Area of Parallelogram | Definition, Formulas & Examples
Last Updated :
23 Jul, 2025
A parallelogram is a four-sided polygon (quadrilateral) where opposite sides are parallel and equal in length. In a parallelogram, the opposite angles are also equal, and the diagonals bisect each other (they cut each other into two equal parts).
The area of a Parallelogram is the space or the region enclosed by the boundary of the parallelogram in a two-dimensional space. It is calculated by multiplying the base of the parallelogram by its height.
The area of a Parallelogram can be determined by multiplying its base by its altitude. Thus, the following formula can be used to determine a parallelogram's area,
Area of Parallelogram = Base × Height
A = b × h
For any parallelogram of base(b) and height(h) whose image is shown below, its area is bh units.
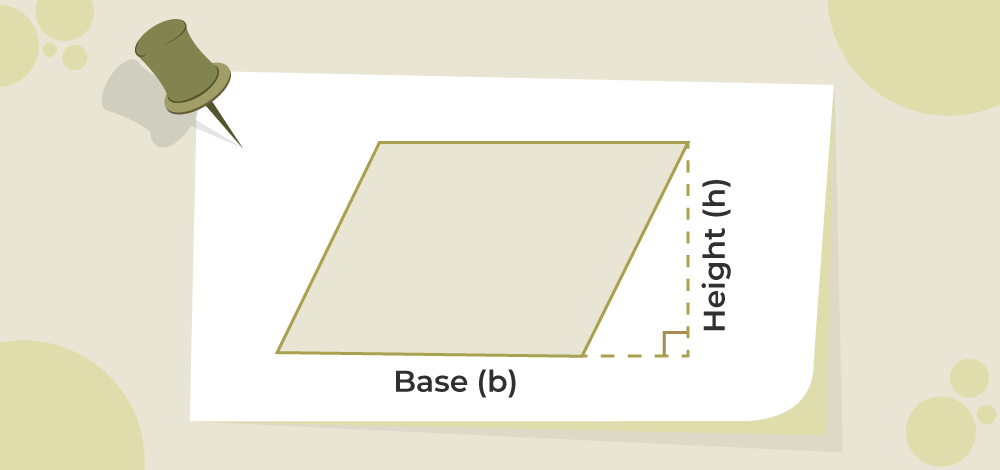
Example: Find the area of a parallelogram whose base is 12 cm and height is 8 cm.
Given,
Base (b) = 12 cm
Height (h) = 8 cm
The formula to calculate the area of a parallelogram is,
A = b × h
A = 12 × 8
A = 96 cm2
Area of Parallelogram using Side Lengths
Area of a Parallelogram can be calculated by using the length of sides and adjacent angles if the height is not given. Mathematically it is written as,
Area of Parallelogram = ab sin (θ)
For any parallelogram of sides 'a' and 'b' and angle between them is 'θ' whose image is shown below, its area is ab sin (θ) units.
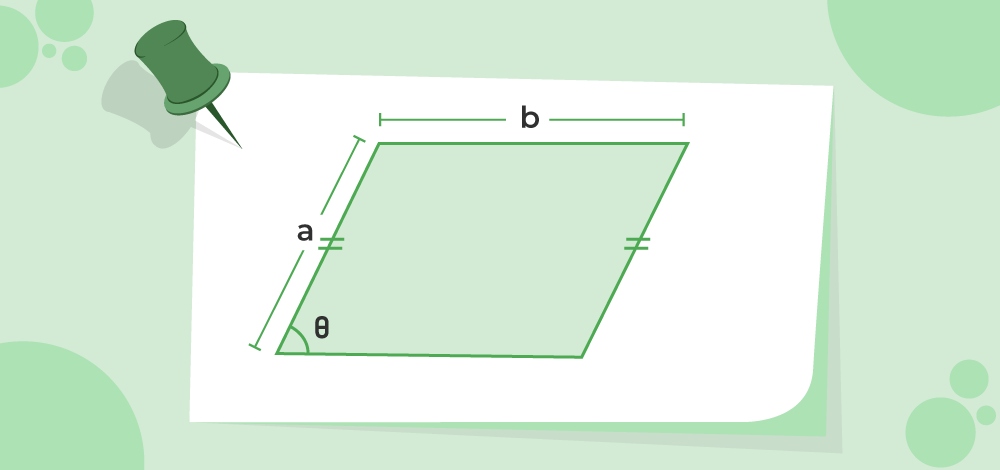
Example: If the angle between two sides of a parallelogram is 30 degrees and the length of its adjacent sides are 5 cm and 6 cm. Determine the area of parallelogram.
