XMLBeans using Java
XMLBeans is a tool developed by Apache Software Foundation that allows users to access and manipulate XML data using the Java programming language. The tool provides an easy-to-use, object-oriented approach to working with XML, making it a popular choice among Java developers. XMLBeans uses the XML
3 min read
JavaBean class in Java
JavaBeans are classes that encapsulate many objects into a single object (the bean). It is a Java class that should follow the following conventions: Must implement Serializable.It should have a public no-arg constructor.All properties in java bean must be private with public getters and setter meth
3 min read