A ratio is a way to compare two or more quantities by showing the relative size of one quantity to another. It expresses how many times one quantity is contained in another or how two quantities relate in proportion.
We use ratios in daily life to compare quantities and make decisions Some real-life examples where we use ratios are:
- Cooking and Recipes: When following a recipe, the ingredients are often given in a specific ratio. For example, a recipe may call for a ratio of 2 cups of flour to 1 cup of sugar, written as 2 : 1.
- Dividing a pizza among a group of friends.
Representation of Ratio
The ratio of two values say 'p' and 'q,' is read as "p is to q." and the standard way to express the ratio is as
p : q, or p/q.
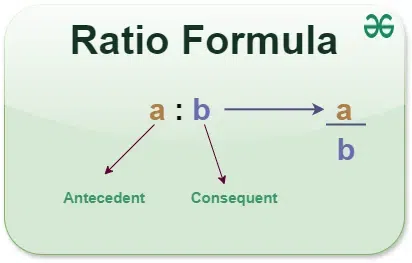 Ratio Formula
Ratio FormulaTypes of Ratios
Various Types of Ratios are:
Compound Ratio: This ratio involves combining two or more simple ratios. It is the result of multiplying two or more ratios together.
Example: If the ratio of A to B is 2 : 3, and the ratio of B to C is 4 : 5, the compound ratio of A : B : C will be (2 × 4) : (3 × 5), or 8 : 15 : 20.
Part-to-Part Ratio: In this ratio we compares different parts of a whole with respect to each other. It shows the relationship between one part and another part within a set.
Example: In a classroom with 8 boys and 12 girls, the part-to-part ratio of boys to girls is 8 : 12, which simplifies to 2 : 3.
Part-to-Whole Ratio: This type of ratio compares one part of a quantity to the whole quantity. This ratio expresses the fraction of the total that one part represents.
Example: If a basket contains 5 red apples and 15 apples in total, the part-to-whole ratio of red apples is 5 : 15, which simplifies to 1 : 3.
Duplicate Ratio: This ratio refers to the square of a given ratio. In other words, if we have a ratio of two quantities, say a : b, the duplicate ratio is simply the ratio of the squares of a and b, which can be represented as a2 : b2.
Example: If the ratio of the lengths of two sides of a rectangle is 3 : 4, the duplicate ratio of their areas would be the square of 3 and 4, i.e., 32 : 42 = 9 : 16.
Ratio Properties
Some Key properties of Ratios are:
Multiplying by the Same Term: If a ratio is multiplied by the same term in both the antecedent (numerator) and the consequent (denominator), the actual ratio remains unchanged.
- Example: If the ratio is 2 : 3 and both terms are multiplied by 4, the new ratio becomes 8 : 12, which is equivalent to the original ratio.
Dividing by the Same Number: If both the antecedent and consequent of a ratio are divided by the same number, the actual ratio does not change.
- Example: If the ratio is 8 : 12 and both terms are divided by 4, the new ratio becomes 2 : 3, which is equivalent to the original ratio.
Reciprocal Property: If two ratios are equal, then their reciprocals are also equal.
- Example: If a : b = c : d , then b : a = d : c.
Cross-Multiplication Property: If two ratios are equal, their cross-products (cross-multiplications) are also equal.
- Example: If a : b = c : d, then a × d = b × c.
Equivalent Ratios with Different Actual Values: Two ratios may be equal in form but represent different actual values.
- Example: 45 : 60 = 5 : 6 and 100 : 120 = 5 : 6, which shows that while the ratio 5 : 6 is the same, the actual values of the terms are different.
How to Calculate Ratios
To calculate the ratio compare two quantities by dividing one by the other. It shows how many times one quantity is contained within another. Before calculating a ratio, ensure that both quantities are in the same unit of measurement.
Example: Suppose you have 15 red marbles and 30 blue marbles. To find the ratio of red marbles to blue marbles, follow these steps:
Step 1: Write the ratio as a fraction
The ratio of red marbles to blue marbles is written as:
\text{Ratio} = \frac{\text{Number of Red Marbles}}{\text{Number of Blue Marbles}} = \frac{15}{30}
Step 2: Simplify the fraction
Next, simplify the ratio by dividing both the numerator and denominator by the same number
15/30 = 1/2
Step 3: Express the ratio
Thus, the ratio of red marbles to blue marbles is:
Ratio = 1 : 2
Read more - Uses of Ratio in Real-life.
Solved Examples on Ratio
Example 1: A basket contains 12 apples and 18 oranges. Find the ratio of apples to oranges.
Solution:
Given:
Number of apples = 12
Number of oranges = 18
To find the ratio of apples to oranges:
Ratio of apples to oranges = 12/18
Now, simplify the ratio by dividing both numbers by 6 (the common factor):
12/18 = (12 ÷ 6)/(18 ÷ 6) = 2/3
So, the ratio of apples to oranges is 2:3.
Example 2: In a school, there are 40 boys and 60 girls. After 20 more boys are admitted, what is the new ratio of boys to girls?
Solution:
Given:
Initial number of boys = 40
Initial number of girls = 60
After the admission of 20 boys: New number of boys = 40 + 20 = 60
Now, the ratio of boys to girls:
Ratio of boys to girls = 60/60
This simplifies to:
60/60 = 1
So, the new ratio of boys to girls is 1:1.
Related Reads:
Explore
Basic Arithmetic
Algebra
Geometry
Trigonometry & Vector Algebra
Calculus
Probability and Statistics
Practice