Given,
Length of One side (a) = 5 cm
Length of Other side (b) = 4 cm
Angle between two adjacent sides (θ) = 30 degrees
Formula to calculate Area of a Parallelogram is,
A = ab sin (θ)
A = 5 × 4 × sin (30)
A = 10 cm2
Area of Parallelogram using Diagonals
A parallelogram consists of two diagonals that intersect each other at a specific angle meeting at a particular point. The area of a parallelogram can be calculated by using the length of its diagonals.
Formula for the area of parallelogram by using the length of diagonals is given by,
Area of Parallelogram = 1/2 × d1 × d2 sin (x)
For any parallelogram of diagonals 'd1' and 'd2' and angle between them is 'x' whose image is shown below, its area is 1/2 × d1 × d2 sin (x) units.

Example: Determine the area of parallelogram, when the angle between two intersecting diagonals of a parallelogram is 90 degrees and the length of its diagonals are 2 cm and 6 cm.
Given,
Length of One Diagonal (d1) = 2 cm
Length of Other Diagonal (d2) = 6 cm
Angle between two intersecting diagonals (x) = 90 degrees
Formula to calculate Area of a Parallelogram is,
A = 1/2 × d1 × d2 sin (x)
A = 1/2 × 2 × 6 × sin (90)
A = 6 cm2
Formulas to Calculate the Area of a Parallelogram |
|---|
Area of a Parallelogram Using Base and Height | A = b × h |
Area of a Parallelogram Using Trigonometry | A = ab sin (x) |
Area of a Parallelogram Using Diagonals | A = ½ × d1 × d2 sin (y) |
Area of Parallelogram in vector form involves using vectors to express the sides of the parallelogram and then calculating the cross-product of those vectors. The magnitude of the cross-product yields the area of the parallelogram.
Let's considering a parallelogram PQRS, with adjacent sides \vec a and \vec b and the diagonals are \vec {d_1}and \vec {d_2}
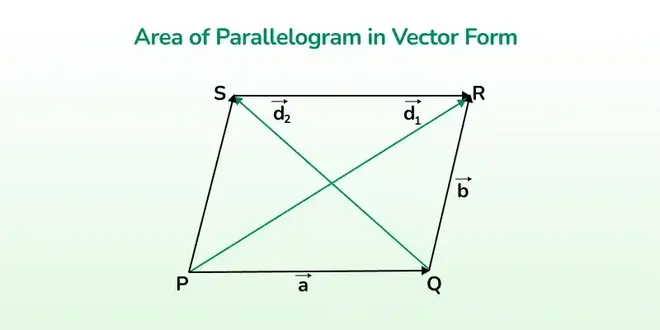 Area of a Parallelogram in Vector
Area of a Parallelogram in VectorNow, Area of Parallelogram in vector form is given using adjacent sides \vec a and \vec b as,
A = |\vec a \times \vec b|
Using the Parallelogram Law of Vector Addition
- \vec a + \vec b = \vec d_1
- \vec b -\vec a = \vec d_2
Now,
\begin{aligned}\vec d_1 \times \vec d_2 &= (\vec a + \vec b)(\vec b - \vec a)\\&=\vec a \times(\vec b - \vec a)+\vec b\times (\vec b - \vec a)\\&=\vec a \times \vec b - \vec a\times \vec a +\vec b\times \vec b - \vec b \times \vec a)\end{aligned}
But, \vec a \times \vec a = 0, \vec b \times \vec b = 0 and \vec a \times \vec b = - \vec b \times \vec a
Therefore,
\begin{aligned}\vec d_1 \times \vec d_2 &=\vec a \times \vec b - 0 +0 - \vec b \times \vec a)\\&=\vec a \times \vec b - (-(\vec a \times \vec b))\\&=2(\vec a\times \vec b)\end{aligned}
|\vec a + \vec b| = \dfrac{1}{2} |(\vec d_1\times \vec d_2)|
The Magnitude of the cross product of the diagonals relates to the area as:
A = \frac{1}{2}|\vec{d_1} \times \vec{d_2}|
Example: Find the area of a parallelogram whose adjacent sides are vectors. A = 2i + 5j and B = 7i - j
Area of Parallelogram = |A × B|
Area = \begin{vmatrix} i& j\\ 2& 5\\ 7& -1\end{vmatrix}
Area = (2)(-1) -5(5)(7) = -2 -35 = |-37|
Area of Prarallelogram is 37 units
Area of Parallelogram Solved Examples
Various examples related to Area of Parallelogram are,
Example 1: Find area of a parallelogram whose base is 10 cm and height is 8 cm.
