Python Program For Finding Intersection Point Of Two Linked Lists
Last Updated :
17 Aug, 2023
There are two singly linked lists in a system. By some programming error, the end node of one of the linked list got linked to the second list, forming an inverted Y-shaped list. Write a program to get the point where two linked lists merge.

Above diagram shows an example with two linked lists having 15 as intersection points.
Method 1(Simply use two loops):
Use 2 nested for loops. The outer loop will be for each node of the 1st list and the inner loop will be for the 2nd list. In the inner loop, check if any of the nodes of the 2nd list is the same as the current node of the first linked list. The time complexity of this method will be O(M * N) where m and n are the numbers of nodes in two lists.
Method 2 (Mark Visited Nodes):
This solution requires modifications to basic linked list data structure. Have a visited flag with each node. Traverse the first linked list and keep marking visited nodes. Now traverse the second linked list, If you see a visited node again then there is an intersection point, return the intersecting node. This solution works in O(m+n) but requires additional information with each node. A variation of this solution that doesn’t require modification to the basic data structure can be implemented using a hash. Traverse the first linked list and store the addresses of visited nodes in a hash. Now traverse the second linked list and if you see an address that already exists in the hash then return the intersecting node.
Method 3(Using difference of node counts):
- Get count of the nodes in the first list, let count be c1.
- Get count of the nodes in the second list, let count be c2.
- Get the difference of counts d = abs(c1 – c2)
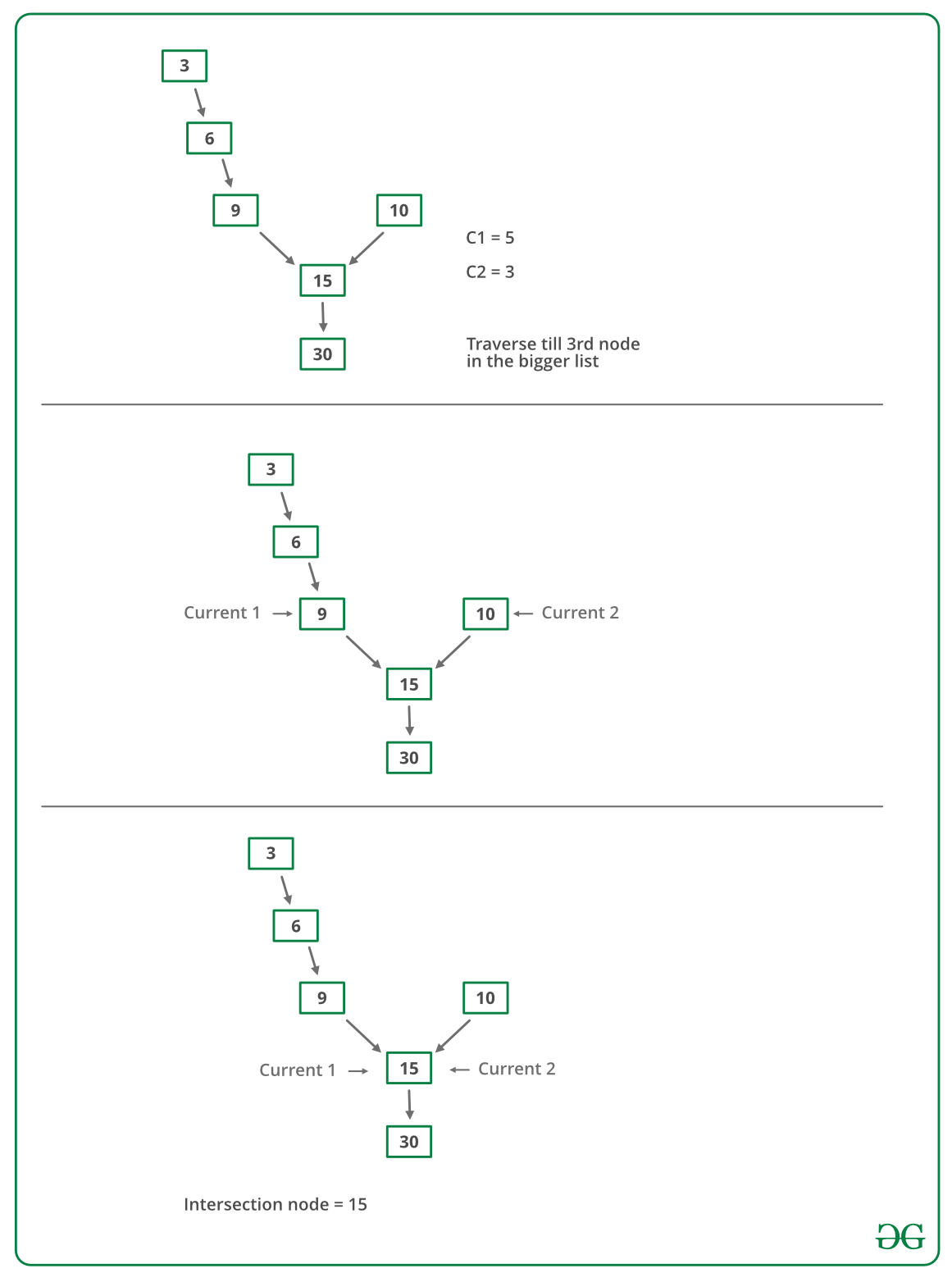
- Now traverse the bigger list from the first node till d nodes so that from here onwards both the lists have equal no of nodes
- Then we can traverse both the lists in parallel till we come across a common node. (Note that getting a common node is done by comparing the address of the nodes)
Below image is a dry run of the above approach:
Below is the implementation of the above approach :
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
def getIntersectionNode(head1, head2):
