Uses of Parallelogram in Daily Life Situations
Last Updated :
23 Jul, 2025
Parallelograms are fundamental geometric shapes in mathematics that are basically used in various fields like architecture, Engineering, and others. They can even be found in common places near you like windows, doors, tables, etc. where their symmetrical characteristics enhance both functionality and beauty.
Understanding the various applications of parallelograms enhances our awareness of the value of geometry in everyday situations.
What is Parallelogram?
A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with two pairs of opposite sides that are parallel and equal in length. Also, the opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal. Suppose, we have a polygon with 4 sides that can be identified by quadrilateral □ ABCD, in which AB ∥ CD and AC ∥ BD.A
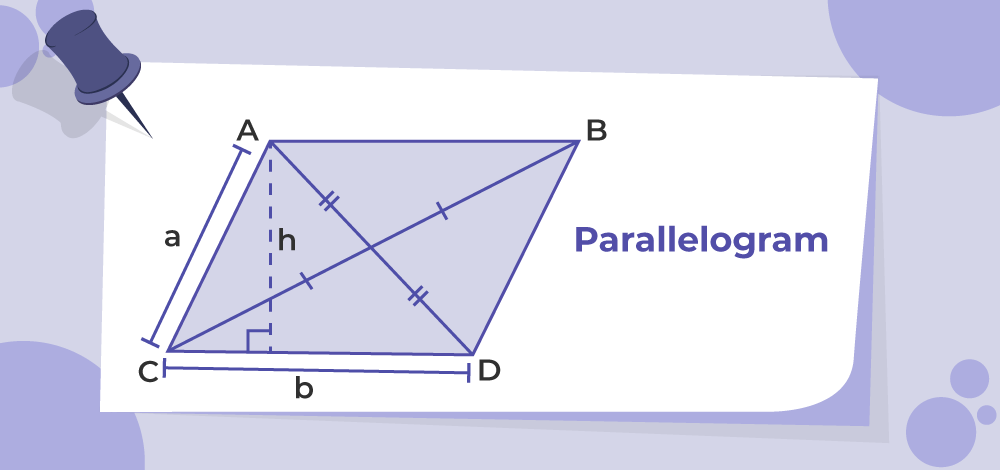
A parallelogram ABCD with height 'h' is shown in the image added below:
Uses of Parallelogram
Various applications of parallelogram includes:
In Architecture
In designing and constructing buildings workers make use of parallelograms in making windows, roofs, doors, rooms, etc. Whereas, Parallelograms are essential in structural engineering design for load-carrying structures, girders, and frameworks because they provide stability and even force distribution. They can be found in floor plans, roofing designs, and supporting structures such as trusses and beams.
In Engineering and Mechanics
Parallelograms are used in engineering and mechanics to analyze forces and vectors. They are often employed to represent the equilibrium of forces in statics problems, as well as to calculate moments and torques in mechanical systems.
In Solar Panels
Two most popular geometric shapes for solar panels are rectangles and parallelograms. Solar panels in the shape of a parallelogram are often chosen because they are easy to secure to the sides of shed roofs.
In Interior Designing
In Interior designing, Parallelograms are important because they help in designing furniture, fixtures, and decorative components for arrangement. For example, parallelogram-shaped surfaces or divisions are commonly found in tables, shelves, and cabinets, and they improve both functionality and visual appeal.
In Environmental Scenario
Parallelograms can be used in any environmental scenarios for activities including estimating land area, creating irrigation systems, and simulating fluid flow patterns.
In Automobile Engineering
In the design of suspension systems, driving systems, and transmission connections, parallelograms are used. Whereas, They contribute to the stability and speed of vehicles by ensuring smooth and controlled motion.
In Imaging and Photography
Parallelograms are used in imaging and photography to coordinate images and correct vision errors. Whereas, They support the preservation of accurate angles and dimensions in landscape and architectural photography.
Properties of Parallelogram
Some common properties of parallelograms are given below;
- Its opposite sides are parallel.
- Its opposite angles are congruent.
- Its consecutive angles are supplementary.
- If one angle of the parallelogram is right, then all remaining angles are also right.
- Diagonals of a parallelogram can bisect each other.
- Sum of all angles will be equal to 360°.
- Adjacent angles of the parallelogram add up to 180°.
Conclusion
In conclusion, parallelograms are fundamental geometric shapes that have a wide range of practical uses. Their symmetrical qualities aid in efficiency and stability in various daily life applications. Simply, we talk about the identifying parallelogram with shapes just to highlight some of the products like, windows, rooms , tables, land areas and so on.
Solved Examples on Parallelogram
Example 1: If EC = 7, Find AC.

Solution:
In the given parallelogram, diagonals AC and BD bisect each other at point E. This means that E is the midpoint of diagonal AC.
Since diagonals bisect each other, we know that:
AE = EC
Given that EC = 7 cm, it follows that:
AE = 7 cm
Now, the total length of diagonal AC is the sum of AE and EC:
AC = AE + EC = 7 cm + 7 cm = 14 cm.
Thus, the length of diagonal AC is 14 cm.
Example 2: Two adjacent sides of a parallelogram are AB = 5 cm and AD = 2 cm. Find its perimeter.

Solution:
In parallelogram opposite sides are always equal.
As we have a parallelogram ABCD;
In this, AB = CD = 5 cm
AD = CB = 2 cm,
Perimeter of Parallelogram = AB + CD + AD + BC
= 5 + 5 + 2 + 2
= 14 cm
Example 3: If m ∠ ABC = 65 and m ∠BAC = 55, Find m∠ DBC.

Solution:
In parallelogram, Consecutive angles are supplementary
So, we have m∠BAC + m∠ABC = 180°
But, m∠ABD = m∠ABC + m∠DBC
m∠ABD = 65 + m∠DBC
Therefore, m∠DBC = 180 - (m∠BAC + m∠ABC)
m∠DBC = 180 - (55 + 65)
m∠DBC = 180 -120
m∠DBC = 60
Explore
Basic Arithmetic
Algebra
Geometry
Trigonometry & Vector Algebra
Calculus
Probability and Statistics
Practice