Solution:
Given,
Base (b) = 10 cm
Height (h) = 8 cm
We have,
A = b × h = 10 × 8 = 80 cm2
Example 2: Find the area of a parallelogram whose base is 5 cm and height is 4 cm.
Solution:
Given,
Base (b) = 5 cm
Height (h) = 4 cm
Area(A) = b × h
A = 5 × 4 = 20 cm2
Example 3: Determine the area of the parallelogram, when the angle between two intersecting diagonals of a parallelogram is 90 degrees and the length of its adjacent sides are 4 cm and 8 cm.
Solution:
Given,
Length of One Diagonal (d1) = 4 cm
Length of Other Diagonal (d2) = 8 cm
Angle between two intersecting diagonals (x) = 90 degrees
Formula to calculate the area of a parallelogram is,
A = 1/2 × d1 × d2 sin (x)
A = 1/2 × 4 × 8 × sin (90)
A = 16 cm2
Example 4: If the angle between two sides of a parallelogram is 60 degrees and the length of its adjacent sides is 3 cm and 6 cm. Determine the area of the parallelogram.
Solution:
Given,
Length of One side (a) = 3 cm
Length of Other side (b) = 6 cm
Angle between two adjacent sides (θ) = 60 degrees
Formula to calculate Area of a Parallelogram is,
A = ab sin (θ)
A = 3 × 6 × sin (60)
A = 15.6 cm2
Example 5: Find the area of a parallelogram whose adjacent sides are 4 cm and 3 cm and the angle between these sides is 90°.
Solution:
Let lengths of sides by a and b with values 4 cm and 3 cm respectively.
Angle between sides 90°
Area = ab sinθ
A = 4 × 3 sin 90°
A = 12 cm2
Practice Questions on Area of Parallelogram
Some practice questions on Area of parallelogram are,
Question 1. Find the area of a parallelogram whose adjacent sides are 12 cm and 14 cm and the angle between these sides is 60°.
Question 2. If angle between two sides of a parallelogram is 30 degrees and the length of its adjacent sides is 3 cm and 6 cm. Find its Area.
Question 3. If base and height of a parallelogram is 4 cm and 8 cm respectively, find its area.
Question 4. What is area of a parallelogram whose breadth is 11 cm and height is 18 cm.
Answer Key
Answer 1: Area of a parallelogram with adjacent sides 12 cm and 14 cm, and an angle of 60°: 145.49 cm²
Answer 2: Area of a parallelogram with adjacent sides 3 cm and 6 cm, and an angle of 30°: 9 cm²
Answer 3: Area of a parallelogram with base 4 cm and height 8 cm: 32 cm²
Answer 4: Area of a parallelogram with breadth 11 cm and height 18 cm: 198 cm²
Explore
Basic Arithmetic
Algebra
Geometry
Trigonometry & Vector Algebra
Calculus
Probability and Statistics
Practice