c1=getCount(head1)
c2=getCount(head2)
if c1 > c2:
d = c1 - c2
return _getIntersectionNode(d, head1,
head2)
else:
d = c2 - c1
return _getIntersectionNode(d, head2,
head1)
def _getIntersectionNode(d, head1, head2):
current1 = head1
current2 = head2
for i in range(d):
if current1 is None:
return -1
current1 = current1.next
while current1 is not None and current2 is not None:
if current1 is current2:
return current1.data
current1 = current1.next
current2 = current2.next
return -1
def getCount(node):
cur=node
count=0
while cur is not None:
count+=1
cur=cur.next
return count
if __name__ == '__main__':
common = Node(15)
head1 = Node(3)
head1.next = Node(6)
head1.next.next = Node(9)
head1.next.next.next = common
head1.next.next.next.next = Node(30)
head2 = Node(10)
head2.next = common
head2.next.next = Node(30)
print("The node of intersection is ",
getIntersectionNode(head1,head2))
|
Output:
The node of intersection is 15
Time Complexity: O(m+n)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Method 4(Make circle in first list):
Thanks to Saravanan Man for providing below solution.
1. Traverse the first linked list(count the elements) and make a circular linked list. (Remember the last node so that we can break the circle later on).
2. Now view the problem as finding the loop in the second linked list. So the problem is solved.
3. Since we already know the length of the loop(size of the first linked list) we can traverse those many numbers of nodes in the second list, and then start another pointer from the beginning of the second list. we have to traverse until they are equal, and that is the required intersection point.
4. remove the circle from the linked list.
Time Complexity: O(m+n)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Method 5 (Reverse the first list and make equations):
Thanks to Saravanan Mani for providing this method.
1) Let X be the length of the first linked list until intersection point.
Let Y be the length of the second linked list until the intersection point.
Let Z be the length of the linked list from the intersection point to End of
the linked list including the intersection node.
We Have
X + Z = C1;
Y + Z = C2;
2) Reverse first linked list.
3) Traverse Second linked list. Let C3 be the length of second list - 1.
Now we have
X + Y = C3
We have 3 linear equations. By solving them, we get
X = (C1 + C3 – C2)/2;
Y = (C2 + C3 – C1)/2;
Z = (C1 + C2 – C3)/2;
WE GOT THE INTERSECTION POINT.
4) Reverse first linked list.
Advantage: No Comparison of pointers.
Disadvantage: Modifying linked list(Reversing list).
Time complexity: O(m+n)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Method 6 (Traverse both lists and compare addresses of last nodes): This method is only to detect if there is an intersection point or not. (Thanks to NeoTheSaviour for suggesting this)
1) Traverse list 1, store the last node address
2) Traverse list 2, store the last node address.
3) If nodes stored in 1 and 2 are same then they are intersecting.
The time complexity of this method is O(m+n) and used Auxiliary space is O(1)
Please refer complete article on Write a function to get the intersection point of two Linked Lists for more details!
Similar Reads
Python Program For Finding Intersection Of Two Sorted Linked Lists
Given two lists sorted in increasing order, create and return a new list representing the intersection of the two lists. The new list should be made with its own memory — the original lists should not be changed. Example: Input: First linked list: 1->2->3->4->6 Second linked list be 2->4->6->8, Ou
4 min read
Python Program For Finding The Length Of Loop In Linked List
Write a function detectAndCountLoop() that checks whether a given Linked List contains loop and if loop is present then returns count of nodes in loop. For example, the loop is present in below-linked list and length of the loop is 4. If the loop is not present, then the function should return 0. Re
4 min read
Python Program For Finding The Middle Element Of A Given Linked List
Given a singly linked list, find the middle of the linked list. For example, if the given linked list is 1->2->3->4->5 then the output should be 3. If there are even nodes, then there would be two middle nodes, we need to print the second middle element. For example, if given linked list
4 min read
Python Program For Inserting A Node In A Linked List
We have introduced Linked Lists in the previous post. We also created a simple linked list with 3 nodes and discussed linked list traversal.All programs discussed in this post consider the following representations of linked list. Python Code # Node class class Node: # Function to initialize the # n
7 min read
Python Program For Deleting A Linked List Node At A Given Position
Given a singly linked list and a position, delete a linked list node at the given position. Example: Input: position = 1, Linked List = 8->2->3->1->7 Output: Linked List = 8->3->1->7 Input: position = 0, Linked List = 8->2->3->1->7 Output: Linked List = 2->3->1
3 min read
Python Program for Deleting a Node in a Linked List
We have discussed Linked List Introduction and Linked List Insertion in previous posts on a singly linked list.Let us formulate the problem statement to understand the deletion process. Given a 'key', delete the first occurrence of this key in the linked list. Iterative Method:To delete a node from
3 min read
Python Program For Insertion Sort In A Singly Linked List
We have discussed Insertion Sort for arrays. In this article we are going to discuss Insertion Sort for linked list. Below is a simple insertion sort algorithm for a linked list. 1) Create an empty sorted (or result) list. 2) Traverse the given list, do following for every node. ......a) Insert curr
5 min read
Python Program For Deleting Last Occurrence Of An Item From Linked List
Using pointers, loop through the whole list and keep track of the node prior to the node containing the last occurrence key using a special pointer. After this just store the next of next of the special pointer, into to next special pointer to remove the required node from the linked list. C/C++ Cod
6 min read
Python Program For Writing A Function To Get Nth Node In A Linked List
Write a GetNth() function that takes a linked list and an integer index and returns the data value stored in the node at that index position. Example: Input: 1->10->30->14, index = 2 Output: 30 The node at index 2 is 30Recommended: Please solve it on "PRACTICE" first, before moving on to th
4 min read
Python Program To Find Decimal Equivalent Of Binary Linked List
Given a singly linked list of 0s and 1s find its decimal equivalent. Input: 0->0->0->1->1->0->0->1->0 Output: 50 Input: 1->0->0 Output: 4 The decimal value of an empty linked list is considered as 0. Recommended: Please solve it on "PRACTICE" first, before moving on to
2 min read